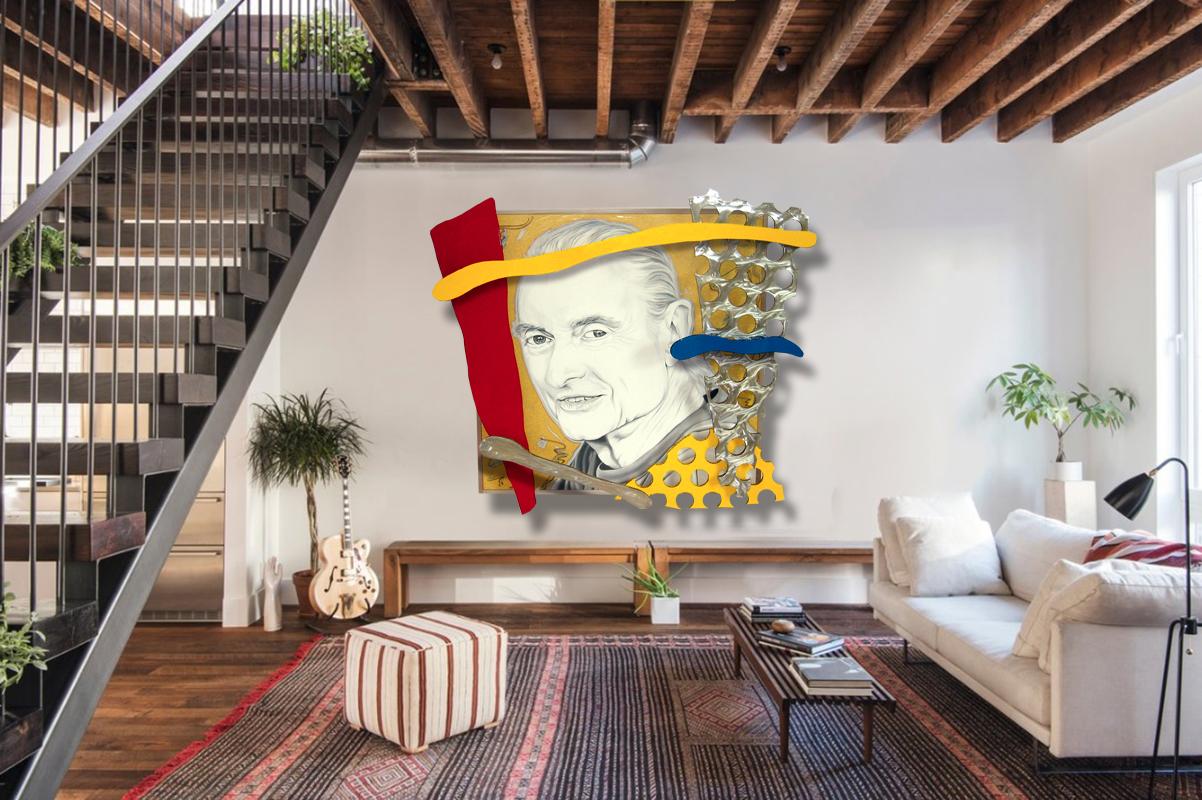
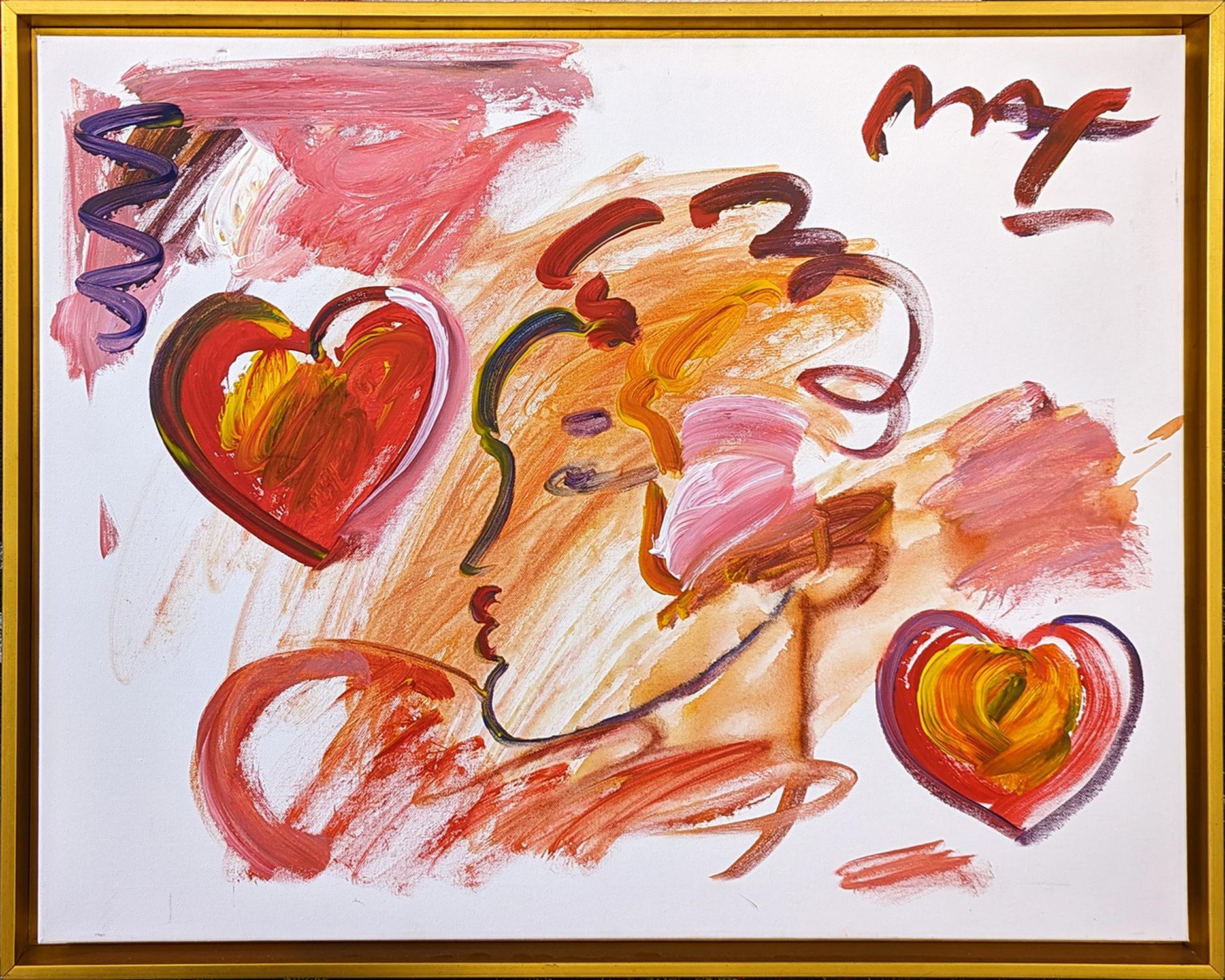"Elvis", Denied Andy Warhol Silver & Black Pop Art Painting by Charles Lutz
View Similar Items
Charles Lutz"Elvis", Denied Andy Warhol Silver & Black Pop Art Painting by Charles Lutz2010
2010
About the Item
- Creator:Charles Lutz (1982, American)
- Creation Year:2010
- Dimensions:Height: 82 in (208.28 cm)Width: 42 in (106.68 cm)Depth: 1.25 in (3.18 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Brooklyn, NY
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU122725032602
Charles Lutz
Charles Lutz received his BFA in painting and art history from Pratt Institute and studied human dissection and anatomy at Columbia University, New York. Lutz's work deals with perceptions and value structures, specifically the idea of the transference of values.
Lutz's 2007 “Warhol Denied” series received international attention calling into question the importance of originality in a work of art. The valuation process (authentication or denial) of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board was used by the artist to create value by submitting recreations of Andy Warhol works for judgment, with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED" of their authenticity. The final product of this conceptual project being "Officially DENIED" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz.
Later in 2013, Lutz went on to do one of his largest public installations to date. At the 100th anniversary of Marcel Duchamp's groundbreaking and controversial Armory Show, Lutz was asked by the curator of Armory Focus: USA and former director of the Andy Warhol Museum, Eric Shiner, to create a site-specific installation representing the United States. The installation "Babel" (based on Pieter Bruegel's famous painting) consisted of 1,500 cardboard replicas of Warhol's Brillo Box (Stockholm Type) stacked 20 feet tall. All 1,500 boxes were then given to the public freely, debasing the Brillo Box as an art commodity by removing its value, in addition to debasing its willing consumers.
Find authentic Charles Lutz paintings and sculptures on 1stDibs.
(Biography provided by Code of Honor)
- "Elvis", Denied Andy Warhol Silver & Black Pop Art Painting by Charles LutzBy Charles LutzLocated in Brooklyn, NYElvis, Metallic Silver and Black Full Length Silkscreen Painting by Charles Lutz Silkscreen and silver enamel painted on vintage 1960's era linen with Artist's Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board. 82" x 40" inches 2010 Lutz's 2007 ''Warhol Denied'' series gained international attention by calling into question the importance of originality or lack thereof in the work of Andy Warhol. The authentication/denial process of the [[Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board]] was used to create value by submitting recreations of Warhol works for judgment with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED". The final product of the conceptual project being "officially denied" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz. Based on the full-length Elvis Presley paintings by Pop Artist Andy Warhol in 1964, this is likely one of his most iconic images, next to Campbell's Soup Cans and portraits of Jackie Kennedy, Marilyn Monroe, Liz Taylor, and Marlon Brando. This is the rarest of the Elvis works from the series, as Lutz sourced a vintage roll of 1960's primed artist linen which was used for this one Elvis. The silkscreen, like Warhol's embraced imperfections, like the slight double image printing of the Elvis image. Lutz received his BFA in Painting and Art History from Pratt Institute and studied Human Dissection and Anatomy at Columbia University, New York. Lutz's work deals with perceptions and value structures, specifically the idea of the transference of values. Lutz's most recently presented an installation of new sculptures dealing with consumerism at Frank Lloyd Wright's Fallingwater House in 2022. Lutz's 2007 Warhol Denied series received international attention calling into question the importance of originality in a work of art. The valuation process (authentication or denial) of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board was used by the artist to create value by submitting recreations of Warhol works for judgment, with the full intention for the works to be formally marked "DENIED" of their authenticity. The final product of this conceptual project is "Officially DENIED" "Warhol" paintings authored by Lutz. Later in 2013, Lutz went on to do one of his largest public installations to date. At the 100th Anniversary of Marcel Duchamp's groundbreaking and controversial Armory Show, Lutz was asked by the curator of Armory Focus: USA and former Director of The Andy Warhol Museum, Eric Shiner to create a site-specific installation representing the US. The installation "Babel" (based on Pieter Bruegel's famous painting) consisted of 1500 cardboard replicas of Warhol's Brillo Box (Stockholm Type) stacked 20 ft tall. All 1500 boxes were then given to the public freely, debasing the Brillo Box as an art commodity by removing its value, in addition to debasing its willing consumers. Elvis was "the greatest cultural force in the Twentieth Century. He introduced the beat to everything, and he changed everything - music, language, clothes, it's a whole new social revolution." Leonard Bernstein in: Exh. Cat., Boston, The Institute of Contemporary Art and traveling, Elvis + Marilyn 2 x Immortal, 1994-97, p. 9. Andy Warhol "quite simply changed how we all see the world around us." Kynaston McShine in: Exh. Cat., New York, Museum of Modern Art (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 1996, p. 13. In the summer of 1963 Elvis Presley was just twenty-eight years old but already a legend of his time. During the preceding seven years - since Heartbreak Hotel became the biggest-selling record of 1956 - he had recorded seventeen number-one singles and seven number-one albums; starred in eleven films, countless national TV appearances, tours, and live performances; earned tens of millions of dollars; and was instantly recognized across the globe. The undisputed King of Rock and Roll, Elvis was the biggest star alive: a cultural phenomenon of mythic proportions apparently no longer confined to the man alone. As the eminent composer Leonard Bernstein put it, Elvis was "the greatest cultural force in the Twentieth Century. He introduced the beat to everything, and he changed everything - music, language, clothes, it's a whole new social revolution." (Exh. Cat., Boston, The Institute of Contemporary Art (and traveling), Elvis + Marilyn 2 x Immortal, 1994, p. 9). In the summer of 1963 Andy Warhol was thirty-four years old and transforming the parameters of visual culture in America. The focus of his signature silkscreen was leveled at subjects he brilliantly perceived as the most important concerns of day to day contemporary life. By appropriating the visual vernacular of consumer culture and multiplying readymade images gleaned from newspapers, magazines and advertising, he turned a mirror onto the contradictions behind quotidian existence. Above all else he was obsessed with themes of celebrity and death, executing intensely multifaceted and complex works in series that continue to resound with universal relevance. His unprecedented practice re-presented how society viewed itself, simultaneously reinforcing and radically undermining the collective psychology of popular culture. He epitomized the tide of change that swept through the 1960s and, as Kynaston McShine has concisely stated, "He quite simply changed how we all see the world around us." (Exh. Cat., New York, Museum of Modern Art (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 1996, p. 13). Thus in the summer of 1963 there could not have been a more perfect alignment of artist and subject than Warhol and Elvis. Perhaps the most famous depiction of the biggest superstar by the original superstar artist, Double Elvis is a historic paradigm of Pop Art from a breath-taking moment in Art History. With devastating immediacy and efficiency, Warhol's canvas seduces our view with a stunning aesthetic and confronts our experience with a sophisticated array of thematic content. Not only is there all of Elvis, man and legend, but we are also presented with the specter of death, staring at us down the barrel of a gun; and the lone cowboy, confronting the great frontier and the American dream. The spray painted silver screen denotes the glamour and glory of cinema, the artificiality of fantasy, and the idea of a mirror that reveals our own reality back to us. At the same time, Warhol's replication of Elvis' image as a double stands as metaphor for the means and effects of mass-media and its inherent potential to manipulate and condition. These thematic strata function in simultaneous concert to deliver a work of phenomenal conceptual brilliance. The portrait of a man, the portrait of a country, and the portrait of a time, Double Elvis is an indisputable icon for our age. The source image was a publicity still for the movie Flaming Star, starring Presley as the character Pacer Burton and directed by Don Siegel in 1960. The film was originally intended as a vehicle for Marlon Brando and produced by David Weisbart, who had made James Dean's Rebel Without a Cause in 1955. It was the first of two Twentieth Century Fox productions Presley was contracted to by his manager Colonel Tom Parker, determined to make the singer a movie star. For the compulsive movie-fan Warhol, the sheer power of Elvis wielding a revolver as the reluctant gunslinger presented the zenith of subject matter: ultimate celebrity invested with the ultimate power to issue death. Warhol's Elvis is physically larger than life and wears the expression that catapulted him into a million hearts: inexplicably and all at once fearful and resolute; vulnerable and predatory; innocent and explicit. It is the look of David Halberstam's observation that "Elvis Presley was an American original, the rebel as mother's boy, alternately sweet and sullen, ready on demand to be either respectable or rebellious." (Exh. Cat., Boston, Op. Cit.). Indeed, amidst Warhol's art there is only one other subject whose character so ethereally defies categorization and who so acutely conflated total fame with the inevitability of mortality. In Warhol's work, only Elvis and Marilyn harness a pictorial magnetism of mythic proportions. With Marilyn Monroe, whom Warhol depicted immediately after her premature death in August 1962, he discovered a memento mori to unite the obsessions driving his career: glamour, beauty, fame, and death. As a star of the silver screen and the definitive international sex symbol, Marilyn epitomized the unattainable essence of superstardom that Warhol craved. Just as there was no question in 1963, there remains still none today that the male equivalent to Marilyn is Elvis. However, despite his famous 1968 adage, "If you want to know all about Andy Warhol, just look at the surface of my paintings" Warhol's fascination held purpose far beyond mere idolization. As Rainer Crone explained in 1970, Warhol was interested in movie stars above all else because they were "people who could justifiably be seen as the nearest thing to representatives of mass culture." (Rainer Crone, Andy Warhol, New York, 1970, p. 22). Warhol was singularly drawn to the idols of Elvis and Marilyn, as he was to Marlon Brando and Liz Taylor, because he implicitly understood the concurrence between the projection of their image and the projection of their brand. Some years after the present work he wrote, "In the early days of film, fans used to idolize a whole star - they would take one star and love everything about that star...So you should always have a product that's not just 'you.' An actress should count up her plays and movies and a model should count up her photographs and a writer should count up his words and an artist should count up his pictures so you always know exactly what you're worth, and you don't get stuck thinking your product is you and your fame, and your aura." (Andy Warhol, The Philosophy of Andy Warhol (From A to B and Back Again), San Diego, New York and London, 1977, p. 86). The film stars of the late 1950s and early 1960s that most obsessed Warhol embodied tectonic shifts in wider cultural and societal values. In 1971 John Coplans argued that Warhol was transfixed by the subject of Elvis, and to a lesser degree by Marlon Brando and James Dean, because they were "authentically creative, and not merely products of Hollywood's fantasy or commercialism. All three had originative lives, and therefore are strong personalities; all three raised - at one level or another - important questions as to the quality of life in America and the nature of its freedoms. Implicit in their attitude is a condemnation of society and its ways; they project an image of the necessity for the individual to search for his own future, not passively, but aggressively, with commitment and passion." (John Coplans, "Andy Warhol and Elvis Presley," Studio International, vol. 181, no. 930, February 1971, pp. 51-52). However, while Warhol unquestionably adored these idols as transformative heralds, the suggestion that his paintings of Elvis are uncritical of a generated public image issued for mass consumption fails to appreciate the acuity of his specific re-presentation of the King. As with Marilyn, Liz and Marlon, Warhol instinctively understood the Elvis brand as an industrialized construct, designed for mass consumption like a Coca-Cola bottle or Campbell's Soup Can, and radically revealed it as a precisely composed non-reality. Of course Elvis offered Warhol the biggest brand of all, and he accentuates this by choosing a manifestly contrived version of Elvis-the-film-star, rather than the raw genius of Elvis as performing Rock n' Roll pioneer. A few months prior to the present work he had silkscreened Elvis' brooding visage in a small cycle of works based on a simple headshot, including Red Elvis, but the absence of context in these works minimizes the critical potency that is so present in Double Elvis. With Double Elvis we are confronted by a figure so familiar to us, yet playing a role relating to violence and death that is entirely at odds with the associations entrenched with the singer's renowned love songs. Although we may think this version of Elvis makes sense, it is the overwhelming power of the totemic cipher of the Elvis legend that means we might not even question why he is pointing a gun rather than a guitar. Thus Warhol interrogates the limits of the popular visual vernacular, posing vital questions of collective perception and cognition in contemporary society. The notion that this self-determinedly iconic painting shows an artificial paradigm is compounded by Warhol's enlistment of a reflective metallic surface, a treatment he reserved for his most important portraits of Elvis, Marilyn, Marlon and Liz. Here the synthetic chemical silver paint becomes allegory for the manufacture of the Elvis product, and directly anticipates the artist's 1968 statement: "Everything is sort of artificial. I don't know where the artificial stops and the real starts. The artificial fascinates me, the bright and shiny..." (Artist quoted in Exh. Cat., Stockholm, Moderna Museet and traveling, Andy Warhol, 1968, n.p.). At the same time, the shiny silver paint of Double Elvis unquestionably denotes the glamour of the silver screen and the attractive fantasies of cinema. At exactly this time in the summer of 1963 Warhol bought his first movie camera and produced his first films such as Sleep, Kiss and Tarzan and Jane Regained. Although the absence of plot or narrative convention in these movies was a purposely anti-Hollywood gesture, the unattainability of classic movie stardom still held profound allure and resonance for Warhol. He remained a celebrity and film fanatic, and it was exactly this addiction that so qualifies his sensational critique of the industry machinations behind the stars he adored. Double Elvis was executed less than eighteen months after he had created 32 Campbell's Soup Cans for his immortal show at the Ferus Gallery, Los Angeles in July and August 1962, and which is famously housed in the Museum of Modern Art, New York. In the intervening period he had produced the series Dollar Bills, Coca-Cola Bottles, Suicides, Disasters, and Silver Electric Chairs, all in addition to the portrait cycles of Marilyn and Liz. This explosive outpouring of astonishing artistic invention stands as definitive testament to Warhol's aptitude to seize the most potent images of his time. He recognized that not only the product itself, but also the means of consumption - in this case society's abandoned deification of Elvis - was symptomatic of a new mode of existence. As Heiner Bastian has precisely summated: "the aura of utterly affirmative idolization already stands as a stereotype of a 'consumer-goods style' expression of an American way of life and of the mass-media culture of a nation." (Exh. Cat., Berlin, Neue Nationalgalerie (and traveling), Andy Warhol: Retrospective, 2001, p. 28). For Warhol, the act of image replication and multiplication anaesthetized the effect of the subject, and while he had undermined the potency of wealth in 200 One Dollar Bills, and cheated the terror of death by electric chair in Silver Disaster # 6, the proliferation of Elvis here emasculates a prefabricated version of character authenticity. Here the cinematic quality of variety within unity is apparent in the degrees to which Presley's arm and gun become less visible to the left of the canvas. The sense of movement is further enhanced by a sense of receding depth as the viewer is presented with the ghost like repetition of the figure in the left of the canvas, a 'jump effect' in the screening process that would be replicated in the multiple Elvis paintings. The seriality of the image heightens the sense of a moving image, displayed for us like the unwinding of a reel of film. Elvis was central to Warhol's legendary solo exhibition organized by Irving Blum at the Ferus Gallery in the Fall of 1963 - the show having been conceived around the Elvis paintings since at least May of that year. A well-known installation photograph shows the present work prominently presented among the constant reel of canvases, designed to fill the space as a filmic diorama. While the Elvis canvases...Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Figurative Paintings
MaterialsEnamel
- Denied Andy Warhol Jackie Black and Blue Painting by Charles LutzBy Charles LutzLocated in Brooklyn, NYDenied Warhol Jackie in Black and Blue Painting by Charles Lutz Silkscreen and acrylic on canvas with Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication ...Category
Early 2000s Pop Art Portrait Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic
- Denied Andy Warhol Repent & Sin No More Black and White Painting by Charles LutzBy Charles LutzLocated in Brooklyn, NYDenied Warhol Repent & Sin No More Black and White Painting by Charles Lutz Silkscreen and acrylic on canvas with Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board. 20 x 16" i...Category
Early 2000s Pop Art Portrait Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic
- Denied Andy Warhol Fright Wig Self Portrait Green Painting by Charles LutzBy Charles LutzLocated in Brooklyn, NYDenied Warhol Green Self Portrait Fright Wig Painting by Charles Lutz Silkscreen and acrylic on linen with Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board. 12 x 12" inches 2...Category
Early 2000s Pop Art Portrait Paintings
MaterialsLinen, Acrylic
- Denied Andy Warhol Fright Wig Self Portrait (Grey) Painting / Charles LutzBy Charles LutzLocated in Brooklyn, NYDenied Warhol Grey Self Portrait Fright Wig Painting by Charles Lutz Silkscreen and acrylic on linen with Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Board. 12 x 12" inches 20...Category
Early 2000s Pop Art Portrait Paintings
MaterialsLinen, Acrylic
- Denied Andy Warhol Dollar Bill Painting / Charles LutzBy Charles LutzLocated in Brooklyn, NYDenied Andy Warhol Dollar Bill Painting / Charles Lutz silkscreen ink on linen with the Denied stamp of the Andy Warhol Art Authentication Boar...Category
Early 2000s Pop Art Portrait Paintings
MaterialsLinen, Acrylic
- "The Last Portrait of Roy Lichtenstein by Ceravolo", 74x82x10" Oil & AluminumBy CeravoloLocated in Southampton, NYCeravolo was introduced to Lichtenstein at a museum show in 1995, at that show, Lichtenstein and Ceravolo discussed the fact that Andy Warhol had painted portraits of Roy in the 1970...Category
1990s Pop Art Portrait Paintings
MaterialsEnamel, Metal
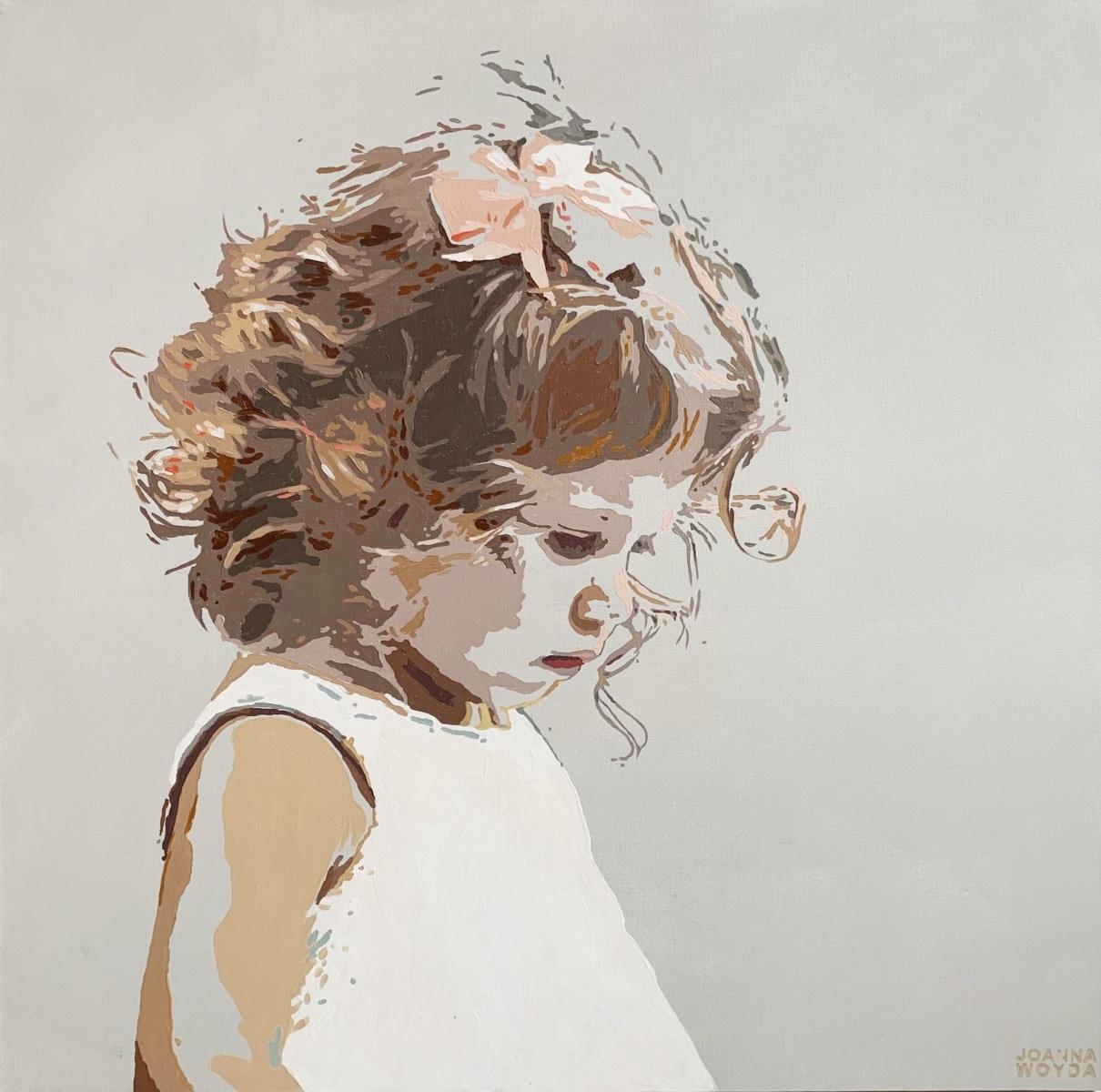
- Beach- White dress. Figurative Acrylic Painting, Minimalism, Pop art, Polish artBy Joanna WoydaLocated in Warsaw, PLContemporary figurative acrylic on canvas painting by Polish artist Joanna Woyda. Painting is in minimalistic, pop art style. The artwork depicts a girl playfully running on a beach....Category
2010s Pop Art Figurative Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic
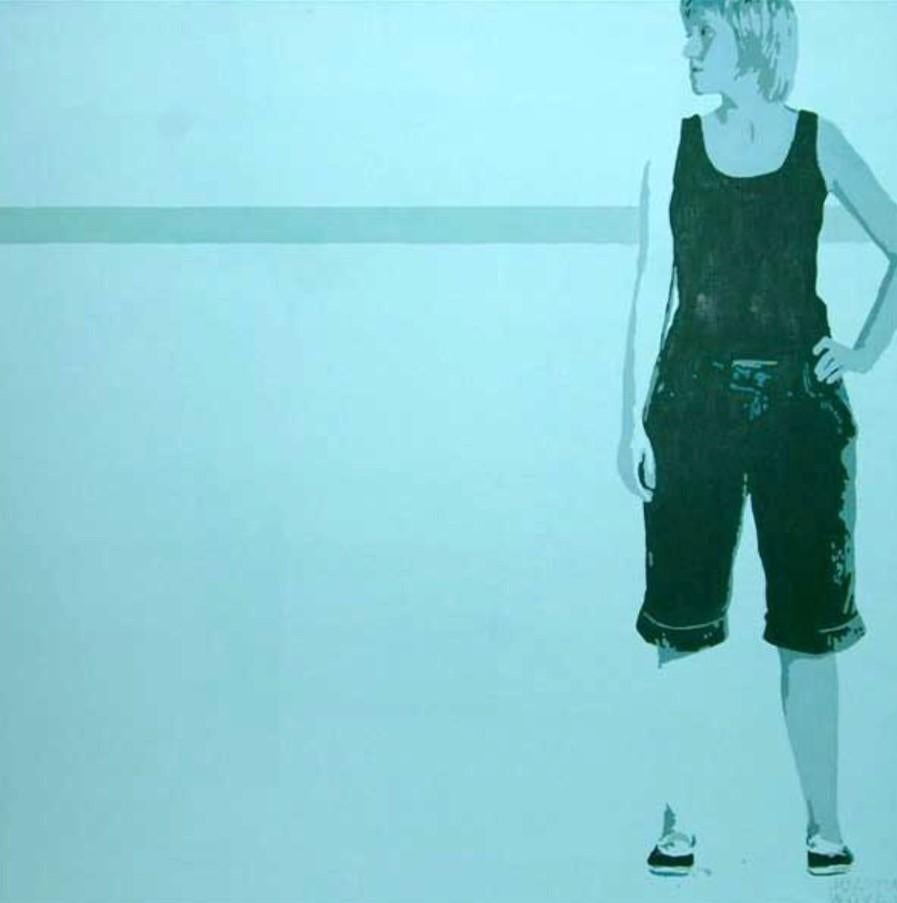
- A Standing Girl - Figurative Acrylic Painting, Minimalism, Pop artBy Joanna WoydaLocated in Warsaw, PLPROVENANCE Exhibited at Katarzyna Napiorkowska Gallery. The gallery is the representative of the artist. The Gallery of Katarzyna Napiorkowska is one of the first private art gall...Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Figurative Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic
- Beach. A sleeve - Figurative Acrylic Painting, Minimalism, Pop artBy Joanna WoydaLocated in Warsaw, PLJoanna Woyda (b. 1981) Studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw (2000-2005). She received her honorary degree in 2005. She was also a scholarship holder of the Ministr...Category
2010s Pop Art Figurative Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic
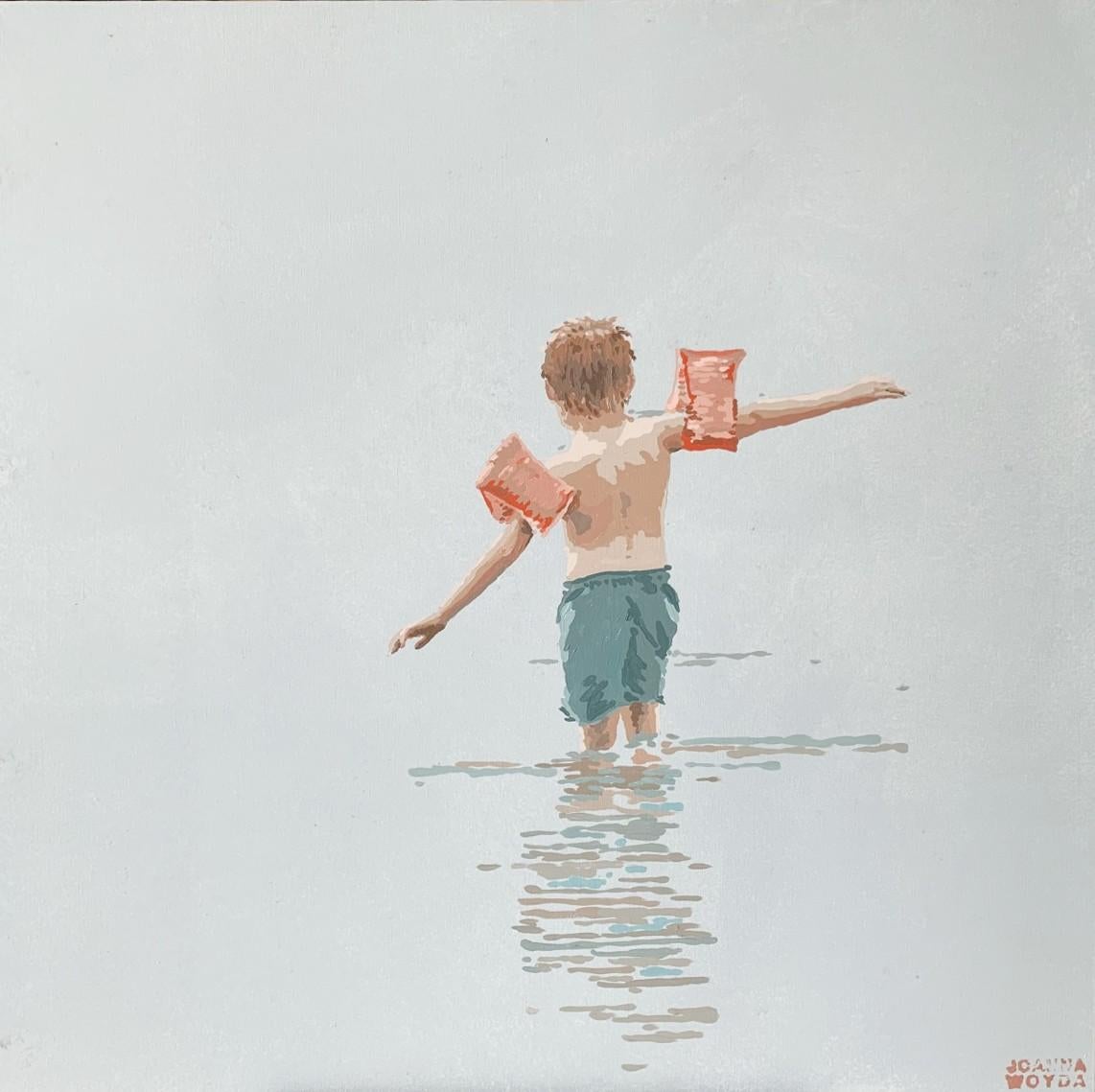
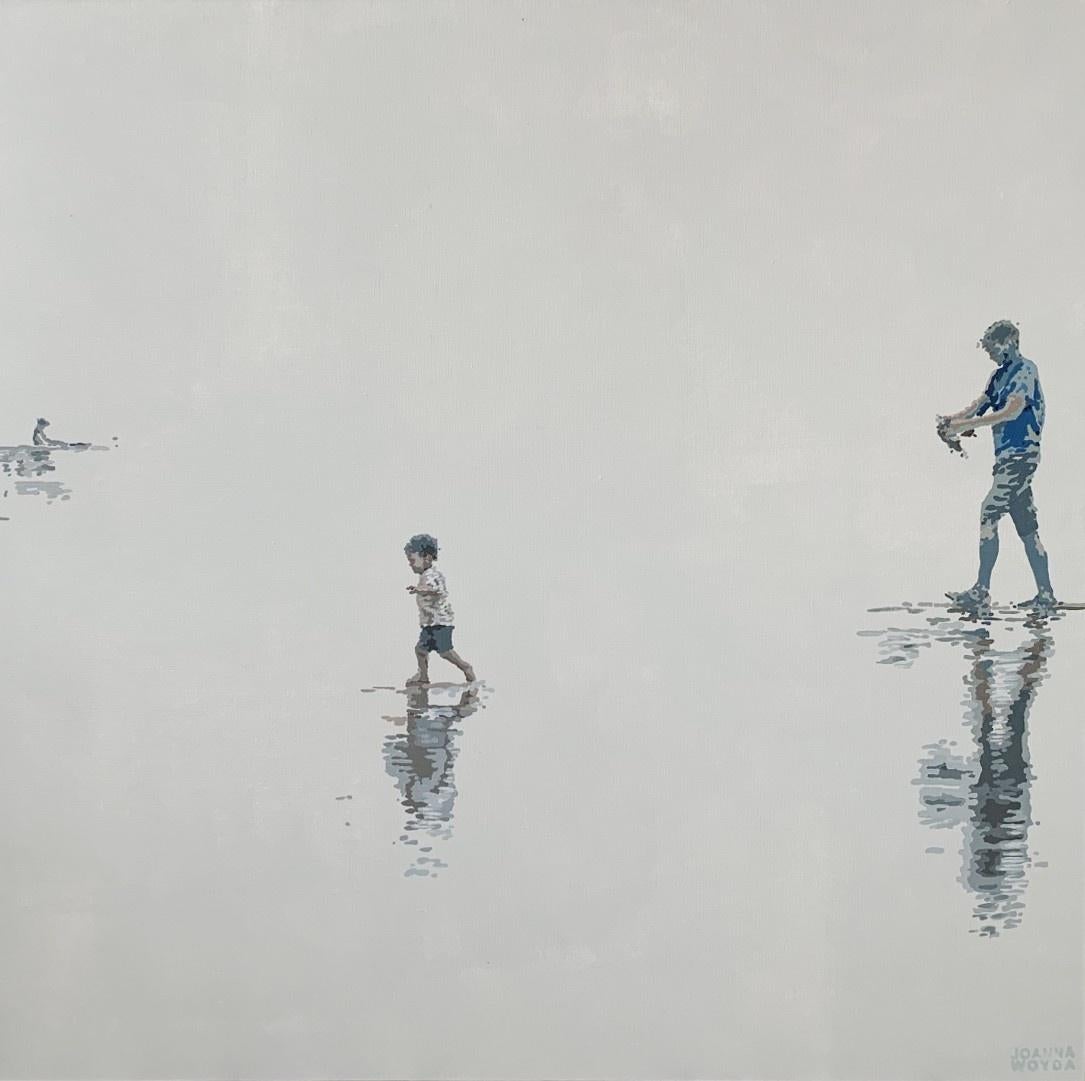
- In red - Figurative Acrylic Painting Minimalism Pop art Polish artistBy Joanna WoydaLocated in Warsaw, PLContemporary figurative acrylic on canvas painting by Polish artist Joanna Woyda. Painting is in minimalistic pop art style. It depicts a playful boy walking into the water, spending...Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Figurative Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic
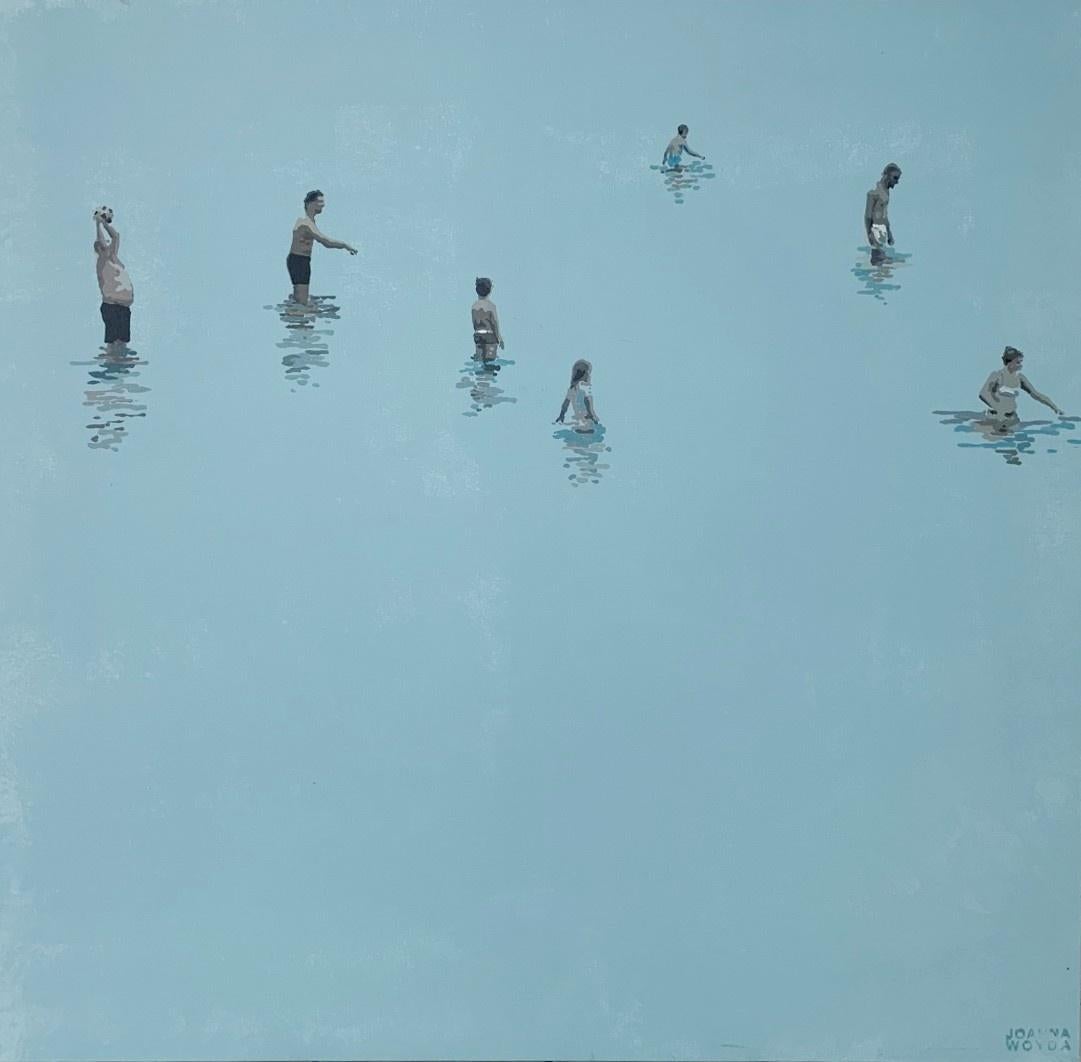
- In the water - Figurative Acrylic Painting Minimalism Pop art Polish artistBy Joanna WoydaLocated in Warsaw, PLARTIST Joanna Woyda (b. 1981) Studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts in Warsaw (2000-2005). She received her honorary degree in 2005. She was also a scholarship holder of the...Category
21st Century and Contemporary Pop Art Figurative Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Acrylic