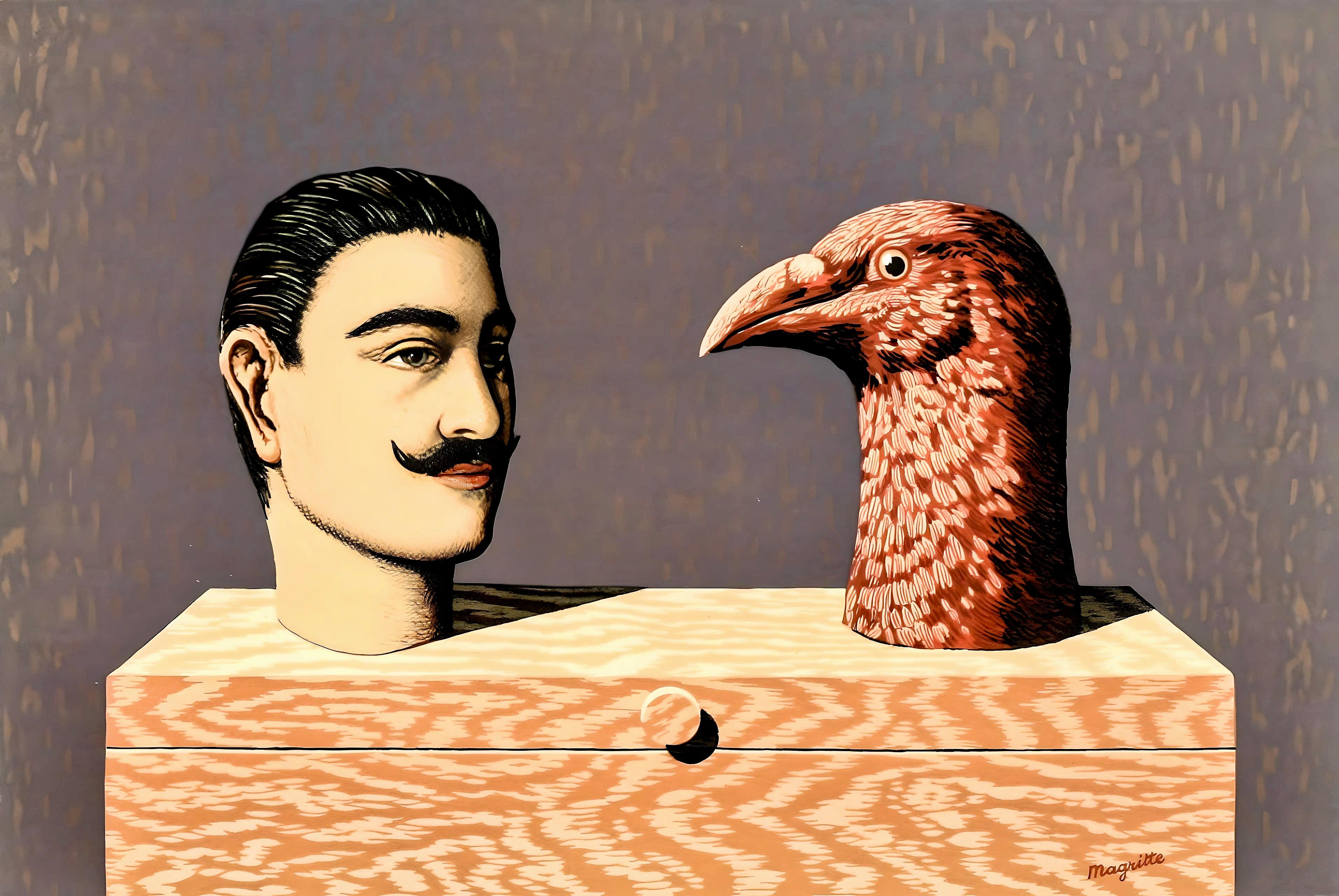
Salvador Dali (after) - Auvergne - Lithograph
View Similar Items
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 14
Auction endedBrowse Current Auctions
(after) Salvador DaliSalvador Dali (after) - Auvergne - Lithograph1969
1969
About the Item
- Creator:(after) Salvador Dali (1904 - 1989, Spanish)
- Creation Year:1969
- Dimensions:Height: 18.31 in (46.5 cm)Width: 13.39 in (34 cm)Depth: 0.04 in (1 mm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU16122290123
About the Seller
4.9
Platinum Seller
These expertly vetted sellers are 1stDibs' most experienced sellers and are rated highest by our customers.
Established in 2015
1stDibs seller since 2015
907 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 1 hour
More From This SellerView All
- Salvador Dali (after) - Auvergne - LithographBy (after) Salvador DaliLocated in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CHLithograph after an original gouache by Salvador Dali for the Societe Nationale des Chemins de Fer Title: S.N.C.F. (Butterfly Suite) Embossed signature Dimensions: 46.5 x 24 cm Edit...Category
1960s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Salvador Dali (after) - Roussillon - LithographBy Salvador DalíLocated in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CHLithograph after Salvador Dali Title: S.N.C.F Blind stamped signature Dimensions: 46.5 x 34 cm Edition: 1700 Numbered in pencil 1969 References : Catalogue raisonne Michler & Lopsi...Category
1960s Surrealist Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Marino Marini - Horse and Rider - Original LithographBy Marino MariniLocated in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CHMarino Marini - Horse and Rider - Original Lithograph 1963 Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm From the art review XXe siècle Unsigned and unumbered as issuedCategory
1960s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Marc Chagall - The Green Horse - Original LithographBy Marc ChagallLocated in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CHMarc Chagall Original Lithograph Title: The Green Horse 1973 Dimensions: 33 x 50 cm Reference: This lithograph was created for the portfolio "Chagall Monu...Category
1970s Surrealist Figurative Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Max Ernst - Birds - Original LithographBy Max ErnstLocated in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CHMax Ernst - Birds - Original Lithograph Birds, 1964 (BNF, 63) Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm Revue Art de France ax Ernst was born in Bruhl, a place near Cologne, in Germany. He was raised in a strict Catholic family, and both of his parents were disciplinarians who were dedicated to training their children into God-fearing and talented individuals. Although his father was deaf, Ernst learned so much from him, particularly when it comes to painting. In fact, much of his early years were lived under the inspiration of his father who was also a teacher. He was the one who introduced painting to Ernst at an early age. In 1914, Ernst attended the University of Bonn where he studied philosophy. However, he eventually dropped out of school because he was more interested in the arts. He claimed that his primary sources of interest included anything that had something to do with painting. Moreover, he became fascinated with psychology, among other subjects in school. Primarily, Ernst's love for painting was the main reason why he became deeply interested with this craft and decided to pursue it later on in his life. During his early years, he became familiar with the works of some of the greatest artists of all time including Claude Monet, Paul Cezanne and Vincent van Gogh. He was also drawn to themes such as fantasy and dream imagery, which were among the common subjects of the works of Giorgio de Chirico. During World War I, Ernst was forced to join the German Army, and he became a part of the artillery division that exposed him greatly to the drama of warfare. A soldier in the War, Ernst emerged deeply traumatized and highly critical of western culture. These charged sentiments directly fed into his vision of the modern world as irrational, an idea that became the basis of his artwork. Ernst's artistic vision, along with his humor and verve come through strongly in his Dada and Surrealists works; Ernst was a pioneer of both movements. It was Ernst's memories of the war and his childhood that helps him create absurd, yet interesting scenes in his artworks. Soon, he took his passion for the arts seriously when he returned to Germany after the war. With Jean Arp, a poet and artist, Ernst formed a group for artists in Cologne. He also developed a close relationship with fellow artists in Paris who propagated Avant-Garde artworks. In 1919, Ernst started creating some of his first collages, where he made use of various materials including illustrated catalogs and some manuals that produced a somewhat futuristic image. His unique masterpieces allowed Ernst to create his very own world of dreams and fantasy, which eventually helped heal his personal issues and trauma. In addition to painting and creating collages, Ernst also edited some journals. He also made a few sculptures that were rather queer in appearance. In 1920s, influenced by the writings of psychologist Sigmund Freud, the literary, intellectual, and artistic movement called Surrealism sought a revolution against the constraints of the rational mind; and by extension, they saw the rules of a society as oppressive. Surrealism also embraces a Marxist ideology that demands an orthodox approach to history as a product of the material interaction of collective interests, and many renown Surrealism artists later on became 20th century Counterculture symbols such as Marxist Che Guevara. In 1922 Ernst moved to Paris, where the surrealists were gathering around Andre Breton. In 1923 Ernst finished Men Shall Know Nothing of This, known as the first Surrealist painting. Ernst was one of the first artists who apply The Interpretation of Dreams by Freud to investigate his deep psyche in order to explore the source of his own creativity. While turning inwards unto himself, Ernst was also tapping into the universal unconscious with its common dream imagery. Despite his strange styles, Ernst gained quite a reputation that earned him some followers throughout his life. He even helped shape the trend of American art during the mid-century, thanks to his brilliant and extraordinary ideas that were unlike those of other artists during his time. Ernst also became friends with Peggy Guggenheim, which inspired him to develop close ties with the abstract expressionists. When Ernst lived in Sedona, he became deeply fascinated with the Southwest Native American navajo art. In fact, the technique used in this artwork inspired him and paved the way for him to create paintings that depicted this style. Thus, Ernst became a main figure of this art technique, including the rituals and spiritual traditions included in this form of art. Pollock, aside from the other younger generations of abstract expressionists, was also inspired by sand painting of the Southwest...Category
1960s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Max Ernst - Composition - Original LithographBy Max ErnstLocated in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CHMax Ernst - Composition - Original Lithograph 1958 Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm XXe siècle Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued Max Ernst was born in Bruhl, a place near Cologne, in Germany. He was raised in a strict Catholic family, and both of his parents were disciplinarians who were dedicated to training their children into God-fearing and talented individuals. Although his father was deaf, Ernst learned so much from him, particularly when it comes to painting. In fact, much of his early years were lived under the inspiration of his father who was also a teacher. He was the one who introduced painting to Ernst at an early age. In 1914, Ernst attended the University of Bonn where he studied philosophy. However, he eventually dropped out of school because he was more interested in the arts. He claimed that his primary sources of interest included anything that had something to do with painting. Moreover, he became fascinated with psychology, among other subjects in school. Primarily, Ernst's love for painting was the main reason why he became deeply interested with this craft and decided to pursue it later on in his life. During his early years, he became familiar with the works of some of the greatest artists of all time including Claude Monet, Paul Cezanne and Vincent van Gogh. He was also drawn to themes such as fantasy and dream imagery, which were among the common subjects of the works of Giorgio de Chirico. During World War I, Ernst was forced to join the German Army, and he became a part of the artillery division that exposed him greatly to the drama of warfare. A soldier in the War, Ernst emerged deeply traumatized and highly critical of western culture. These charged sentiments directly fed into his vision of the modern world as irrational, an idea that became the basis of his artwork. Ernst's artistic vision, along with his humor and verve come through strongly in his Dada and Surrealists works; Ernst was a pioneer of both movements. It was Ernst's memories of the war and his childhood that helps him create absurd, yet interesting scenes in his artworks. Soon, he took his passion for the arts seriously when he returned to Germany after the war. With Jean Arp, a poet and artist, Ernst formed a group for artists in Cologne. He also developed a close relationship with fellow artists in Paris who propagated Avant-Garde artworks. In 1919, Ernst started creating some of his first collages, where he made use of various materials including illustrated catalogs and some manuals that produced a somewhat futuristic image. His unique masterpieces allowed Ernst to create his very own world of dreams and fantasy, which eventually helped heal his personal issues and trauma. In addition to painting and creating collages, Ernst also edited some journals. He also made a few sculptures that were rather queer in appearance. In 1920s, influenced by the writings of psychologist Sigmund Freud, the literary, intellectual, and artistic movement called Surrealism sought a revolution against the constraints of the rational mind; and by extension, they saw the rules of a society as oppressive. Surrealism also embraces a Marxist ideology that demands an orthodox approach to history as a product of the material interaction of collective interests, and many renown Surrealism artists later on became 20th century Counterculture symbols such as Marxist Che Guevara. In 1922 Ernst moved to Paris, where the surrealists were gathering around Andre Breton. In 1923 Ernst finished Men Shall Know Nothing of This, known as the first Surrealist painting. Ernst was one of the first artists who apply The Interpretation of Dreams by Freud to investigate his deep psyche in order to explore the source of his own creativity. While turning inwards unto himself, Ernst was also tapping into the universal unconscious with its common dream imagery. Despite his strange styles, Ernst gained quite a reputation that earned him some followers throughout his life. He even helped shape the trend of American art during the mid-century, thanks to his brilliant and extraordinary ideas that were unlike those of other artists during his time. Ernst also became friends with Peggy Guggenheim, which inspired him to develop close ties with the abstract expressionists. When Ernst lived in Sedona, he became deeply fascinated with the Southwest Native American navajo art. In fact, the technique used in this artwork inspired him and paved the way for him to create paintings that depicted this style. Thus, Ernst became a main figure of this art technique, including the rituals and spiritual traditions included in this form of art. Pollock, aside from the other younger generations of abstract expressionists, was also inspired by sand painting of the Southwest...Category
1960s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
You May Also Like
- Joan Miro Le Chien Aboyant a La LuneBy Joan MiróLocated in Washington, DCArtist: Joan Miro Title: Le Chien Aboyant a La Lune "Barking Dog" Portfolio: Verve Vol VII No. 27-28 Medium: Lithograph Year: 1953 Edition: 6000 Framed Size: 21 1/2" x 28 1/4 Sheet S...Category
1950s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- American Trotting Horses No. IBy Salvador DalíLocated in Paonia, COAmerican Trotting Horses No.1 is from the series “The World Of Currier And Ives as interpreted by Salvador Dali” published by Phyllis...Category
1970s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Cybernetic Lobster Telephone (Imagination & Objects), Salvador DaliBy Salvador DalíLocated in Fairfield, CTArtist: Salvador Dali (1904-1989) Title: Cybernetic Lobster Telephone (Imagination & Objects of the Future Portfolio) Year: 1975 Medium: Lithograph ...Category
1970s Surrealist Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph, Mixed Media
$22,800 Sale Price20% Off - Large Surrealist Photo Realist Silkscreen Lithograph Print Swan DreamsLocated in Surfside, FLBorn in Stoke-on-Trent in 1953, Frederick Phillips studied Fine Art at Burslem College of Art when Arthur Berry was Head of the Fine Art (Painting) ...Category
1990s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph, Screen
- ELK FIGHT Signed Lithograph, Surrealist Group, Panic Movement, Arrabal, ToporLocated in Union City, NJELK FIGHT is a hand drawn, stone lithograph by the French artist Chrisitian Zeimert printed in Paris France c.1974 using hand lithography techniques on archival Rives BFK printmaking paper, 100% acid free. ELK FIGHT presents a surreal, close-up portrait of a two male elk head-butting with a group of books between their opposing heads. Visible on the books spines are the names of members belonging to the 1960s Panic Movement group. Print size - 13 x 15.25 in., unframed, very good condition, pencil signed printers proof, inscribed H.C. with personal dedication to the master printer "Joseph", edition size unknown Image size - 8.25 x 10.5 in. Year - c.1974 Christian Zeimer (1934 - 2020) was a French painter, the son of an upholsterer and designer who also worked as a salesman and Le Bon Marché. After he left the École Boulle, he learned how to engrave on jewelry. He then studied at the École nationale supérieure des arts décoratifs, where he studied under the painter Marcel Gromaire. A libertarian and anarchist, he worked alongside Fernando Arrabal, Alejandro Jodorowsky, Olivier O. Olivier, and Roland Topor and participated in the Panic Movement in the 1960s. He contributed to the newspaper Le Fou Parle and the magazine Hara-Kiri. Alongside Henri Cueco, Jacques Jouet, Hervé Le...Category
1970s Surrealist Animal Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Vintage MOMA Francesco Clemente Museum of Modern Art 1986 dream myth posterBy Francesco ClementeLocated in New York, NYThis three-part work spanning 10 feet was printed from the plates of Francesco Clemente’s mythological landscape Untitled A on the occasion of the 1986 MoMA, New York show of Clement...Category
1980s Surrealist Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph, Offset