Nativity Adoration Italy Baroque Paint Oil on canvas 17th Century Flandre
View Similar Items
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 14
Circle Of Gaspar De CrayerNativity Adoration Italy Baroque Paint Oil on canvas 17th Century Flandre 1630
1630
About the Item
- Creator:Circle Of Gaspar De Crayer (1582 - 1662)
- Creation Year:1630
- Dimensions:Height: 55.52 in (141 cm)Width: 67.72 in (172 cm)
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Riva del Garda, IT
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU98813991951
About the Seller
4.8
Platinum Seller
These expertly vetted sellers are 1stDibs' most experienced sellers and are rated highest by our customers.
Established in 2017
1stDibs seller since 2018
202 sales on 1stDibs
More From This SellerView All
- Van Den Bossche Alexander The Great Paint Oil on canvas 17/18th Century FlemishLocated in Riva del Garda, ITBalthasar Van Den Bossche (Antwerp, 1681 - 1715) Alexander the Great and Campaspe in the studio of the painter Apelles The canvas was exhibited in Perugia (Museo di Palazzo della Pe...Category
17th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil
$43,486 Sale Price20% Off - Christ Salvator Mundi Paint Oil on copper 16/17th Century Flemish schoolLocated in Riva del Garda, ITAntique painting depicting the Face of Christ as Salvator Mundi Flemish painter, 16th-17th century Oil on copper 22 x 18 cm./ framed 42 x ...Category
16th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil
$3,776 Sale Price20% Off - Deposition Atala De Roussy-trioson Paint Oil on canvas 19/20th Century FrenchLocated in Riva del Garda, ITThe deposition of Atala Follower of Anne-Louis Girodet de Roussy-Trioson (Montargis, 1767 - Paris, 1824) 19th-20th century Oil on canvas 47 x 65 cm. - Framed 67 x 84 cm The propos...Category
Late 19th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil
$1,936 Sale Price20% Off - De Wit Flowers Still life Paint Oil on canvas 18th Century Flemish Cupids ArtLocated in Riva del Garda, ITJacob De Wit (Amsterdam, 1695 - 1754) attributable/ workshop Pair of Cupids with Garland of Flowers Oil on canvas 91 x 103 cm. - Framed 104 x 115 cm. Provenance: Christie's (London, Old master Painting 12.12.1996) lot 82 This magnificent composition depicts two cupids holding a garland of flowers, placed on a fine architecture with bas-reliefs and masks, presumably the top of a fountain. One of the two cupids sympathetically holds a part of it with his hands, while his head turns towards the viewer; the second cupid, on the other hand, must have clumsily broken the thread holding its end, and is sitting sullenly with a torch and a tear streaking his chubby cheek. The work, given its stylistic features and compositional taste, can be attributed to the Flemish artist Jacob de Wit (Amsterdam, 1695 - 1754), or to an artist from his workshop, with his typical triumphal and opulent style, which reveals clear influences from Rubens and Van Dijck, but also from Gerard de Lairesse...Category
18th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil
$13,732 Sale Price20% Off - Coastal Landscape Capriccio Saeys Paint Oil on canvas 17/18th century FlemishLocated in Riva del Garda, ITJacob Ferdinand Saeys (Antwerp 1658 - Vienna 1726) and workshop Architectural capriccio with a coastal view at sunset and figures oil painting on canvas 60 x 91 cm., With frame 75 x...Category
17th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil
$8,582 Sale Price20% Off - Perroneau Portrait Lady Woman Paint Oil on canvas 18th Century Old master FrenchLocated in Riva del Garda, ITJean-Baptiste Perroneau (Paris, 1715 – Amsterdam, 1783) Portrait of a lady Oil on oval canvas 60 x 50 cm. - In frame 77 x 66 cm. Work accompanied by expertise: Raffaelle Colace (Cremona), Ferdinando Arisi Reference bibliography: d’Arnoult, Dominique (2014) Jean-Baptiste Perronneau, c 1715-1783, un portraitiste dans l’Europe des Lumières Excerpt from the expertise of Dr. Colace: This refined portrait of a lady is a perfect example of the style of Jean-Baptiste Perroneau, a very talented French painter, whose most beautiful works are located, just like this one, between the fifth and sixth decades of the eighteenth century. "Perroneaeu is more naturally colored than La Tour, the est, in the peinture de poussière colorée, tout plein de tons clairs, frais, presque humides": this is how his brothers wrote about him in La Maison d...Category
18th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil
$10,871 Sale Price20% Off
You May Also Like
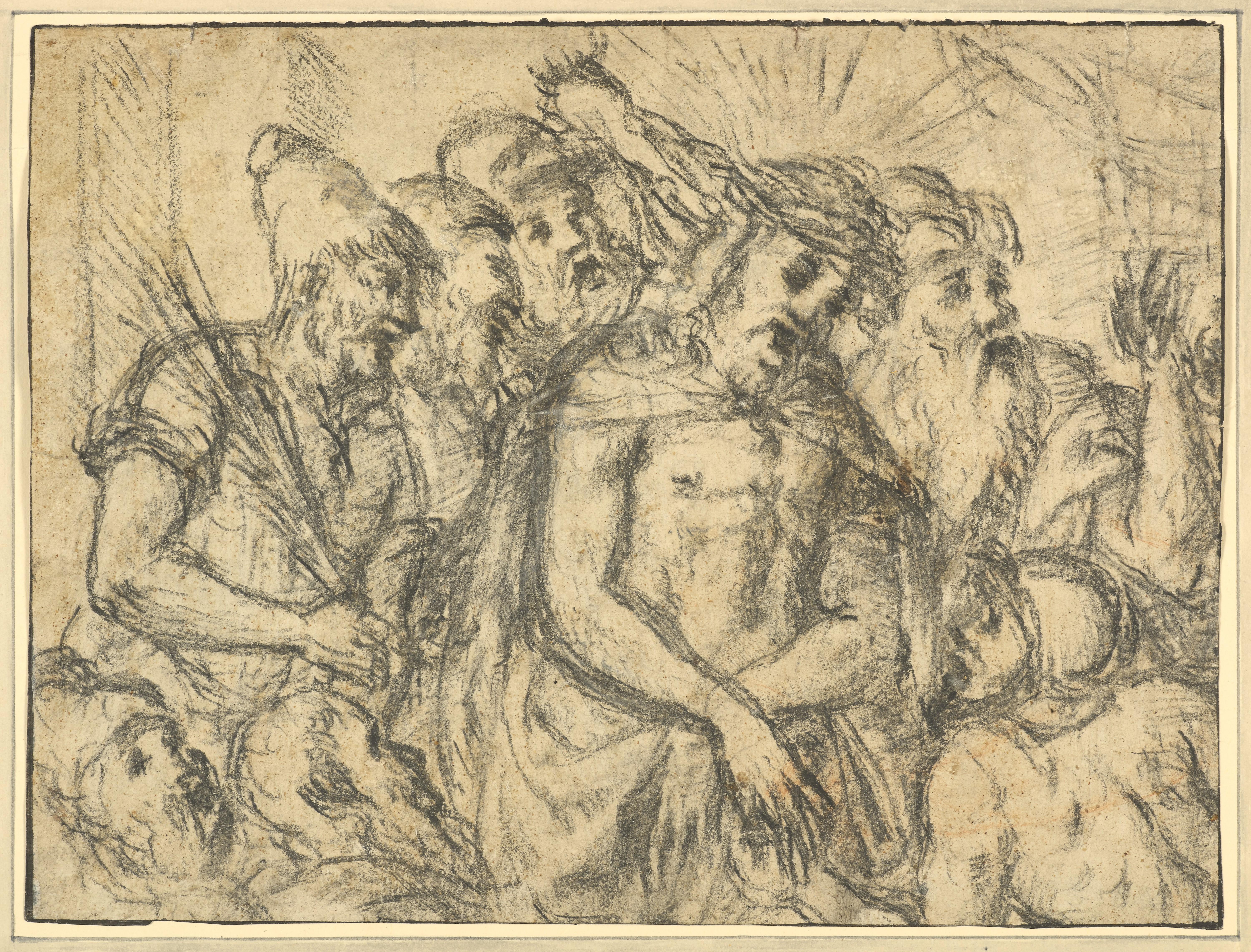
- Christ before Herod, a drawing from the School of TitianLocated in PARIS, FRThis vigorous drawing is clearly inspired by the numerous compositions on the Ecce Homo theme which were produced by Titian and his workshop at the painter's maturity. However, the number of characters and their expressionist treatment, the many variations to Titian's paintings reveal a drawing made by an original artist, perhaps of foreign origin, belonging to the peripheral circle of the "Titian solar system”, as described by the art historian Enrico Maria del Pozzolo. 1. Titian, the leading artist of 16th century Venetian painting and his botteghe Tiziano Vecelli (or Vecellio), known as Titian, was born between 1489 and 1490 in Pieve di Cadore in the Veneto region of Italy into a wealthy family of soldiers and lawyers. At the age of 15, he joined the studio of Giovanni Bellini, where he became friend with Giorgione, ten years his senior. Giorgione introduced him to a new pictorial style in which forms are defined by colour and pictorial substance, freeing himself from the meticulous underlying drawings characteristic of Bellini's painting. Titian became the official painter of the Republic of Venice upon Bellini's death in 1516. In 1518, the completion of his Assumption for the church of Santa Maria Gloriosa dei Frari in Venice established his reputation as the leading painter of the Venetian school: throughout his career, Titian had a considerable impact on other artists of his time, whether they were direct collaborators, occasional contributors, or other artists under his influence. Considered one of the greatest portraitists of his time, his fame spread throughout Europe and he became the official painter of the greatest European families: the Gonzagas, the Farneses (Alessandro Farnese, of whom he executed several portraits, was elected pope in 1534 under the name of Paul III), the Habsburgs (he went to Augsburg in 1548 to paint the portrait of Charles V and King Philip II of Spain, his successor, later became the artist's main patron). As Titian almost reached the age of 90 years, he saw during his lifetime the death of many of his loved ones (his wife Cecilia, his brother Francesco and his son Orazio). A pathetic feeling appears in his late artworks, such as his famous Pieta, his last work intended to decorate his tomb which remained unfinished. Titian's success was also based on the establishment of a large and versatile workshop, which, alongside the traditional assistance in the production of certain paintings, ensured the publication of numerous woodcuts, allowing the master's works to be widely distributed. Long ignored by art historians, the individual stories of these various collaborators, the organisation of this workshop and the interactions of the collaborators with the master are at the heart of contemporary studies on the artist. 2. A complex composition with expressionist overtones Executed with great virtuosity in black chalk, the composition of our drawing is complex, even slightly confused and probably reflects several phases of execution, if not several hands. The scene is organised around the characters of Christ and an executioner wearing a Phrygian cap. Christ is presented at mid-body, slightly at an angle, his torso bare, his shoulders draped in a cloak, his hands clasped together and probably bound. His head, as if weighed down by the crown of thorns, is slightly bent forward. The eyes and mouth are hollowed out by the black chalk to better express his sorrow. The man wearing a Phrygian cap holds a whip in his right hand, while his left hand, barely outlined, seems to be pulling aside Christ's tunic as if he were about to scourge him. Two other men, who may have been added at a later stage, occupy the space between the executioner and Christ. One is depicted in profile, while the one behind Christ appears to be wearing a military helmet. In an indistinct gesture, his left arm is raised as if to strike Christ. Slightly behind Jesus on his left side, appears a bearded old man wearing a turban. With his left arm raised, he holds out the palm of his hand in a gesture of amazement. His face is finely executed and contrasts with the hand depicted in a rather crude manner. This character may also have been added at a later stage, as he does not fit in perfectly behind the group formed by Jesus and his executioner. This frieze is completed in the left foreground by two additional figures depicted in three-quarter view. Soberly sketched but with great fluidity, only their heads emerge, as if Christ and his executioners were situated on a pedestal above a large crowd. Finally, on the right-hand side of the composition, a second helmeted soldier is depicted. His musculature can be seen under his armour while he stares intently at Christ. He is smaller than the other figures, even though he appears in the front row, revealing a certain clumsiness on the part of the artist. 3. Ecce Homo, one of Titian’s favourite subjects in his twilight years In 1543, Titian tackled the theme of the Ecce Homo in a masterly composition now in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. Christ is presented by Pilate, dressed in an antique costume, at the top of a staircase, in a large, highly architectural setting animated by a crowd of characters. The title of the painting refers to a passage from the Gospel of St John (19, 1-5): “Then Pilate took Jesus and had him flogged. The soldiers twisted together a crown of thorns and put it on his head. They clothed him in a purple robe and went up to him again and again, saying, “Hail, king of the Jews!” And they slapped him in the face. Once more Pilate came out and said to the Jews gathered there, “Look, I am bringing him out to you to let you know that I find no basis for a charge against him.” When Jesus came out wearing the crown of thorns and the purple robe, Pilate said to them, “Here is the man!” From the 1540s onwards, Titian and his workshop repeatedly depicted the Christ of Sorrows for their principal patrons. In these paintings, Titian returned to the half-body format that he had practically abandoned since 1520 and refocused the composition (compared to the large 1543 Ecce Homo) on the figure of Christ, who is depicted alone or accompanied by a few figures. With his eyes lowered and his head slightly bowed, Titian's Christ seems calmly resigned to his fate. Powerless and submissive, he arouses deep pathos from the viewer. The tondo in the Louvre Museum shows Christ in a position very similar to that of our drawing, a position that will be found in most of Titian's Ecce Homo. To his right stands a helmeted soldier who seems to be baring his shoulder and to his left a servant of Pilate wearing a Phrygian cap. These two figures are reminiscent of the soldier in the lower right corner and the executioner in the left most part of our drawing. Various versions were executed by Titian and his workshop until the late 1560s, and the version that seems closest to the right-hand side of our drawing is the one in the Prado Museum. Although of uneven quality, it is interesting to note the gesture of Pilate's hand, holding out the palm of his left hand towards the viewer, as if to distance himself from the decision that the crowd will make. Recent X-rays of the painting have shown that the executioner on the right, depicted from behind, was originally depicted in profile (as in our drawing), and that the other two figures (Pilate on the left of Christ and a servant wearing a Phrygian cap on his right) were added later. The painting was then organised around the diagonal that crosses the canvas from left to right, emphasised by the light coming from the window, and centred on the exchange of glances between Christ and the executioner on his left. The profile of the old man in the foreground on the left could be inspired by that of the elderly Titian as it appears repeatedly in the painter's late artworks, such as the Madonna of Mercy in the Palatine Gallery. 4. A deeply original drawing, at the risk of confusion We saw in the last paragraph the various borrowings from Titian's depictions of the Ecce Homo that can be found in this drawing: the position of Christ, the presence of executioners wearing Phrygian caps and of helmeted soldiers, one of whom is looking at Christ in a position that evokes the repentance visible with X-ray in the Madrid painting...Category
16th Century Old Masters Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
MaterialsChalk
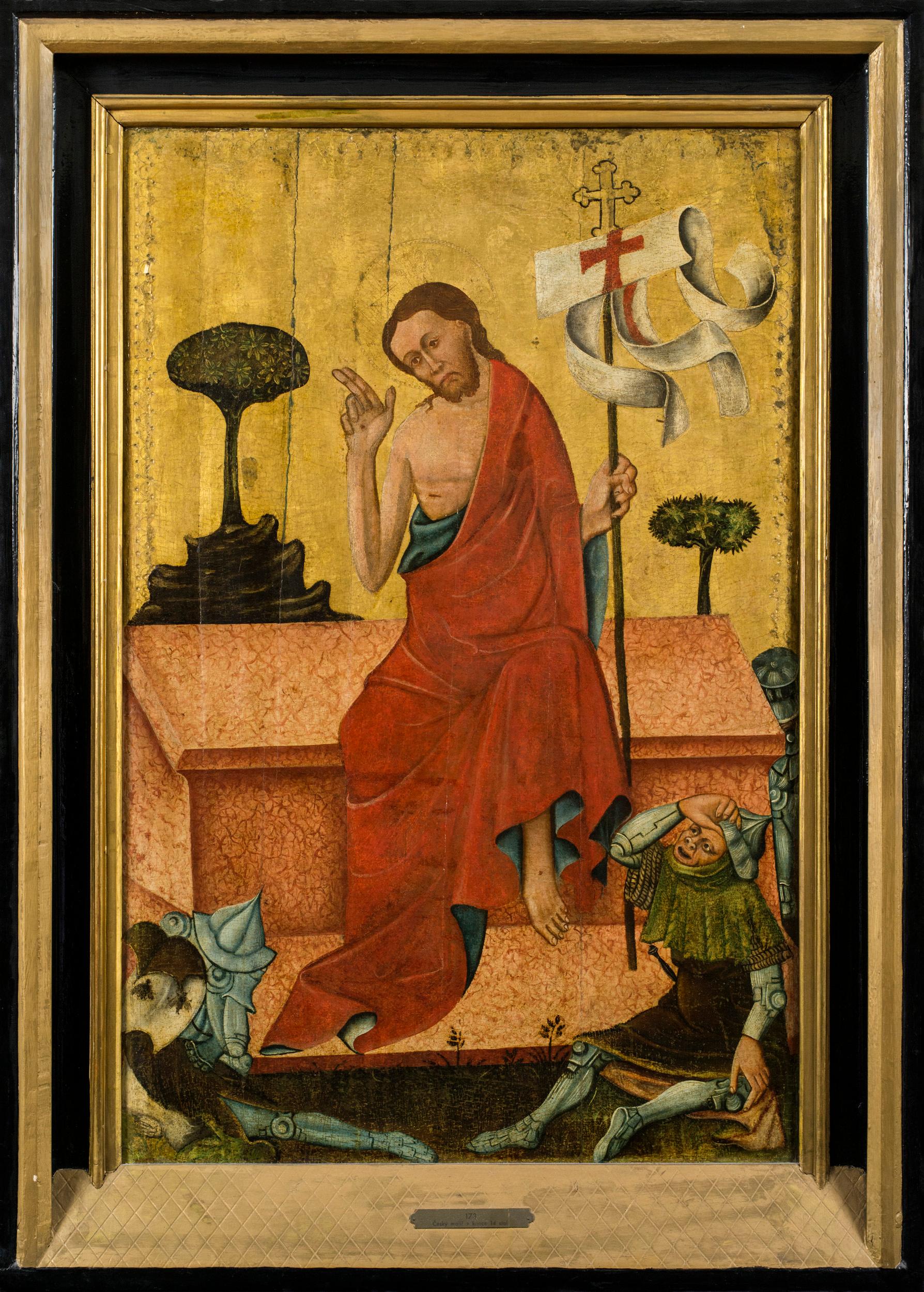
- The Resurrection of ChristLocated in New York, NYProvenance: with “Mr. Scheer,” Vienna, by July 1918; where acquired by: Jindřich Waldes, Prague, 1918–1941; thence by descent to: Private Collection, New York Literature: Rudolf Kuchynka, “České obrazy tabulové ve Waldesově obrazárně,” Památky archeologické, vol. 31 (1919), pp. 62-64, fig. 5. Jaroslav Pešina, “K datování deskových obrazů ve Waldesově obrazárně,” Ročenka Kruhu pro Pěstování Dějin Umění: za rok (1934), pp. 131-137. Jaroslav Pešina, Pozdně gotické deskové malířství v Čechách, Prague, 1940, pp. 150-151, 220. Patrik Šimon, Jindřich Waldes: sběratel umění, Prague, 2001, pp. 166, 168, footnote 190. Ivo Hlobil, “Tři gotické obrazy ze sbírky Jindřicha Waldese,” Umění, vol. 52, no. 4 (2004), p. 369. Executed sometime in the 1380s or 1390s by a close associate of the Master of the Třeboň Altarpiece, this impressive panel is a rare work created at the royal court in Prague and a significant re-discovery for the corpus of early Bohemian painting. It has emerged from an American collection, descendants of the celebrated Czech industrialist and collector Jindřich Waldes, who died in Havana fleeing Nazi-occupied Europe. The distinctive visual tradition of the Bohemian school first began to take shape in the middle of the fourteenth century after Charles IV—King of Bohemia and later Holy Roman Emperor—established Prague as a major artistic center. The influx of foreign artists and the importation of significant works of art from across Europe had a profound influence on the development of a local pictorial style. Early Italian paintings, especially those by Sienese painters and Tommaso da Modena (who worked at Charles IV’s court), had a considerable impact on the first generation of Bohemian painters. Although this influence is still felt in the brilliant gold ground and the delicate tooling of the present work, the author of this painting appears to be responding more to the paintings of his predecessors in Prague than to foreign influences. This Resurrection of Christ employs a compositional format that was popular throughout the late medieval period but was particularly pervasive in Bohemian painting. Christ is shown sitting atop a pink marble sarcophagus, stepping down onto the ground with one bare foot. He blesses the viewer with his right hand, while in his left he holds a triumphal cross with a fluttering banner, symbolizing his victory over death. Several Roman soldiers doze at the base of the tomb, except for one grotesque figure, who, beginning to wake, shields his eyes from the light and looks on with a face of bewilderment as Christ emerges from his tomb. Christ is wrapped in a striking red robe with a blue interior lining, the colors of which vary subtly in the changing light. He stands out prominently against the gold backdrop, which is interrupted only by the abstractly rendered landscape and trees on either side of him. The soldiers’ armor is rendered in exacting detail, the cool gray of the metal contrasting with the earth tones of the outer garments. The sleeping soldier set within a jumble of armor with neither face nor hands exposed, is covered with what appears to be a shield emblazoned with two flies on a white field, somewhat resembling a cartouche (Fig. 1). This may be a heraldic device of the altarpiece’s patron or it may signify evil, referencing either the Roman soldiers or death, over both of which Christ triumphs. This painting formed part of the collection assembled by the Czech industrialist and founder of the Waldes Koh-i-noor Company, Jindřich Waldes, in the early twentieth century. As a collector he is best remembered for establishing the Waldes Museum in Prague to house his collection of buttons (totaling nearly 70,000 items), as well as for being the primary patron of the modernist painter František Kupka. Waldes was also an avid collector of older art, and he approached his collecting activity with the goal of creating an encyclopedic collection of Czech art from the medieval period through to the then-present day. At the conclusion of two decades of collecting, his inventory counted 2331 paintings and drawings, 4764 prints, and 162 sculptures. This collection, which constituted the Waldesova Obrazárna (Waldes Picture Gallery), was first displayed in Waldes’ home in Prague at 44 Americká Street and later at his newly built Villa Marie at 12 Koperníkova Street. This Resurrection of Christ retains its frame from the Waldes Picture Gallery, including its original plaque “173 / Česky malíř z konce 14 stol.” (“Czech painter from the end of the 14th century”) and Waldes’ collection label on the reverse. The Resurrection of Christ was one of the most significant late medieval panel...Category
15th Century and Earlier Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsTempera, Panel
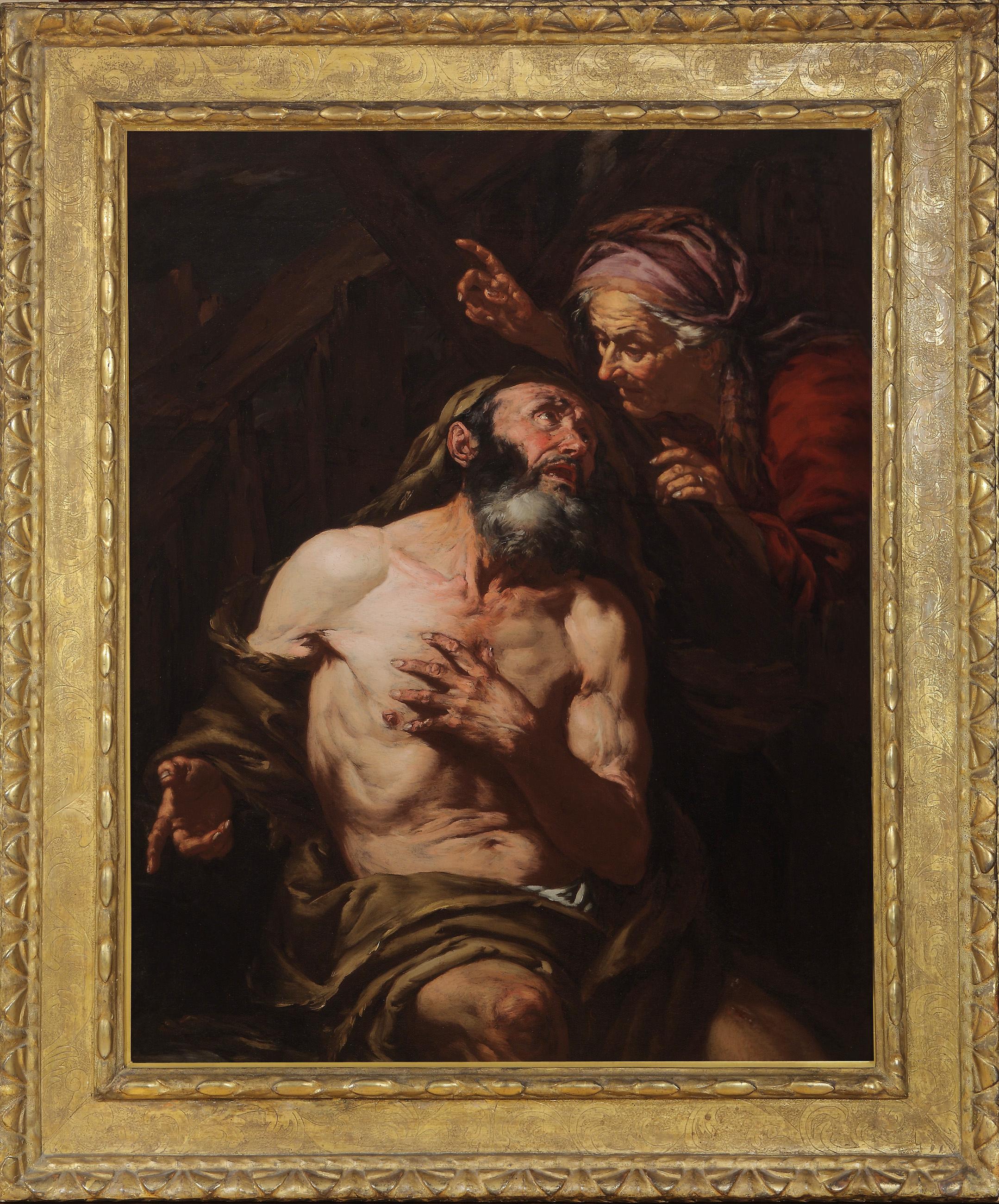
- Job Cursed by His WifeBy Giovanni Battista LangettiLocated in New York, NYProvenance: Alfred (1883-1961) and Hermine Stiassni (1889-1962), Brno, Czech Republic, by 1925; thence London, 1938-1940; thence Los Angeles, 1940-1962; thence by descent to: Susanne Stiassni Martin and Leonard Martin, San Francisco, until 2005; thence by descent to: Private Collection, California Exhibited: Künstlerhaus, Brünn (Brno), 1925, as by Ribera. “Art of Collecting,” Flint Institute of Art, Flint, Michigan, 23 November 2018 – 6 January 2019. Literature: Alte Meister...Category
1670s Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Oil
- Portrait of a Lady with a ChiqueadorLocated in New York, NYProvenance: Torres Family Collection, Asunción, Paraguay, ca. 1967-2017 While the genre of portraiture flourished in the New World, very few examples of early Spanish colonial portraits have survived to the present day. This remarkable painting is a rare example of female portraiture, depicting a member of the highest echelons of society in Cuzco during the last quarter of the 17th century. Its most distinctive feature is the false beauty mark (called a chiqueador) that the sitter wears on her left temple. Chiqueadores served both a cosmetic and medicinal function. In addition to beautifying their wearers, these silk or velvet pouches often contained medicinal herbs thought to cure headaches. This painting depicts an unidentified lady from the Creole elite in Cuzco. Her formal posture and black costume are both typical of the established conventions of period portraiture and in line with the severe fashion of the Spanish court under the reign of Charles II, which remained current until the 18th century. She is shown in three-quarter profile, her long braids tied with soft pink bows and decorated with quatrefoil flowers, likely made of silver. Her facial features are idealized and rendered with great subtly, particularly in the rosy cheeks. While this portrait lacks the conventional coat of arms or cartouche that identifies the sitter, her high status is made clear by the wealth of jewels and luxury materials present in the painting. She is placed in an interior, set off against the red velvet curtain tied in the middle with a knot on her right, and the table covered with gold-trimmed red velvet cloth at the left. The sitter wears a four-tier pearl necklace with a knot in the center with matching three-tiered pearl bracelets and a cross-shaped earing with three increasingly large pearls. She also has several gold and silver rings on both hands—one holds a pair of silver gloves with red lining and the other is posed on a golden metal box, possibly a jewelry box. The materials of her costume are also of the highest quality, particularly the white lace trim of her wide neckline and circular cuffs. The historical moment in which this painting was produced was particularly rich in commissions of this kind. Following his arrival in Cuzco from Spain in the early 1670’s, bishop Manuel de Mollinedo y Angulo actively promoted the emergence of a distinctive regional school of painting in the city. Additionally, with the increase of wealth and economic prosperity in the New World, portraits quickly became a way for the growing elite class to celebrate their place in society and to preserve their memory. Portraits like this one would have been prominently displayed in a family’s home, perhaps in a dynastic portrait gallery. We are grateful to Professor Luis Eduardo Wuffarden for his assistance cataloguing this painting on the basis of high-resolution images. He has written that “the sober palette of the canvas, the quality of the pigments, the degree of aging, and the craquelure pattern on the painting layer confirm it to be an authentic and representative work of the Cuzco school of painting...Category
17th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Oil
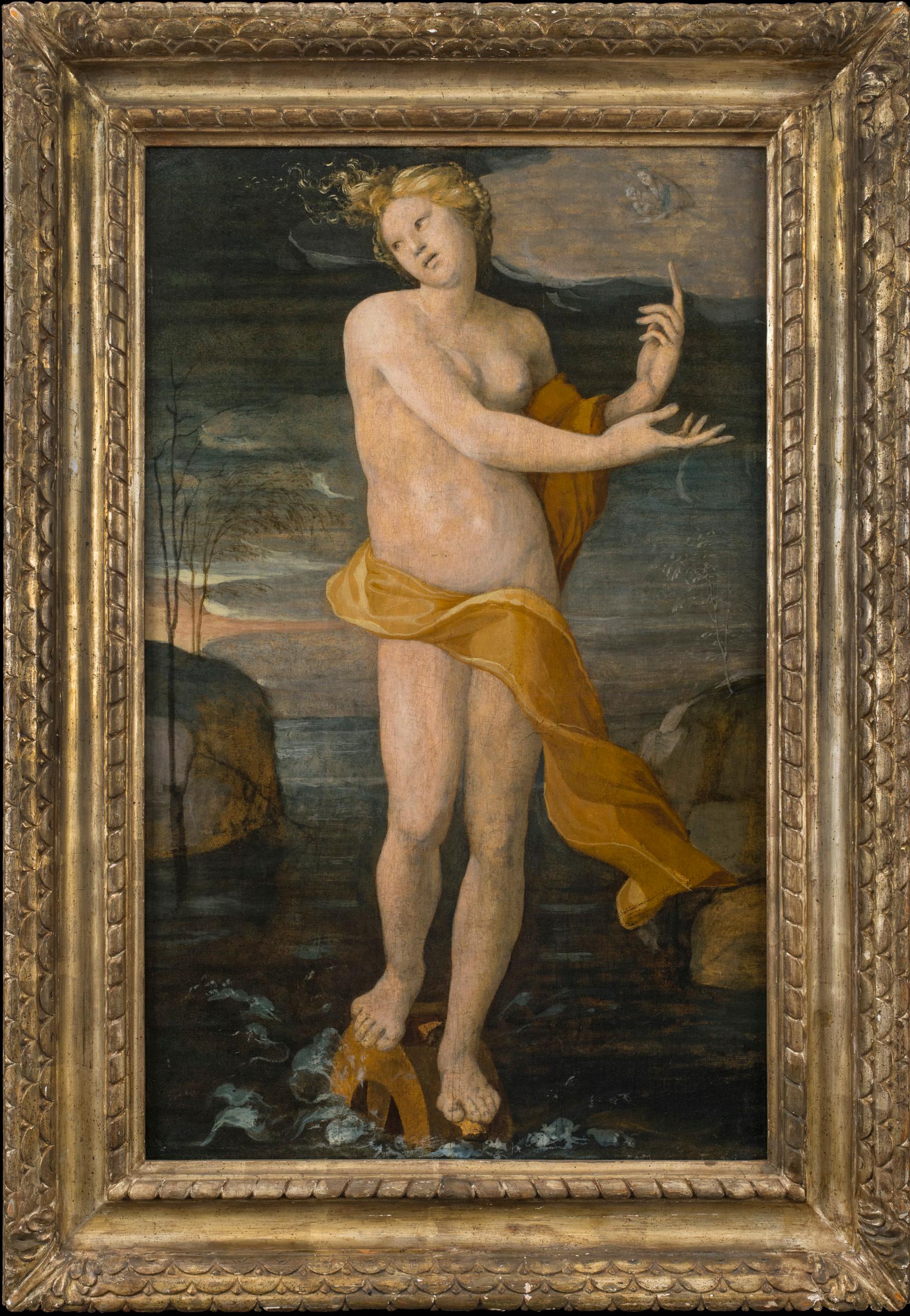
- Allegory of FortuneLocated in New York, NYProvenance: S. Spinelli Collection, Florence; their sale, Galleria Pesaro, Milan, July 11-14, 1928, lot 112 (unsold); reoffered Galleria Luigi Bellini, Florence, April 23-26, 1934, lot 132, as manner of Baldassare Peruzzi Dr. Giacomo Ancona, Florence, 1930s, and after 1939, San Francisco; thence by descent to his son: Mario Ancona, San Francisco; thence by descent to his children: Mario Ancona III and Victoria Ancona, San Francisco, until 1995; thence to: Phyllis Ancona Green, widow of Mario Ancona, Los Angeles (1995-2012) Literature: Donato Sanminiatelli, Domenico Beccafumi. Milan 1967, p. 170 (under paintings attributed to Beccafumi) Among the precious survivors of Renaissance secular paintings for domestic interiors are several unusual and particularly attractive panels painted in Siena at the end of the fifteenth and beginning of the sixteenth centuries. These paintings depict exemplary figures from antiquity—heroes or heroines, as well as allegorical, literary, and mythological figures. For the most part, these panels have survived in groups of three, although it is possible that some of these works were painted either as part of larger series or as individual projects. One such trio by Beccafumi consists of two paintings now at the National Gallery, London (Marcia and Tanaquil) and a third in the Galleria Doria-Pamphilj, Rome (Cornelia). These were commissioned around 1517–1519 for the bedroom of Francesco di Camillo Petrucci in Siena and were most likely placed together as elements in the wall decoration (spalliere) or installed above the back of a bench or cassapanca. Another, earlier (ca. 1495–1500), set of three—Guidoccio Cozzarelli’s Hippo, Camilla, and Lucretia (Private Collection, Siena) survives with its original wooden framework—a kind of secular triptych. Judith, Sophonisba, and Cleopatra in the collection of the Monte dei Paschi, Siena, are by an anonymous artist close to Beccafumi called the “Master of the Chigi-Saracini Heroines.” Girolamo di Benvenuto’s Cleopatra, Tuccia, and Portia are dispersed (homeless, Prague, Chambery), and Brescianino’s Faith, Hope, and Charity are in the Pinacoteca Nazionale in Siena. The present painting first appeared in the Spinelli sale in Florence in 1934, at which time it was sold with two panels of identical size and format. Each was catalogued as being by the “manner of Baldassare Peruzzi” and of unidentified subject. Of these, the painting depicting a male figure turned to the right has recently reappeared in a private Italian collection, while the location of the third work, portraying a cloaked figure turned three-quarters left, remains unknown. Our panel depicts the allegorical figure of Fortune. Here she is represented in typical fashion as a nude female figure balanced on a wheel (sometimes called the Rota Fortunae), her billowing drapery indicating that she is as changeable as the wind. The appearance of the Virgin and Child in the cloud at the upper right is an unusual addition to the iconography. The subjects of the two pendant male...Category
16th Century Old Masters Paintings
MaterialsOil, Panel
- 18th century allegorical painting of The Triumph of BeautyLocated in London, GBExhibited: London, Royal Academy, 1800, no. 93 What was happening in British history painting in around 1800? In recent discussions of the emergence of a British School of history painting following the foundation of the Royal Academy in 1768, this is a question which is rarely posed and one which is not easily answered. Examination of surviving Royal Academy exhibition catalogues reveals a profusion of artists’ names and titles, few of which remain immediately recognizable, whilst endeavours to explain the impact of exhibition culture on painting - such as the 2001 Courtauld show Art on the Line - have tended to focus on the first and second generation of Royal Academician, rather than young or aspiring artists in the early nineteenth century. This makes the discovery and identification of the work under discussion of exceptional importance in making sense of currents in English painting around 1800. Executed by Edward Dayes...Category
18th Century Old Masters Figurative Paintings
MaterialsCanvas, Oil
Recently Viewed
View AllMore Ways To Browse
Nativity Painting
Nordic School
Pair Of 17th Century Portraits
Concrete Dog
Flemish Painting Pair
Adoration Magi
Adoration Of The Magi
Italian Nativity
Woman Baby Drawing
Antique Nativity Scene
Antique Nativity Scenes
Nativity Scene Antique
Nativity Oil
Nativity Oil Painting
Antique Baby Photos
Antique Nativity Italy
French Nativity
Black Nativity