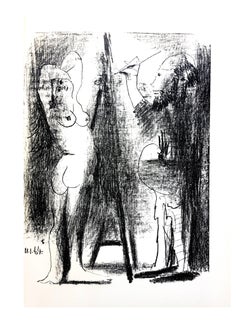Galerie Harmonia More Prints
to
159
24
17
4
Overall Width
to
Overall Height
to
105
73
19
2
1
46
21
19
15
13
201
3
1
1
9
43
104
25
1
15
176
27
1
148
39
8
7
3
204
Jean Cocteau - Vision - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Bull - Man - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Bulls - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Pablo Picasso - Painter and His Model - Original Lithograph
By Pablo Picasso
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Pablo Picasso - Painter and His Model - Original Lithograph
1964
Dimensions: 30 x 20 cm
Edition of 200 (one of the 200 on Vélin de Rives)
Mourlot Press, 1964
Cramer, 128
Unsigned an...
Category
1960s Modern Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - For Paul Valery - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Paul Valery Poems
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 32 x 25.5 cm
Edition: 200
1959
Publisher: Bibliophiles Du Palais
Unnumbered as issued
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Reflections - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Reflections
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 32 x 25.5 cm
Edition: 200
1959
Publisher: Bibliophiles Du Palais
Unnumbered as issued
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Bulls - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
From the last po...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Bulls - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Profile - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Portrait - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Portrait - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Portrait - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
Jean Cocteau
W...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Portrait - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
From the last po...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Henri Matisse - Fruits - Original Lithograph
By Henri Matisse
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Henri Matisse - Fruits - Original Lithograph
1964
Dimensions: 30 x 20 cm
Edition of 200 (one of the 200 on Vélin de Rives)
Mourlot Press, 1964
Unsigned and unumbered as issued
Category
1960s Modern Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Joan Miro - Peacock Feathers - Original Lithograph
By Joan Miró
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Joan Miro - Peacock Feathers - Original Lithograph
Artist: Joan Miro
Dimensions: 9 x 14-/12 inches (sheet), with the usual centerfold, as published in "Joan Miro" by Jacques Prevert ...
Category
1950s Abstract Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Joan Miro - Blue Maze - Original Lithograph
By Joan Miró
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Joan Miro - Blue Maze - Original Lithograph
Artist: Joan Miro
Editor: Maeght
Year: 1956
Dimensions: 23 x 38 cm
Unsigned and unnumbered as issued
From Miro by Jacques Prevert
Referenc...
Category
1950s Abstract Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Original Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Reference: Chagall Lithographe 1957-1962. VOLUME II.
Unsigned edition of over 5,000
Condition : Excellent
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Inspiration - Original Lithograph from "Chagall Lithographe" v. 2
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph from Chagall Lithographe 1957-1962. VOLUME II.
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
From the unsigned edition of 10000 copies without margins
Reference: Mourlot 398
Condition : Excellent
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish Theater...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Original Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Reference: Chagall Lithographe 1957-1962. VOLUME II.
Condition : Excellent
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish Theater...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Original Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Reference: Chagall Lithographe 1957-1962. VOLUME II.
Unsigned edition of over 5,000
Condition : Excellent
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Flowered Clown - Original Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
From Chagall Lithograph II
Reference: Mourlot 399
Condition : Excellent
Unsigned and unumbered as issued
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Original Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Reference: Chagall Lithographe 1957-1962. VOLUME II.
Condition : Excellent
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish Theater...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Sonia Delaunay - Composition - Original Lithograph
By Sonia Delaunay
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Sonia Delaunay - Composition
Original Lithograph
1969
Dimensions: 32 x 25 cm
Revue XXe Siècle
Cahiers d'art published under the direction of G. di San Lazzaro.
Sonia Delaunay was known for her vivid use of color and her bold, abstract patterns, breaking down traditional distinctions between the fine and applied arts as an artist, designer and printmaker.
Born Sarah Stern on November 14, 1885 in Gradizhsk, Ukraine, she was adopted in 1890 by her maternal uncle, Henri Terk, a lawyer in St. Petersburg, where she grew up, exposed to music and art, and learning several foreign languages. In 1903, she moved to Germany to study drawing with Ludwig Schmidt-Reutler (1863–1909) at the Karlsruhe academy of fine arts; Arnold Schoenberg (1874–1951), composer-to-be, was among her classmates there. In 1905, she traveled to Paris where she attended art classes at the Académie de la Palette, learned printmaking from Rudolf Grossman (1889–1941), and met Amédée Ozenfant (1886–1966), André Dunoyer de Segonzac (1884–1974), and Jean-Louis Boussingault (1883–1943). Sonia spent much of her time at exhibitions and galleries in Paris, which showed works by Paul Cézanne, Vincent Van Gogh, Pierre Bonnard, and Edouard Vuillard, as well as Les Fauves, Henri Matisse and André Derain. She did, however, maintain contact with Germany, exhibiting at the Galerie Der Sturm, Berlin, in 1913, 1920 and 1921.
During her first year in Paris, Sonia met the German collector and art-dealer, Wilhelm Uhde (1874–1947), whom she married on December 5, 1908, and whose Montparnasse gallery, the Galerie Notre-Dame des Champs, showed her first solo exhibition. Through Uhde, Sonia encountered many painters, including Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque, Maurice de Vlaminck, and Robert Delaunay (1885–1941). In 1910, Sonia divorced Uhde by mutual agreement, married Delaunay that same year, and gave birth to their son, Charles, in January 1911.
Together Sonia and Robert Delaunay pursued the study of color, influenced by theories of Michel-Eugène Chevreul (1786–1889). Sonia’s interest in simultaneous contrast, as evidenced in her early collages, book bindings, small painted boxes, cushions, waistcoats and lampshades, led to one of her first large-scale works, the painting of the Bal Bullier (1912–1913), a popular Parisian dance-hall. Sonia’s first “simultaneous dresses,” a mix of squares and triangles of taffeta, tulle, flannelette, moiré, and corded silk, date from this period.
Friendship with the poet Blaise Cendrars...
Category
1970s Abstract Geometric Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Pierre Soulages - Original Lithograph
By Pierre Soulages
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Pierre Soulages - Original Lithograph
Published in the deluxe art review "XXe siècle"
1970
Unsigned as published
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Pierre Soulages or the "painter of black" as ...
Category
1970s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Blue Lady - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Blue Lady
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 32 x 25.5 cm
Edition: 200
1959
Publisher: Bibliophiles Du Palais
Unnumb...
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Torrero - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Taureaux
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 40 x 30 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Trinckvel
1965
From the last po...
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - A Midsummer Night's dream - Original Handsigned Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall - A Midsummer Night's dream - Original Handsigned Lithograph
1975
Dimensions: Sheet : 97.5 x 71.5 cm Image : 80 x 60 cm
Handsigned and numbered
Edition: 50
Reference: ...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Joan Miro - The Party - Original Lithograph
By Joan Miró
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Joan Miro - The Party - Original Lithograph
Artist: Joan Miro
Editor: Maeght
Year: 1956
Dimensions: 23 x 38 cm
Reference: Mourlot 236
A unique collaboration between Miró (responsible for the central image), the art critic...
Category
1950s Abstract Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
André Lanskoy - Composition - Original Etching
By André Lanskoy
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
André Lanskoy - Composition - Original Etching
From Dédale
Edition: 190
Dimensions: 32 x 18 cm
This etching is from the first series of etching Lanskoy m...
Category
1960s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Cocteau - Immortal Goat - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Immortal Goat
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 38 x 28 cm
Edition: 200
1958
Jean Cocteau
Writer, artist and film director Jean Cocteau was...
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
After Georges Braque - Les oiseaux de nuit - Lithograph
By Georges Braque
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Georges Braque - Les oiseaux de nuit
Lithograph after the gouache
1964
Dimensions: 30 x 20 cm
Edition of 200 (one of the 200 on Vélin de Rives)
Mourlot Pre...
Category
1960s Modern Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Summer's Dream - Original Handsigned Lithograph
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall - Summer's Dream - Original Handsigned Lithograph
1983
Printed by Mourlot
Dimensions: 48 x 65 cm
Handsigned in pencil
Justified EA (Epreuve D'artiste, Artist proof) asi...
Category
1980s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Marc Chagall - Bath-Sheba at the Feet of David - Original Handsigned Etching
By Marc Chagall
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Marc Chagall - Bath-Sheba at the Feet of David - Original Handsigned Etching
1958
Printed by Tériade
Dimensions: 54 x 39 cm
Handsigned and numbered
handcolored
Edition: 100
Reference: Cramer 30.
Etching with hand-coloring, circa 1930, initialled in pencil, numbered 75/100 (there were also twenty hors-commerce copies) , published 1958 by Tériade, Paris, on Arches wove paper
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish Theater, where he would paint a series of murals titled Introduction to the Jewish Theater as well. In 1921, Chagall also found work as a teacher at a school for war orphans. By 1922, however, Chagall found that his art had fallen out of favor, and seeking new horizons he left Russia for good.
Flight
After a brief stay in Berlin, where he unsuccessfully sought to recover the work exhibited at Der Sturm before the war, Chagall moved his family to Paris in September 1923. Shortly after their arrival, he was commissioned by art dealer and publisher Ambroise Vollard to produce a series of etchings for a new edition of Nikolai Gogol's 1842 novel Dead Souls. Two years later Chagall began work on an illustrated edition of Jean de la Fontaine’s Fables, and in 1930 he created etchings for an illustrated edition of the Old Testament, for which he traveled to Palestine to conduct research.
Chagall’s work during this period brought him new success as an artist and enabled him to travel throughout Europe in the 1930s. He also published his autobiography, My Life (1931), and in 1933 received a retrospective at the Kunsthalle in Basel, Switzerland. But at the same time that Chagall’s popularity was spreading, so, too, was the threat of Fascism and Nazism. Singled out during the cultural "cleansing" undertaken by the Nazis in Germany, Chagall’s work was ordered removed from museums throughout the country. Several pieces were subsequently burned, and others were featured in a 1937 exhibition of “degenerate art” held in Munich. Chagall’s angst regarding these troubling events and the persecution of Jews in general can be seen in his 1938 painting White Crucifixion.
With the eruption of World War II, Chagall and his family moved to the Loire region before moving farther south to Marseilles following the invasion of France. They found a more certain refuge when, in 1941, Chagall’s name was added by the director of the Museum of Modern Art (MOMA) in New York City to a list of artists and intellectuals deemed most at risk from the Nazis’ anti-Jewish campaign. Chagall and his family would be among the more than 2,000 who received visas and escaped this way.
Haunted Harbors
Arriving in New York City in June 1941, Chagall discovered that he was already a well-known artist there and, despite a language barrier, soon became a part of the exiled European artist community. The following year he was commissioned by choreographer Léonide Massine to design sets and costumes for the ballet Aleko, based on Alexander Pushkin’s “The Gypsies” and set to the music of Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky.
But even as he settled into the safety of his temporary home, Chagall’s thoughts were frequently consumed by the fate befalling the Jews of Europe and the destruction of Russia, as paintings such as The Yellow Crucifixion...
Category
1960s Surrealist Figurative Prints
Materials
Etching
(after) Sonia Delaunay - Composition - Pochoir
By Sonia Delaunay
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
(after) Sonia Delaunay - Composition - Pochoir
1956
Dimensions: 32 x 25 cm
Revue XXe Siècle
Cahiers d'art published under the direction of G. di San Lazzaro.
Unsigned and unumbered ...
Category
1950s Abstract Geometric Figurative Prints
Materials
Stencil
Jean Cocteau - Woman Portrait - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Woman Portrait
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 32 x 25.5 cm
Edition: 200
1959
Publisher: Bibliophiles Du Palais
Unnumbered as issued
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Joan Miro - Plate 8, from Lézard aux plumes d'or
By Joan Miró
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Joan Miro - Plate 8, from Lézard aux plumes d'or - Original Handsigned Lithograph
Year: 1967
Handsigned in pencil
Edition: 100 numbered in Arabic numbers, plus 20 in Roman numerals
...
Category
1960s Abstract Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Serge Poliakoff (after) - Composition - Pochoir
By Serge Poliakoff
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Serge Poliakoff (after) - Composition - Pochoir
Published in the deluxe art review, XXe Siecle
1956
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Publisher: G. di San Lazzaro.
Unsigned and unumbered as is...
Category
1950s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Stencil
Serge Poliakoff - Abstract Beach - Original Lithograph
By Serge Poliakoff
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Serge Poliakoff - Abstract Beach - Original Lithograph
Published in the deluxe art review, XXe Siecle
1968
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Publisher: G. di San ...
Category
1960s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Europe and the World - Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Europe and the World
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 33 x 46 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Sciaky
1961
Category
1960s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Joan Miro - I Work Like a Gardener - Original Handsigned Lithograph
By Joan Miró
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Joan Miro - I Work Like a Gardener - Original Handsigned Lithograph
Year: 1964
Handsigned and numbered in pencil
Edition: 2 / 30
Printer : Mourlot, Paris
Dimensions: 22.5 x 23 cm
Ref...
Category
1960s Abstract Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - The Kiss - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: The Kiss
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 32 x 25.5 cm
Edition: 200
1959
Publisher: Bibliophiles Du Palais
Unnumbered as issued
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Young Girl - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - Young Girl - Original Lithograph
Signed and dated in the plate
Stampsigned
Dimensions: 53 x 42 cm
1956
Provenance : Succession Dermit, Cocteau's heir
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - Olé - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - Olé - Original Lithograph
1934
Signed and dated in the plate
Numbered in pencil
Edition : /200
Dimensions: 50 x 33 cm
Provenance : Succession Dermit, Cocteau's heir
Category
1930s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Etching
1998
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Edition: /40
From La Déchirure
Jean Miotte, 1926 - 2016
Miotte came of artistic age in the decade after World War II when non-figurative gestural abstraction was emerging on both sides of the Atlantic as the contemporary artistic language. The term, "L'Art Informel," was coined by the French critic, Michel Tapi, to connote "without form." The negation of traditional form, a radical break from established notions of order and composition, was particularly suited to a cultural environment born out of the circumstances of post war Europe where abuse of morals and fascist ideology had led to such horror and destruction.
While Informel is often regarded as the European equivalent of Abstract Expressionism, it is distinguished from its American counterpart, by a loss of faith in progress and the collective possibilities of an avant garde. Rather the artists who came to be grouped as Informel, Jean Miotte, Jean-Paul Riopelle, Emil Schumacher...
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Etching
1998
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Edition: /40
From La Déchirure
Jean Miotte, 1926 - 2016
Miotte came of artistic age in the decade after World War II when non-figurative gestural abstraction was emerging on both sides of the Atlantic as the contemporary artistic language. The term, "L'Art Informel," was coined by the French critic, Michel Tapi, to connote "without form." The negation of traditional form, a radical break from established notions of order and composition, was particularly suited to a cultural environment born out of the circumstances of post war Europe where abuse of morals and fascist ideology had led to such horror and destruction.
While Informel is often regarded as the European equivalent of Abstract Expressionism, it is distinguished from its American counterpart, by a loss of faith in progress and the collective possibilities of an avant garde. Rather the artists who came to be grouped as Informel, Jean Miotte, Jean-Paul Riopelle, Emil Schumacher...
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Cocteau - Christ - Original Handsigned and Handcolored Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - Christ - Original Handsigned and Handcolored Lithograph
Signed in the plate
Handsigned and dated in color pencil.
Handcolored in pencil.
Dimensions: 50.5 x 33 cm
1957
...
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Joan Miro - Plate IV from Espriu -Etching
By Joan Miró
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Joan Miro Plate IV from Espriu.
Year: 1975
Handsigned in pencil
Edition: HC (Hors Commerce) aside from the edition of 50.
On watermarked Sala Gaspar
Publisher : Sala Gaspar, Barcelo...
Category
1970s Abstract Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Cocteau - Angel - Original Handcolored Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - Angel - Original Handcolored Lithograph
Signed in the plate
Stampsigned
Handcolored in pencil.
Edition : /XXV
Dimensions: 47.5 x...
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Signed Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Signed Etching
1994
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Signed and numbered in pencil
Edition: /60
From Près du mur
Jean Miotte, 1926 - 2016
Miotte came of artistic age i...
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Etching
1998
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Edition: /40
From La Déchirure
Jean Miotte, 1926 - 2016
Miotte came of artistic age in the decade after World War II when non-figurative gestural abstraction was emerging on both sides of the Atlantic as the contemporary artistic language. The term, "L'Art Informel," was coined by the French critic, Michel Tapi, to connote "without form." The negation of traditional form, a radical break from established notions of order and composition, was particularly suited to a cultural environment born out of the circumstances of post war Europe where abuse of morals and fascist ideology had led to such horror and destruction.
While Informel is often regarded as the European equivalent of Abstract Expressionism, it is distinguished from its American counterpart, by a loss of faith in progress and the collective possibilities of an avant garde. Rather the artists who came to be grouped as Informel, Jean Miotte, Jean-Paul Riopelle, Emil Schumacher...
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Signed Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Signed Etching
1994
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Signed and numbered in pencil
Edition: /60
From Près du mur
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Cocteau - Blue Eagle - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - Blue Eagle - Original Lithograph
1956
Stampsigned lower left
Signed and dated in the plate
Numbered in pencil
Edition : /XXV
Dimensions: 50 x...
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Cocteau - King Oedipus - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - King Oedipus - Original Lithograph
1956
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 66 x 50 cm
Provenance : Succession Dermit, Cocteau's heir
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
(after) Robert Delaunay - La fenêtre no. 2 - Pochoir
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
(after) Robert Delaunay - La fenêtre no. 2 - Pochoir
From the literary review "XXe Siècle"
1957
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Publisher: G. di San Lazzaro.
Category
1950s Abstract Geometric More Prints
Materials
Stencil
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Etching
1998
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Edition: /40
From La Déchirure
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Signed Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Signed Etching
1994
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Signed and numbered in pencil
Edition: /60
From Près du mur
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Cocteau - Study for the Wall - Original Handsigned Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Cocteau - Study for the Wall - Original Handsigned Lithograph
Signed in pencil and numbered
Dimensions: 65 x 50 cm
Edition: 150
1956
Category
1950s Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Signed Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Signed Etching
1994
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Signed and numbered in pencil
Edition: /60
From Près du mur
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Jean Miotte - Abstract Composition - Original Etching
By Jean Miotte
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Jean Miotte - Original Etching
1998
Dimensions: 41 x 33 cm
Edition: /40
From La Déchirure
Category
1990s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Etching
Henri Michaux - Beach - Original Lithograph
By Henri Michaux
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Henri Michaux - Beach - Original Lithograph
1956
Dimensions: 32 x 25 cm
Edition: G. di San Lazzaro.
From the art review XXème siècle
Unsigned and unumbered as issued
Category
1950s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph