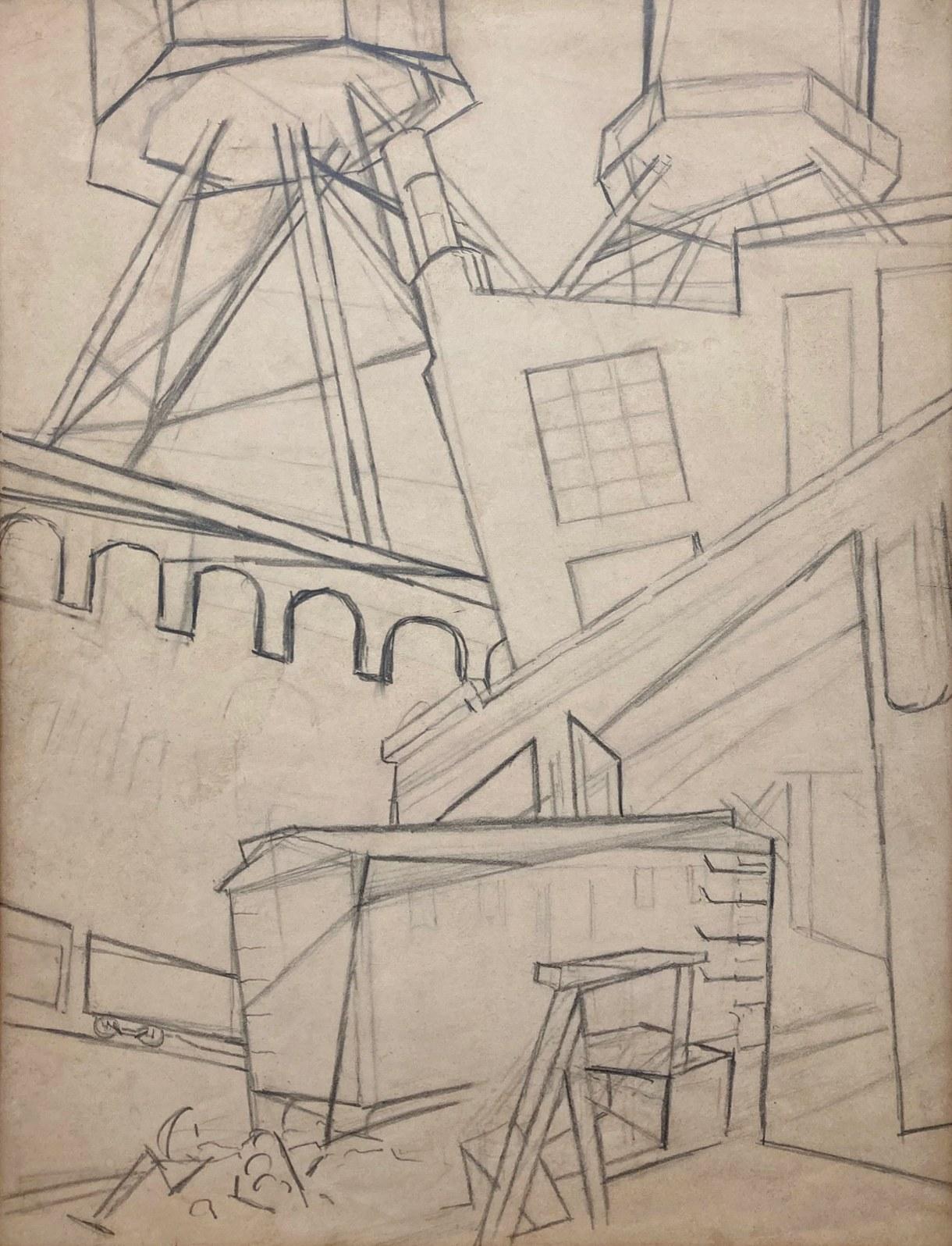
Items Similar to "East Providence" Oscar Bluemner, Drawing of East Providence, Architectural
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 3
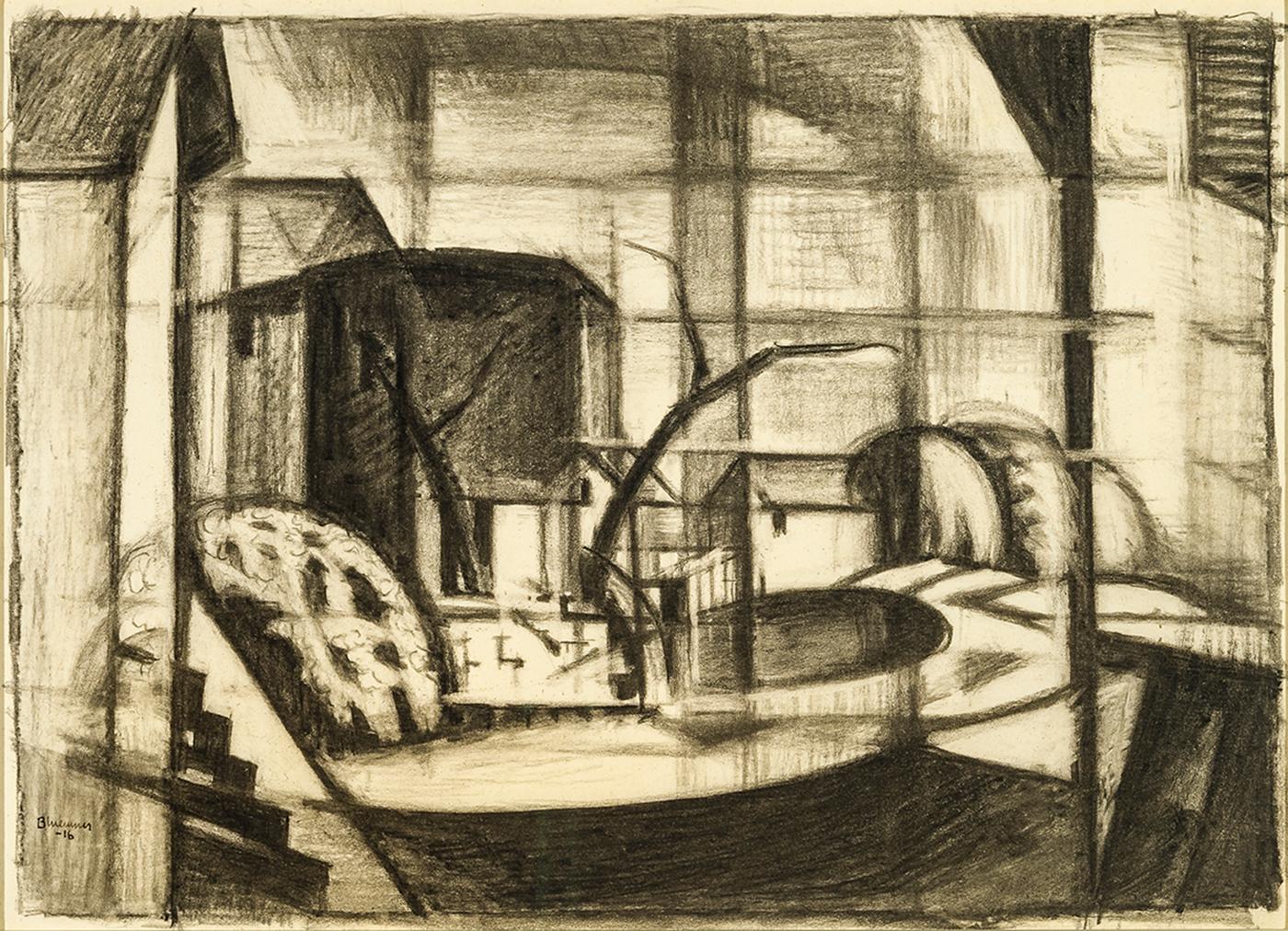
Oscar Bluemner"East Providence" Oscar Bluemner, Drawing of East Providence, Architectural1926
1926
$2,500
£1,897.96
€2,170.86
CA$3,492.86
A$3,884.83
CHF 2,028.54
MX$47,274.20
NOK 25,907.49
SEK 24,296.66
DKK 16,201.95
Shipping
Retrieving quote...The 1stDibs Promise:
Authenticity Guarantee,
Money-Back Guarantee,
24-Hour Cancellation
About the Item
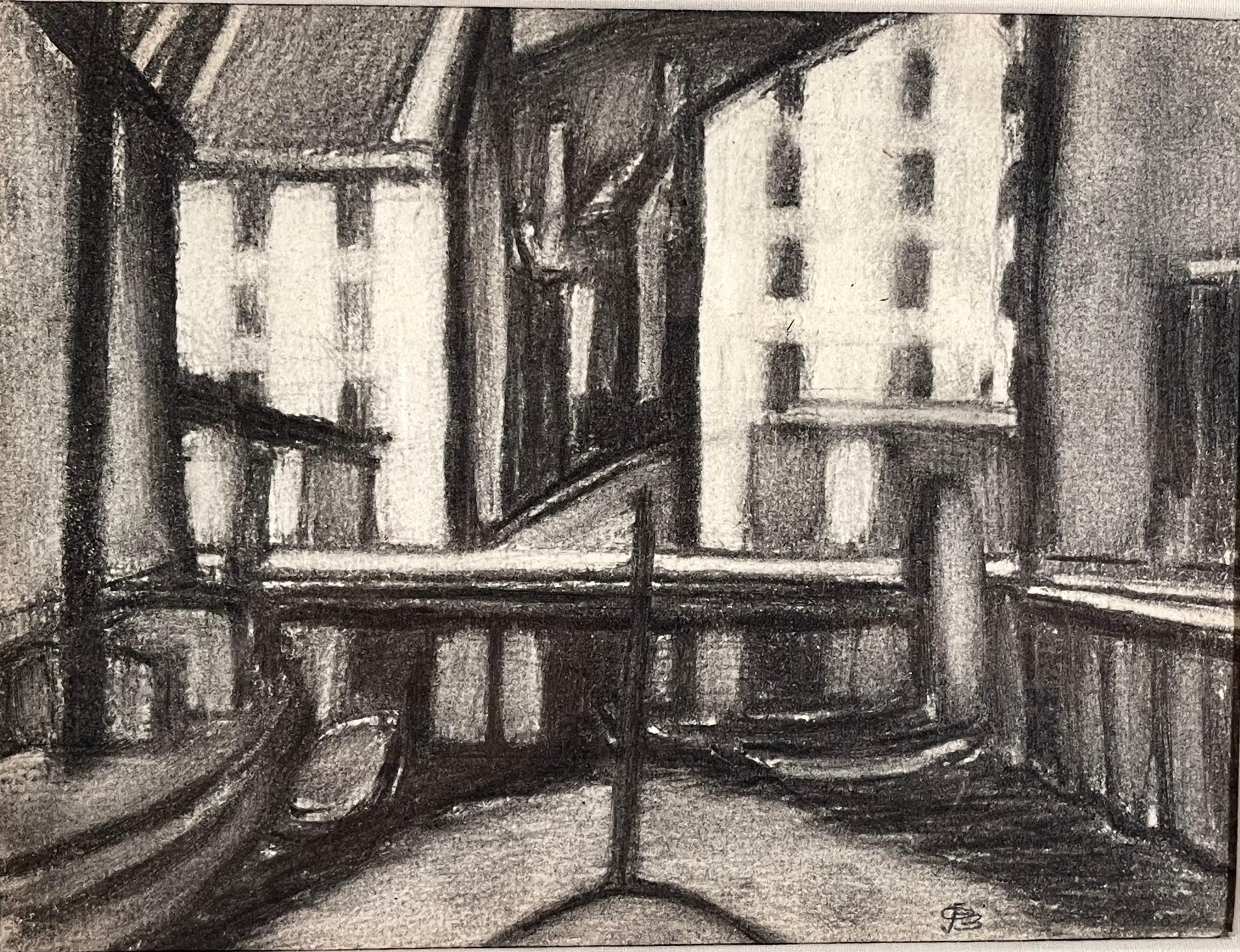
Oscar Bluemner
East Providence, December 21st, 1926
Inscribed with location and dated, upper left "East Providence Dec 21-26"
Black crayon on paper
5 x 7 7/8 inches
Julius Oskar Blümner (Oscar Bluemner) was born June 21, 1867, in Prenzlau, Prussia (now Germany). His family moved due to his father’s work as a master mason, so his early exposure to art occurred in various locales. Bluemner had his first formal training at age nine, soon after began sketching from nature, and by 1883 was an accomplished watercolorist. At age 18 he was given a solo exhibition at his secondary school, but he changed his major from art to architecture just before graduating.
From 1886 to 1892 Bluemner studied at Berlin’s prestigious Königliche Technische Hochschule (Royal Technical Academy). After earning his architecture degree, he became dissatisfied with the conservative climate in Germany and what he perceived as the neglect of his work. He decided to forego the military draft and immigrate to America. He worked briefly in New York and then as a draftsman at the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, and continued to travel between the two cities periodically looking for work. Bluemner married Lina Schumm in Chicago in 1896, and the couple had their first of two children that year.
In 1900 Bluemner was once again in New York and still struggling to establish himself. Four years later his designs for the Bronx Borough Courthouse for architect Michael J. Garvin were approved. Garvin, however, did not honor his promise to split fees and credit, leading to multiple lawsuits that would not be settled until 1911. In 1907, a frustrated Bluemner resolved to design country houses—echoing his longtime interest in sketching freestanding buildings and the landscape—while preparing to shift his career to painting. He frequented New York’s museums and galleries, studied art history, theory (particularly color theory), and painting techniques, and summarized his experiences in a journal titled “My Own Principles of Painting.” He met the influential dealer Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864 - 1946) and began rendering landscapes in a neoimpressionist style. In 1912, Bluemner, having arranged an exhibition of his oils and watercolors at a gallery in Berlin, embarked on an intensive seven-month trip to Europe. He absorbed the new trends in German art, particularly expressionism and futurism, through exhibitions and publications, while closely studying the old masters and sketching outdoors in Germany, Italy, France, the Netherlands, and England.
Upon his return to New York Bluemner began to publish articles and actively exhibit his work, most notably in the 1913 Armory Show, in a one-artist exhibition at Stieglitz’s 291 gallery in 1915, and in the Forum Exhibition at Anderson Gallery in 1916. However, he continued to clash with dealers, preferring to promote his work himself. Sales were nonexistent, and for the next ten years he and his family relocated nearly every six months within New Jersey, unable to meet their rent. Despite these financial hardships, Bluemner remained productive and looked to Asian and Old Master art as new sources of inspiration.
When Bluemner’s wife died in 1926, he and his daughter moved to South Braintree, Massachusetts, to live with his son. Grief-stricken, Bluemner explored the associations between emotions and color in a series of watercolors on board depicting suns and moons that were shown at Stieglitz’s Intimate Gallery in 1928. Bluemner also continued to write prolifically—his passion for red and its many meanings led him to adopt the pseudonym of “The Vermillionaire” in 1929, the year he privately published “What and When is Painting? Today.” Also that year he had a one-person show at the Whitney Studio Galleries, which strained his relationship with Stieglitz.
Bluemner’s only critically acclaimed one-person exhibition took place in 1935 at the Marie Harriman Gallery in New York. With the country still in the midst of the Great Depression, it did not yield a single sale. In 1938, after becoming increasingly ill and losing his eyesight, the artist took his own life.
- Creator:Oscar Bluemner (1867 - 1938, American)
- Creation Year:1926
- Dimensions:Height: 5 in (12.7 cm)Width: 7.875 in (20.01 cm)
- More Editions & Sizes:Unique workPrice: $2,500
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Framing:Framing Options Available
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:New York, NY
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU1841214417682
About the Seller
5.0
Platinum Seller
Premium sellers with a 4.7+ rating and 24-hour response times
Established in 2022
1stDibs seller since 2022
114 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: <1 hour
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Shipping from: New York, NY
- Return Policy
Authenticity Guarantee
In the unlikely event there’s an issue with an item’s authenticity, contact us within 1 year for a full refund. DetailsMoney-Back Guarantee
If your item is not as described, is damaged in transit, or does not arrive, contact us within 7 days for a full refund. Details24-Hour Cancellation
You have a 24-hour grace period in which to reconsider your purchase, with no questions asked.Vetted Professional Sellers
Our world-class sellers must adhere to strict standards for service and quality, maintaining the integrity of our listings.Price-Match Guarantee
If you find that a seller listed the same item for a lower price elsewhere, we’ll match it.Trusted Global Delivery
Our best-in-class carrier network provides specialized shipping options worldwide, including custom delivery.More From This Seller
View All"Sheepshead, Brooklyn, Long Island" Oscar Bluemner, Modernist Watercolor
By Oscar Bluemner
Located in New York, NY
Oscar Bluemner
Sheepshead, Long Island, 1907
Signed with the artist's conjoined initials "OB" and dated "4-30 - 5 - 30" / "Aug 3, 07"
Watercolor on paper
6 x 10 inches
Provenance:
J...
Category
Early 1900s American Modern Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Watercolor
"Factory on the River" Modernist and Precisionist WPA Industrial New York Scene
By William Sharp
Located in New York, NY
William Sharp (1900 - 1961)
Factory on the River
Oil on canvas
17 1/2 x 23 1/4 inches
Initialed lower right: WS
Provenance:
Estate of the artist
Private Collection, New York
Swann Auction Galleries, American Art, June 13, 2019, Lot 178
William Sharp was born on June 13, 1900, in Lemberg, Austria, where he attended college and the Academy for Arts and Industry. He later studied in Kraków, Poland, and in Berlin and Munich, Germany. Sharp began his career as a designer of stained-glass windows and as a painter of murals. He served in the German army during World War I. After the war he became a newspaper artist in Berlin and a well-known etcher.
Sharp drew political cartoons that were bitterly critical of the growing Nazi movement. As the influence of National Socialism intensified, he began to contribute drawings, under a pseudonym, to publications that were hostile to Hitler. After Hitler assumed power, Sharp was confronted with these drawings and told that he would be sent to a concentration camp. However, in 1934, he escaped to the United States.
His first newspaper assignment in America was making courtroom sketches for The New York Mirror...
Category
Mid-20th Century American Realist Landscape Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Paint, Oil
$5,600 Sale Price
20% Off
"Train Station, " Max Kuehne, Industrial City Scene, American Impressionism
By Max Kuehne
Located in New York, NY
Max Kuehne (1880 - 1968)
Train Station, circa 1910
Watercolor on paper
8 1/4 x 10 1/4 inches
Signed lower right
Provenance:
Private Collection, Illinois
Max Kuehne was born in Halle, Germany on November 7, 1880. During his adolescence the family immigrated to America and settled in Flushing, New York. As a young man, Max was active in rowing events, bicycle racing, swimming and sailing. After experimenting with various occupations, Kuehne decided to study art, which led him to William Merritt Chase's famous school in New York; he was trained by Chase himself, then by Kenneth Hayes Miller. Chase was at the peak of his career, and his portraits were especially in demand. Kuehne would have profited from Chase's invaluable lessons in technique, as well as his inspirational personality. Miller, only four years older than Kuehne, was another of the many artists to benefit from Chase's teachings. Even though Miller still would have been under the spell of Chase upon Kuehne's arrival, he was already experimenting with an aestheticism that went beyond Chase's realism and virtuosity of the brush. Later Miller developed a style dependent upon volumetric figures that recall Italian Renaissance prototypes.
Kuehne moved from Miller to Robert Henri in 1909. Rockwell Kent, who also studied under Chase, Miller, and Henri, expressed what he felt were their respective contributions: "As Chase had taught us to use our eyes, and Henri to enlist our hearts, Miller called on us to use our heads." (Rockwell Kent, It's Me O Lord: The Autobiography of Rockwell Kent. New York: Dodd, Mead and Co., 1955, p. 83). Henri prompted Kuehne to search out the unvarnished realities of urban living; a notable portion of Henri's stylistic formula was incorporated into his work.
Having received such a thorough foundation in art, Kuehne spent a year in Europe's major art museums to study techniques of the old masters. His son Richard named Ernest Lawson as one of Max Kuehne's European traveling companions. In 1911 Kuehne moved to New York where he maintained a studio and painted everyday scenes around him, using the rather Manet-like, dark palette of Henri.
A trip to Gloucester during the following summer engendered a brighter palette. In the words of Gallatin (1924, p. 60), during that summer Kuehne "executed some of his most successful pictures, paintings full of sunlight . . . revealing the fact that he was becoming a colorist of considerable distinction." Kuehne was away in England the year of the Armory Show (1913), where he worked on powerful, painterly seascapes on the rocky shores of Cornwall. Possibly inspired by Henri - who had discovered Madrid in 1900 then took classes there in 1906, 1908 and 1912 - Kuehne visited Spain in 1914; in all, he would spend three years there, maintaining a studio in Granada. He developed his own impressionism and a greater simplicity while in Spain, under the influence of the brilliant Mediterranean light. George Bellows convinced Kuehne to spend the summer of 1919 in Rockport, Maine (near Camden). The influence of Bellows was more than casual; he would have intensified Kuehne's commitment to paint life "in the raw" around him.
After another brief trip to Spain in 1920, Kuehne went to the other Rockport (Cape Ann, Massachusetts) where he was accepted as a member of the vigorous art colony, spearheaded by Aldro T. Hibbard. Rockport's picturesque ambiance fulfilled the needs of an artist-sailor: as a writer in the Gloucester Daily Times explained, "Max Kuehne came to Rockport to paint, but he stayed to sail." The 1920s was a boom decade for Cape Ann, as it was for the rest of the nation. Kuehne's studio in Rockport was formerly occupied by Jonas Lie.
Kuehne spent the summer of 1923 in Paris, where in July, André Breton started a brawl as the curtain went up on a play by his rival Tristan Tzara; the event signified the demise of the Dada movement. Kuehne could not relate to this avant-garde art but was apparently influenced by more traditional painters — the Fauves, Nabis, and painters such as Bonnard. Gallatin perceived a looser handling and more brilliant color in the pictures Kuehne brought back to the States in the fall. In 1926, Kuehne won the First Honorable Mention at the Carnegie Institute, and he re-exhibited there, for example, in 1937 (Before the Wind). Besides painting, Kuehne did sculpture, decorative screens, and furniture work with carved and gilded molding. In addition, he designed and carved his own frames, and John Taylor Adams encouraged Kuehne to execute etchings. Through his talents in all these media he was able to survive the Depression, and during the 1940s and 1950s these activities almost eclipsed his easel painting. In later years, Kuehne's landscapes and still-lifes show the influence of Cézanne and Bonnard, and his style changed radically.
Max Kuehne died in 1968. He exhibited his work at the National Academy of Design, the Art Institute of Chicago, the Carnegie Institute in Pittsburgh, the Memorial Art Gallery of the University of Rochester, and in various New York City galleries. Kuehne's works are in the following public collections: the Detroit Institute of Arts (Marine Headland), the Whitney Museum (Diamond Hill...
Category
1910s American Impressionist Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Watercolor
"Colonial Sand and Stone Company, New York, " Industrial WPA Scene, Precisionist
By William Sharp
Located in New York, NY
William Sharp (1900 - 1961)
Factory on the River
Oil on canvas
20 1/2 x 28 1/2 inches
Initialed lower left: WS
Provenance:
Estate of the artist
Private Collection, New York
Swann Auction Galleries, American Art, June 13, 2019, Lot 178
Private Collection, New York
Colonial Sand and Stone Co., founded by Generoso Pope, was once the country’s largest sand and gravel business, providing the concrete for much of New York City’s skyline, including the Empire State Building, Rockefeller Center, Radio City Music Hall, airports and subways.
William Sharp was born on June 13, 1900, in Lemberg, Austria, where he attended college and the Academy for Arts and Industry. He later studied in Kraków, Poland, and in Berlin and Munich, Germany. Sharp began his career as a designer of stained-glass windows and as a painter of murals. He served in the German army during World War I. After the war he became a newspaper artist in Berlin and a well-known etcher.
Sharp drew political cartoons that were bitterly critical of the growing Nazi movement. As the influence of National Socialism intensified, he began to contribute drawings, under a pseudonym, to publications that were hostile to Hitler. After Hitler assumed power, Sharp was confronted with these drawings and told that he would be sent to a concentration camp. However, in 1934, he escaped to the United States.
His first newspaper assignment in America was making courtroom sketches for The New York Mirror...
Category
Mid-20th Century American Realist Landscape Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Paint, Oil
"Glasco Landscape" Albert Heckman, circa 1940 New York Modernist Landscape
By Albert Heckman
Located in New York, NY
Albert Heckman
Glasco Landscape, circa 1940
Signed lower right
Oil on canvas
25 1/4 x 39 1/2 inches
Albert Heckman was born in Meadville, Western Pennsylvania, 1893. He went to New York City to try his hand at the art world in 1915 after graduating from high school and landing a job at the Meadville Post Office. In 1917, at the age of 24, Heckman enrolled part-time in Teachers' College, Columbia University's Fine Arts Department to begin his formal art education. He worked as a freelance ceramic and textile designer and occasionally as a lecturer at the Metropolitan Museum of Art. In the early 1920s, at the age of almost 30, he graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree from Columbia Teachers College. He was especially impacted by his instructor at Columbia, Arthur Wesley Dow.
After graduating, he was hired by the Teachers' College as a Fine Arts instructor. He stayed with Columbia Teachers' College until 1929, when he left to attend the Leipzig Institute of Graphic Arts in Leipzig, Germany. Isami Doi (1903-1965), who was born in Hawaii, was arguably his most impressive student at Columbia. Doi is now regarded as one of the most prominent artists hailing from Hawaii. Heckman became an active member and officer of the Keramic Society and Design Guild of New York in the 1920s as part of his early commercial art career. The Society's mission was to share knowledge and showcase textile and ceramic design exhibits.
In 1922, Heckman married Florence Hardman, a concert violinist. Mrs. Heckman's concert schedule during the 1920s kept Albert and Florence Heckman apart for a significant portion of the time, but they spent what little time they had together designing and building their Woodstock, New York, summer house and grounds. A small house and an acre of surrounding land on Overlook Mountain, just behind the village of Woodstock, were purchased by Albert and Florence Heckman at the time of their marriage. Their Woodstock home, with its connections, friendships, and memories, became a central part of their lives over the years, even though they had an apartment in New York City.
Heckman's main artistic focus shifted to the house on Overlook Mountain and the nearby towns and villages, Kingston, Eddyville, and Glasco. After returning from the Leipzig Institute of Graphic Arts in 1930, Mr. Heckman joined Hunter College as an assistant professor of art. He worked there for almost thirty years, retiring in 1956. Throughout his tenure at Hunter, Mr. Heckman and his spouse spent the summers at their Woodstock residence and the winters in New York City. They were regular and well-known guests at the opera and art galleries in New York. Following his retirement in 1956, the Heckmans settled in Woodstock permanently, with occasional trips to Florida or Europe during the fall and winter. Mr. Heckman's close friends and artistic career were always connected to Woodstock or New York City. He joined the Woodstock art group early on and was greatly influenced by artists like Paul and Caroline Rohland, Emil Ganso, Yasuo Kuniyoshi, Andre Ruellan, and her husband, Jack...
Category
1940s American Modern Figurative Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil
"Untitled I" Jane Freilicher, Hamptons Landscape Drawing, Mid-century Abstract
By Jane Freilicher
Located in New York, NY
Jane Freilicher
Untitled I, 1958-59
Signed lower right
Charcoal on paper
11 1/2 x 8 3/4 inches
Provenance:
Tibor de Nagy Gallery, New York
Private Collection, New York
Jane Freilic...
Category
1950s Modern Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Charcoal
You May Also Like
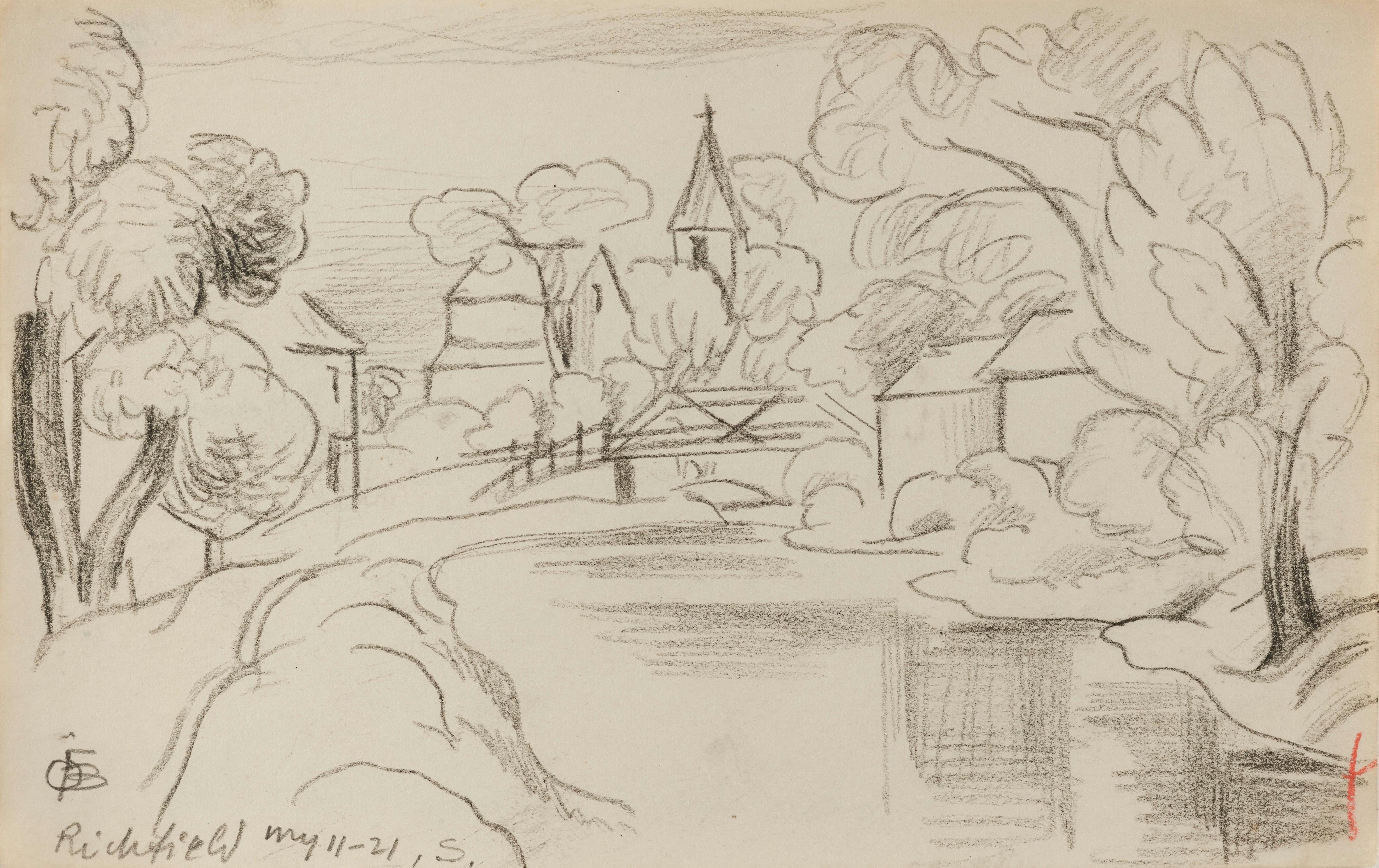
Richfield
By Oscar Bluemner
Located in London, GB
Exceptional rare sketch by American modernist Oscar Bluemner. Very, very good condition. Framed beautifully.
Category
Early 20th Century American Modern Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Carbon Pencil
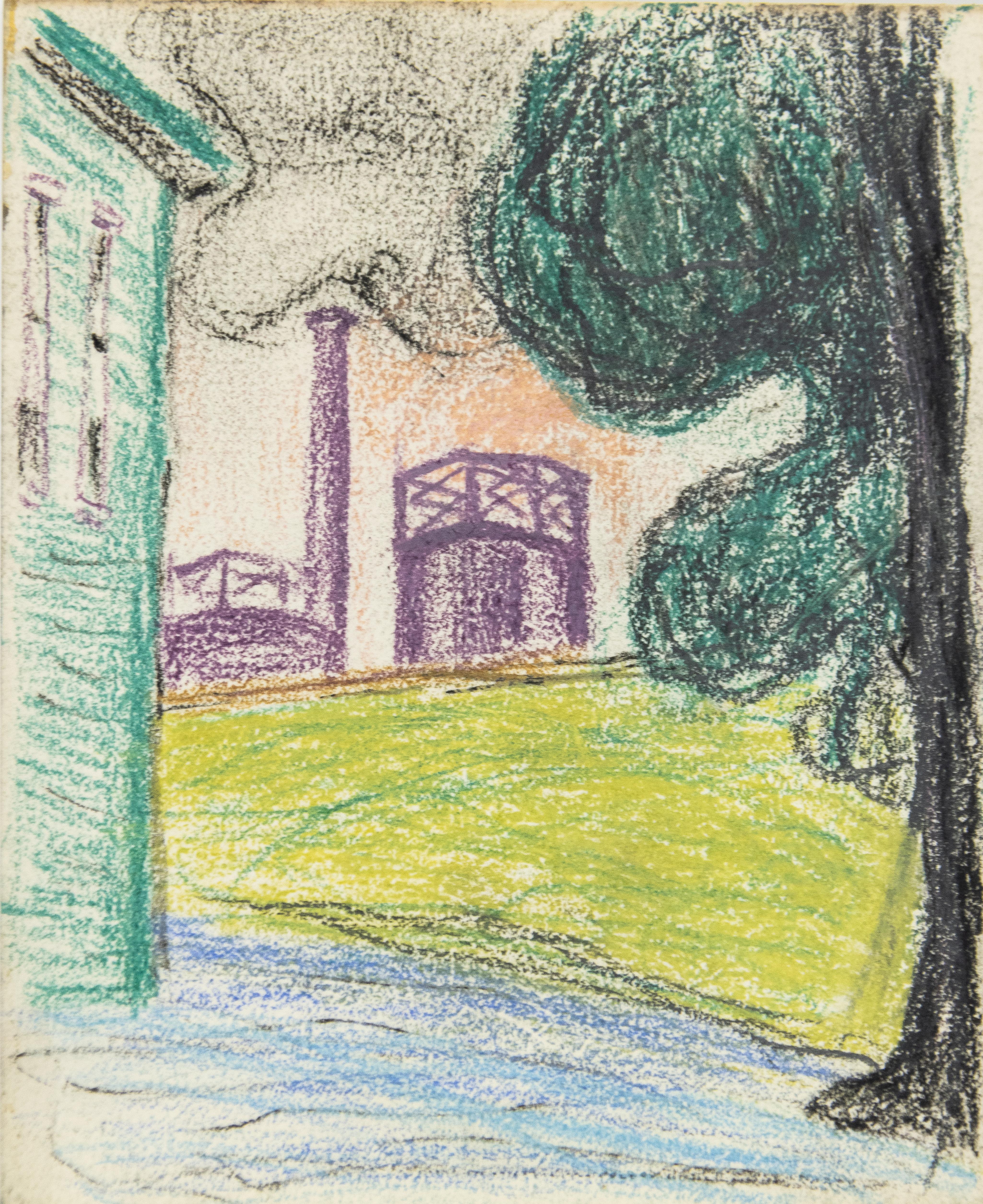
Rural Industrial Scene
By Oscar Bluemner
Located in New York, NY
Rural Industrial Scene
Color crayons on cream wove paper
5 x 4.25 inches
This work is offered by ClampArt in New York City.
Category
Early 20th Century Contemporary Drawings and Watercolor Paintings
Materials
Paper, Crayon
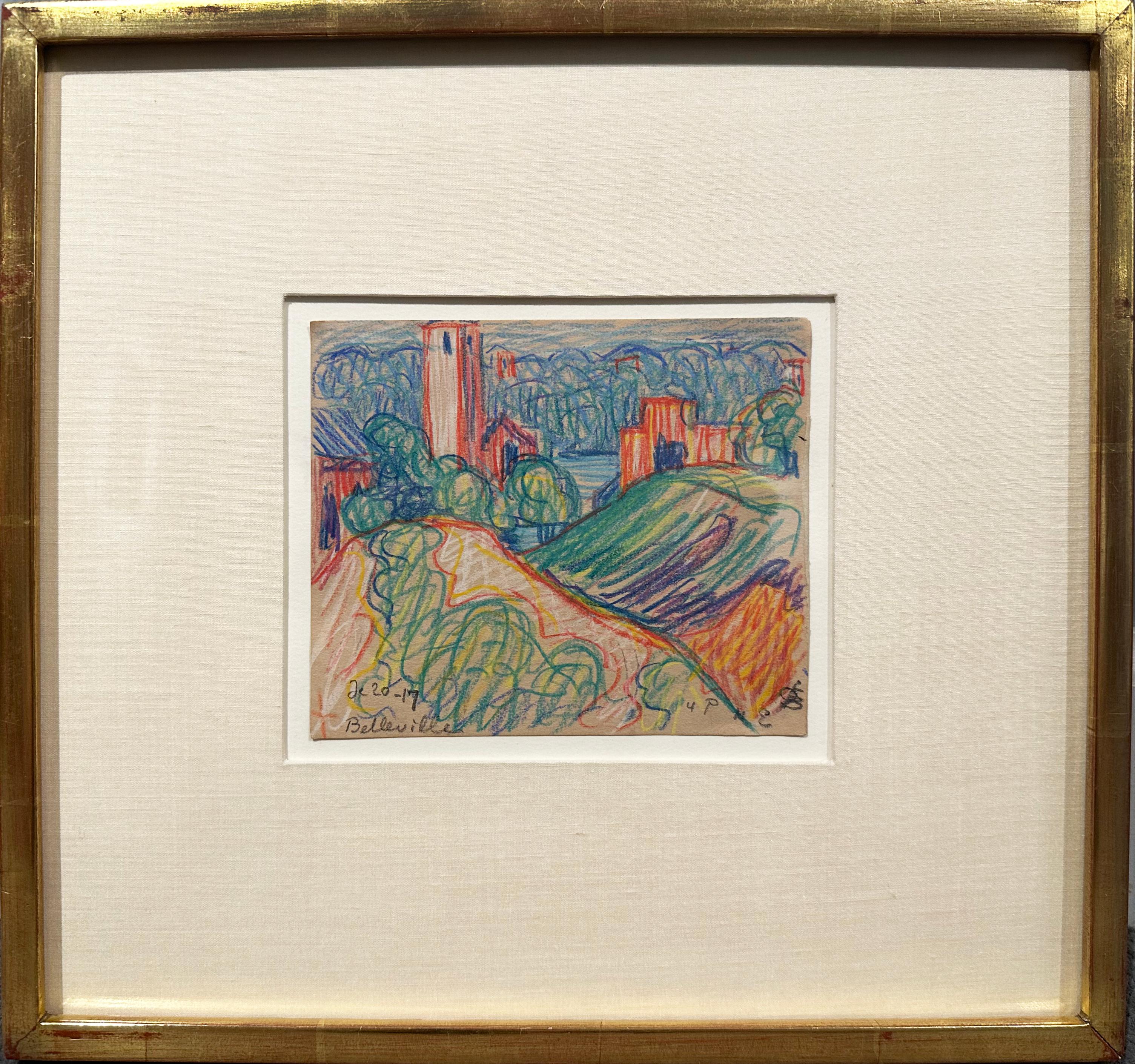
Belleville, NJ
By Oscar Bluemner
Located in London, GB
The Modernist painter Oscar Bluemner was born in Hanover, Germany, in 1867. As a young man, he followed in the architectural careers of his father and grandfather. In the early 1880s...
Category
Early 20th Century American Modern Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Carbon Pencil
Study for Old Canal, Red and Blue (Rockaway, Morris Canal)
By Oscar Florianus Bluemner
Located in New York, NY
Oscar Bluemner was a German and an American, a trained architect who read voraciously in art theory, color theory, and philosophy, a writer of art criticism both in German and English, and, above all, a practicing artist. Bluemner was an intense man, who sought to express and share, through drawing and painting, universal emotional experience. Undergirded by theory, Bluemner chose color and line for his vehicles; but color especially became the focus of his passion. He was neither abstract artist nor realist, but employed the “expressional use of real phenomena” to pursue his ends. (Oscar Bluemner, from unpublished typescript on “Modern Art” for Camera Work, in Bluemner papers, Archives of American Art, Smithsonian Institution, as cited and quoted in Jeffrey R. Hayes, Oscar Bluemner [1991], p. 60. The Bluemner papers in the Archives [hereafter abbreviated as AAA] are the primary source for Bluemner scholars. Jeffrey Hayes read them thoroughly and translated key passages for his doctoral dissertation, Oscar Bluemner: Life, Art, and Theory [University of Maryland, 1982; UMI reprint, 1982], which remains the most comprehensive source on Bluemner. In 1991, Hayes published a monographic study of Bluemner digested from his dissertation and, in 2005, contributed a brief essay to the gallery show at Barbara Mathes, op. cit.. The most recent, accessible, and comprehensive view of Bluemner is the richly illustrated, Barbara Haskell, Oscar Bluemner: A Passion for Color, exhib. cat. [New York: Whitney Museum of American Art, 2005.])
Bluemner was born in the industrial city of Prenzlau, Prussia, the son and grandson of builders and artisans. He followed the family predilection and studied architecture, receiving a traditional and thorough German training. He was a prize-winning student and appeared to be on his way to a successful career when he decided, in 1892, to emigrate to America, drawn perhaps by the prospect of immediate architectural opportunities at the Chicago World’s Fair, but, more importantly, seeking a freedom of expression and an expansiveness that he believed he would find in the New World.
The course of Bluemner’s American career proved uneven. He did indeed work as an architect in Chicago, but left there distressed at the formulaic quality of what he was paid to do. Plagued by periods of unemployment, he lived variously in Chicago, New York, and Boston. At one especially low point, he pawned his coat and drafting tools and lived in a Bowery flophouse, selling calendars on the streets of New York and begging for stale bread. In Boston, he almost decided to return home to Germany, but was deterred partly because he could not afford the fare for passage. He changed plans and direction again, heading for Chicago, where he married Lina Schumm, a second-generation German-American from Wisconsin. Their first child, Paul Robert, was born in 1897. In 1899, Bluemner became an American citizen. They moved to New York City where, until 1912, Bluemner worked as an architect and draftsman to support his family, which also included a daughter, Ella Vera, born in 1903.
All the while, Oscar Bluemner was attracted to the freer possibilities of art. He spent weekends roaming Manhattan’s rural margins, visiting the Bronx, Brooklyn, Queens, and New Jersey, sketching landscapes in hundreds of small conté crayon drawings. Unlike so many city-based artists, Bluemner did not venture out in search of pristine countryside or unspoiled nature. As he wrote in 1932, in an unsuccessful application for a Guggenheim Fellowship, “I prefer the intimate landscape of our common surroundings, where town and country mingle. For we are in the habit to carry into them our feelings of pain and pleasure, our moods” (as quoted by Joyce E. Brodsky in “Oscar Bluemner in Black and White,” p. 4, in Bulletin 1977, I, no. 5, The William Benton Museum of Art, Storrs, Connecticut). By 1911, Bluemner had found a powerful muse in a series of old industrial towns, mostly in New Jersey, strung along the route of the Morris Canal.
While he educated himself at museums and art galleries, Bluemner entered numerous architectural competitions. In 1903, in partnership with Michael Garven, he designed a new courthouse for Bronx County. Garven, who had ties to Tammany Hall, attempted to exclude Bluemner from financial or artistic credit, but Bluemner promptly sued, and, finally, in 1911, after numerous appeals, won a $7,000 judgment.
Barbara Haskell’s recent catalogue reveals more details of Bluemner’s architectural career than have previously been known. Bluemner the architect was also married with a wife and two children. He took what work he could get and had little pride in what he produced, a galling situation for a passionate idealist, and the undoubted explanation for why he later destroyed the bulk of his records for these years. Beginning in 1907, Bluemner maintained a diary, his “Own Principles of Painting,” where he refined his ideas and incorporated insights from his extensive reading in philosophy and criticism both in English and German to create a theoretical basis for his art. Sometime between 1908 and 1910, Bluemner’s life as an artist was transformed by his encounter with the German-educated Alfred Stieglitz, proprietor of the Little Galleries of the Photo-Secession at 291 Fifth Avenue. The two men were kindred Teutonic souls. Bluemner met Stieglitz at about the time that Stieglitz was shifting his serious attention away from photography and toward contemporary art in a modernist idiom. Stieglitz encouraged and presided over Bluemner’s transition from architect to painter. During the same period elements of Bluemner’s study of art began to coalesce into a personal vision. A Van Gogh show in 1908 convinced Bluemner that color could be liberated from the constraints of naturalism. In 1911, Bluemner visited a Cézanne watercolor show at Stieglitz’s gallery and saw, in Cézanne’s formal experiments, a path for uniting Van Gogh’s expressionist use of color with a reality-based but non-objective language of form.
A definitive change of course in Bluemner’s professional life came in 1912. Ironically, it was the proceeds from his successful suit to gain credit for his architectural work that enabled Bluemner to commit to painting as a profession. Dividing the judgment money to provide for the adequate support of his wife and two children, he took what remained and financed a trip to Europe. Bluemner traveled across the Continent and England, seeing as much art as possible along the way, and always working at a feverish pace. He took some of his already-completed work with him on his European trip, and arranged his first-ever solo exhibitions in Berlin, Leipzig, and Elberfeld, Germany. After Bluemner returned from his study trip, he was a painter, and would henceforth return to drafting only as a last-ditch expedient to support his family when his art failed to generate sufficient income.
Bluemner became part of the circle of Stieglitz artists at “291,” a group which included Marsden Hartley, John Marin, and Arthur Dove. He returned to New York in time to show five paintings at the 1913 Armory Show and began, as well, to publish critical and theoretical essays in Stieglitz’s journal, Camera Work. In its pages he cogently defended the Armory Show against the onslaught of conservative attacks. In 1915, under Stieglitz’s auspices, Bluemner had his first American one-man show at “291.” Bluemner’s work offers an interesting contrast with that of another Stieglitz architect-turned-artist, John Marin, who also had New Jersey connections.
The years after 1914 were increasingly uncomfortable. Bluemner remained, all of his life, proud of his German cultural legacy, contributing regularly to German language journals and newspapers in this country. The anti-German sentiment, indeed mania, before and during World War I, made life difficult for the artist and his family. It is impossible to escape the political agenda in Charles Caffin’s critique of Bluemner’s 1915 show. Caffin found in Bluemner’s precise and earnest explorations of form, “drilled, regimented, coerced . . . formations . . . utterly alien to the American idea of democracy” (New York American, reprinted in Camera Work, no. 48 [Oct. 1916], as quoted in Hayes, 1991, p. 71).
In 1916, seeking a change of scene, more freedom to paint, and lower expenses, Bluemner moved his family to New Jersey, familiar terrain from his earlier sketching and painting. During the ten years they lived in New Jersey, the Bluemner family moved around the state, usually, but not always, one step ahead of the rent collector. In 1917, Stieglitz closed “291” and did not reestablish a Manhattan gallery until 1925. In the interim, Bluemner developed relationships with other dealers and with patrons. Throughout his career he drew support and encouragement from art cognoscenti who recognized his talent and the high quality of his work. Unfortunately, that did not pay the bills. Chronic shortfalls were aggravated by Bluemner’s inability to sustain supportive relationships. He was a difficult man, eternally bitter at the gap between the ideal and the real. Hard on himself and hard on those around him, he ultimately always found a reason to bite the hand that fed him.
Bluemner never achieved financial stability. He left New Jersey in 1926, after the death of his beloved wife, and settled in South Braintree, Massachusetts, outside of Boston, where he continued to paint until his own death in 1938. As late as 1934 and again in 1936, he worked for New Deal art programs designed to support struggling artists. Bluemner held popular taste and mass culture in contempt, and there was certainly no room in his quasi-religious approach to art for accommodation to any perceived commercial advantage. His German background was also problematic, not only for its political disadvantages, but because, in a world where art is understood in terms of national styles, Bluemner was sui generis, and, to this day, lacks a comfortable context.
In 1933, Bluemner adopted Florianus (definitively revising his birth names, Friedrich Julius Oskar) as his middle name and incorporated it into his signature, to present “a Latin version of his own surname that he believed reinforced his career-long effort to translate ordinary perceptions into the more timeless and universal languages of art” (Hayes 1982, p. 189 n. 1). In 1939, critic Paul Rosenfeld, a friend and member of the Stieglitz circle, responding to the difficulty in categorizing Bluemner, perceptively located him among “the ranks of the pre-Nazi German moderns” (Hayes 1991, p. 41). Bluemner was powerfully influenced in his career by the intellectual heritage of two towering figures of nineteenth-century German culture, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel. A keen student of color theory, Bluemner gave pride of place to the formulations of Goethe, who equated specific colors with emotional properties. In a November 19, 1915, interview in the German-language newspaper, New Yorker Staats-Zeitung (Abendblatt), he stated:
I comprehend the visible world . . . abstract the primary-artistic . . . and after these elements of realty are extracted and analyzed, I reconstruct a new free creation that still resembles the original, but also . . . becomes an objectification of the abstract idea of beauty.
The first—and most conspicuous mark of this creation is . . . colors which accord with the character of things, the locality . . . [and which] like the colors of Cranach, van der Weyden, or Durer, are of absolute purity, breadth, and luminosity. . . . I proceed from the psychological use of color by the Old Masters . . . [in which] we immediately recognize colors as carriers of “sorrow and joy” in Goethe’s sense, or as signs of human relationship. . . . Upon this color symbolism rests the beauty as well as the expressiveness, of earlier sacred paintings. Above all, I recognize myself as a contributor to the new German theory of light and color, which expands Goethe’s law of color through modern scientific means (as quoted in Hayes 1991, p. 71).
Hayes has traced the global extent of Bluemner’s intellectual indebtedness to Hegel (1991, pp. 36–37). More specifically, Bluemner made visual, in his art, the Hegelian world view, in the thesis and antithesis of the straight line and the curve, the red and the green, the vertical and the horizontal, the agitation and the calm. Bluemner respected all of these elements equally, painting and drawing the tension and dynamic of the dialectic and seeking ultimate reconciliation in a final visual synthesis. Bluemner was a keen student of art, past and present, looking, dissecting, and digesting all that he saw. He found precedents for his non-naturalist use of brilliant-hued color not only in the work Van Gogh and Cezanne, but also in Gauguin, the Nabis, and the Symbolists, as well as among his contemporaries, the young Germans of Der Blaue Reiter.
Bluemner was accustomed to working to the absolute standard of precision required of the architectural draftsman, who adjusts a design many times until its reality incorporates both practical imperatives and aesthetic intentions. Hayes describes Bluemner’s working method, explaining how the artist produced multiple images playing on the same theme—in sketch form, in charcoal, and in watercolor, leading to the oil works that express the ultimate completion of his process (Hayes, 1982, pp. 156–61, including relevant footnotes). Because of Bluemner’s working method, driven not only by visual considerations but also by theoretical constructs, his watercolor and charcoal studies have a unique integrity. They are not, as is sometimes the case with other artists, rough preparatory sketches. They stand on their own, unfinished only in the sense of not finally achieving Bluemner’s carefully considered purpose.
The present charcoal drawing is one of a series of images that take as their starting point the Morris Canal as it passed through Rockaway, New Jersey. The Morris Canal industrial towns that Bluemner chose as the points of departure for his early artistic explorations in oil included Paterson with its silk mills (which recalled the mills in the artist’s childhood home in Elberfeld), the port city of Hoboken, Newark, and, more curiously, a series of iron ore mining and refining towns, in the north central part of the state that pre-dated the Canal, harkening back to the era of the Revolutionary War. The Rockaway theme was among the original group of oil paintings that Bluemner painted in six productive months from July through December 1911 and took with him to Europe in 1912. In his painting journal, Bluemner called this work Morris Canal at Rockaway N.J. (AAA, reel 339, frames 150 and 667, Hayes, 1982, pp. 116–17), and exhibited it at the Galerie Fritz Gurlitt in Berlin in 1912 as Rockaway N. J. Alter Kanal. After his return, Bluemner scraped down and reworked these canvases. The Rockaway picture survives today, revised between 1914 and 1922, as Old Canal, Red and Blue (Rockaway River) in the collection of the Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden, Smithsonian Institution, Washington D. C. (color illus. in Haskell, fig. 48, p. 65).
For Bluemner, the charcoal expression of his artistic vision was a critical step in composition. It represented his own adaptation of Arthur Wesley’s Dow’s (1857–1922) description of a Japanese...
Category
20th Century American Modern Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Charcoal
PORTLAND ALLEY
By Oscar Bluemner
Located in Portland, ME
Bluemner, Oscar (American, born Germany, 1867-1938). NIGHT IN PORTLAND MAINE - ALLEY. Charcoal on paper, 1919. Signed with the artist's monogram "OFB" ...
Category
1910s Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Charcoal
A ca. 1940s Graphite on Paper Mural Study of a City Scene by Rudolph Weisenborn
By Rudolph Weisenborn
Located in Chicago, IL
A ca. 1940s graphite on paper mural study of a Chicago city scene by notable Modern artist Rudolph Weisenborn. Artwork size: 12 1/2" x 9 1/4". Archivally matted to 18" x 16". Provenance: Estate of the artist.
Rudolph Weisenborn was born in Strassburg, Germany in 1881, but was orphaned at the age of nine. He was taken-in by Mid-Western farmer Thomas Westaby and spent his early years in Wisconsin, Iowa and North Dakota. Weisenborn first attended the University of North Dakota in 1898, then the Students School of Art in Denver. Various accounts have him working out west as a gold miner and cowboy.
Around 1912, he settled in Chicago and worked as a window designer for Marshall Field’s. Weisenborn is best known as the founder of the Chicago No-Jury Society of Artists. The group was founded because many artists could not get their work accepted into the mainstream Art Institute shows. Weisenborn is quoted as saying that he harbored feelings of disdain for any jury and that his own paintings were frequently rejected by conservative jurors. He was also involved and helped found other radical artist’s groups such as the Salon des Refuses, Cor Ardens and Neo-Arlimusic. In 1936, he helped found the New York-based American Abstract Artist’s Group. He created the only abstract mural for the 1933 Century of Progress Exhibition in Chicago and also worked for the Federal Arts Project in the Easel Division. His WPA murals can be found in Crane Technical High School and Nettlehorst Elementary School in Chicago, IL. In 1945, Chicago businessman Herman Spertus...
Category
1940s American Modern Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Graphite
More Ways To Browse
Architecture Drawing
Architectural Drawing Study
Technical Drawing
Drawings Of Couples
Italian Architectural Drawings
French Architectural Drawings
Antique Architectural Drawings
Old Master Italian Drawings
East German Art
Antique House Architectural Design
Providence Art
Architectural Rendering
Just Anderson
Netherlands Painting Early 20th Century
Antique Forum
Columbian Exposition
Antique Art Forum
Julius 7