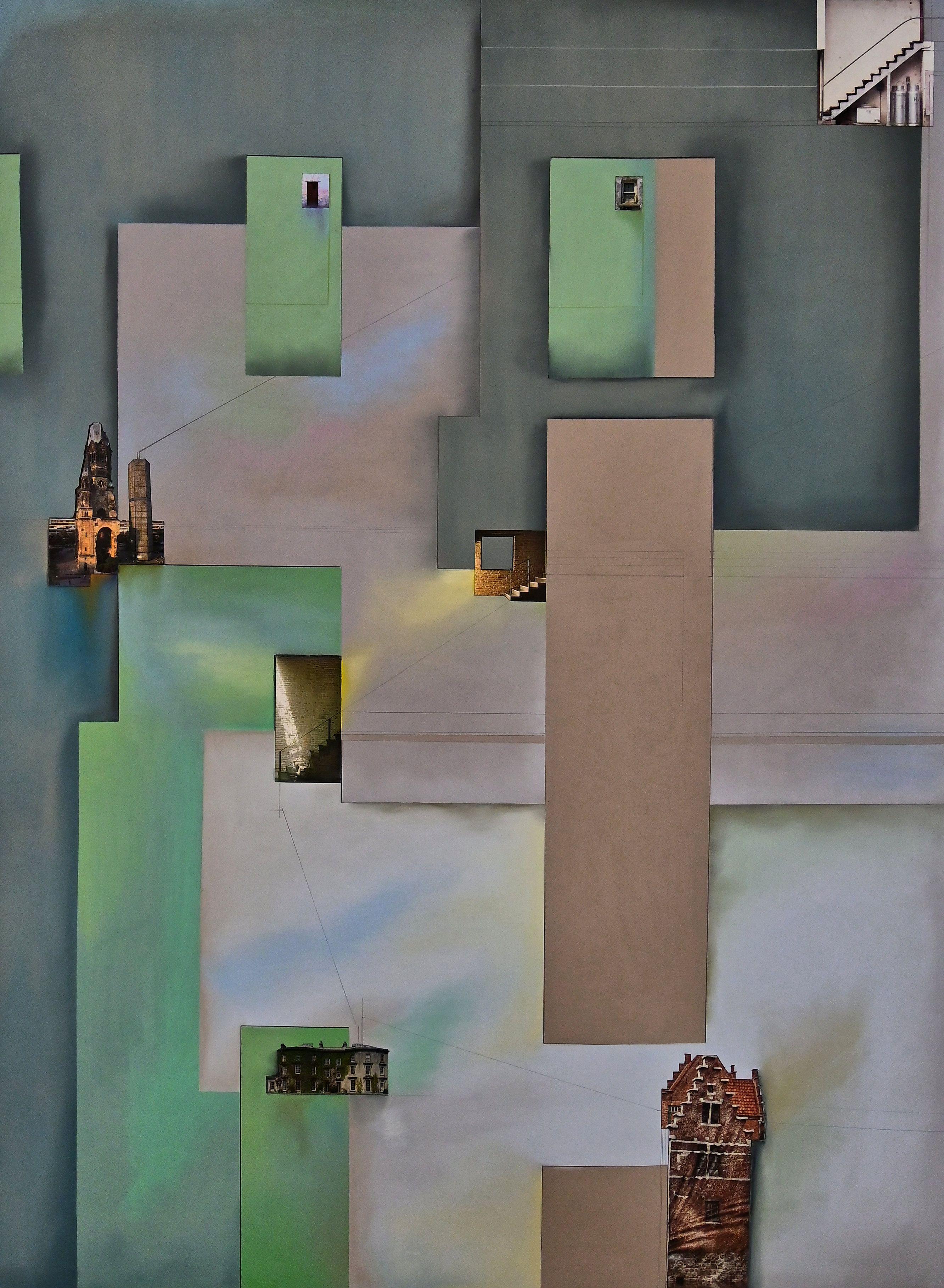Items Similar to Contemporary Mid Century Inspired Blue & Green Toned Neighborhood Aerial Pastel
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 14
R. Michael WommackContemporary Mid Century Inspired Blue & Green Toned Neighborhood Aerial Pastel21st Century
21st Century
$4,800
£3,669.86
€4,226.93
CA$6,726.27
A$7,509.25
CHF 3,934.73
MX$91,920.59
NOK 49,971.16
SEK 47,116.46
DKK 31,546.03
About the Item
Mid century inspired aerial landscape pastel drawing by contemporary artist R. Michael Wommack. The work features a birds eye view of a planned neighborhood at night with glowing swimming pools in each of the backyards. Signed in pencil in the front lower right corner. Currently hung in a black floating frame with matching matting.
Dimensions Without Frame: H 33 in. x W 45 in.
About the Work From the Artist: This series of drawings, now in its 10th year, was inspired by a dream that stuck with me in a vivid wash of color. In my dream I was swimming in pools that were connected to each other, at night. I was in my childhood neighborhood, Levittown in Pennsylvania, an early example of the archetypal American suburban development built in the early 1950’s. The houses were all dark, and the illuminated pools were casting an ethereal glow over the entire neighborhood. I was drifting from back yard to back yard without another soul in sight. I found this dream a little odd, since I am not a particularly good swimmer, but the vivid colors really stayed with me.
We moved to Juniper Hill in the early 60’s when I was six years old. The houses were newly built. As far as the eye could see there was the same house, in one of three alternating colors, in a gently curving and undulating artificial landscape. The trees were mere sticks, and no one had put up fences. Surrounded by plowed fields, on which Levittown was built, the visual impact was compounded when approaching this community of 17,000 homes in a car. As a first grader having previously lived in a country house, this experience was profound. I remember much from this time. It may be that our early impressions are made more vivid by the simple fact we have had fewer of them. Our brains are uncrowded with decades of memories. I can remember the smell of mint as I was trying to catch a Praying Mantis in the garden next door when I was 7 years old, but I can’t remember what I was doing at a specific time last week.
Because of this, I became interested in the idea of the subconscious and working from memory. I pulled my soft pastels out of storage, not having used them for years and started drawing from memory. The pastels turned out to be the perfect medium, the powdered pigment being so pure of color, and the softness of the pastel captured perfectly the feeling of the dream. I am also interested in the fact that most Americans have lived in a place like this at one time or another, and of the social ramifications of living in such a manner.
I don’t care to deconstruct any of the dreams, but I am interested in tapping the imagery. I am not concerned with historical accuracy, but in the emotions caused by living in such a place at an early age. I am not interested in making a specific social statement. I like to keep aspects of the drawings ambiguous, to allow the viewer their own interpretation of what it means to live in the American suburbs.
Artist Biography: I received my BFA from the Tyler School of Art in Philadelphia, after attending the first session of the Pennsylvania Governor’s School of the Arts. In my early years, I was a muralist for many private and government clients, some of the murals measuring 80 feet wide. The subject matter ranged from the silly to the serious. In the eighties I was the colorist at the Fabric Workshop and Museum, working with artists such as Red Grooms on specially designed fabrics.
In 1984 I began assisting internationally known architects Robert Venturi and Denise Scott Brown on an assortment of special painting projects, including in the National Gallery of Art in London, the Museum of Contemporary Art in San Diego, the Philadelphia Museum of Art to name just a few.
Recent prizes include Best of Show at Art City Austin in Texas, Old Town Art Fair in Chicago, Brookside Art Annual in Kansas City and the Beth El Art Festival in St Petersburg, Florida. Also Awards of Excellence at the Des Moines Arts Festival, BAM Artsfair in Bellevue, Washington, Lakefront Festival of the Arts in Milwaukee and the Winter Park Sidewalk Art Festival in Florida. Best in Drawing awards were at the Bethesda Row Art Festival in Maryland, Kimball Arts Festival in Park City, Utah, Scottsdale Art Festival in Arizona and the Sausalito Art Festival in California.
- Creator:R. Michael Wommack (1956)
- Creation Year:21st Century
- Dimensions:Height: 37.5 in (95.25 cm)Width: 49.5 in (125.73 cm)Depth: 2.25 in (5.72 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Houston, TX
- Reference Number:Seller: A2025.0307.64931stDibs: LU551315993372

About the Seller
5.0
Gold Seller
Premium sellers maintaining a 4.3+ rating and 24-hour response times
Established in 1969
1stDibs seller since 2014
869 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 9 hours
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Shipping from: Houston, TX
- Return Policy
Authenticity Guarantee
In the unlikely event there’s an issue with an item’s authenticity, contact us within 1 year for a full refund. DetailsMoney-Back Guarantee
If your item is not as described, is damaged in transit, or does not arrive, contact us within 7 days for a full refund. Details24-Hour Cancellation
You have a 24-hour grace period in which to reconsider your purchase, with no questions asked.Vetted Professional Sellers
Our world-class sellers must adhere to strict standards for service and quality, maintaining the integrity of our listings.Price-Match Guarantee
If you find that a seller listed the same item for a lower price elsewhere, we’ll match it.Trusted Global Delivery
Our best-in-class carrier network provides specialized shipping options worldwide, including custom delivery.More From This Seller
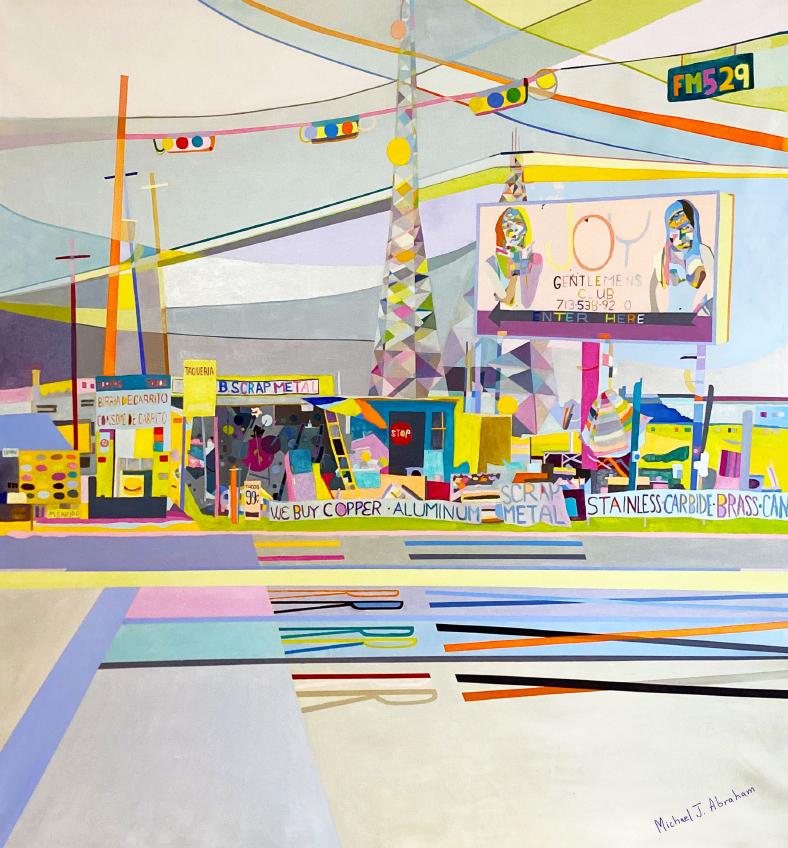
View All"No Zoning" Contemporary Pastel Toned Abstract Urban Landscape Painting
Located in Houston, TX
Contemporary pastel toned abstract urban landscape painting by Texas-based artist Michael J. Abraham. Recently featured in "Michael J. Abraham: Quasi-Realism" at Reeves Art + Design ...
Category
2010s Contemporary Landscape Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil
"Static Conundrum" Contemporary Teal, Green, & Pink Abstract Cubist Painting
By Paul Reeves
Located in Houston, TX
Teal, green, and pink abstract Cubist style painting by Texas artist Paul Reeves. The work features the geometric structure of traditional Cubism, combined with the brushwork of abstract expressionism. Currently hung in a black wood floating frame.
Dimensions Without Frame: H 42 in. x W 35.13 in.
Artist Biography: Paul Reeves is the owner of Reeves Antiques...
Category
2010s Abstract Abstract Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Acrylic
“G’s Paper City” Contemporary Pastel Peach and Blue Toned Abstract Painting
Located in Houston, TX
Contemporary pastel toned abstract painting by Houston based artist Kristen Anton. The work features peach, blue, and white blocks of color accented with layers of brushwork. Signed,...
Category
2010s Abstract Abstract Paintings
Materials
Acrylic, Canvas
"Hycean Replicants" Contemporary Geometric Blue Tone Hard-Edge Abstract Painting
Located in Houston, TX
Contemporary abstract painting by local Houston artist Emmanuel Araujo. Currently featured in the show "5 Artists 5 Rooms" at Reeves Art + Design in Houston, TX.
Artist Biography: ...
Category
2010s Contemporary Abstract Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Acrylic
Modern Realist Green and Blue-Toned Rural Village Market Landscape Painting
Located in Houston, TX
Modern realist daily life landscape painting by Haitian artist Felix Defournoy. The work features a bustling rural village market scene of vendors selling their various goods set against a dense, lush...
Category
Late 20th Century Abstract Landscape Paintings
Materials
Acrylic
Post Impressionist Inspired Modern Blue & Green Abstract Village Landscape Scene
Located in Houston, TX
Blue and green toned abstract village landscape by Haitian artist Franklin M. Joseph. The work features loosely rendered figures going about their daily lives. Signed in front lower left corner. Currently hung in a silver and burlap frame.
Dimensions With Frame: H 15.63” x W 19.75”
Artist Biography: Franklin M. Joseph was born in Cap-Haitien, Haiti in 1951. He studied at the Lycee Pierre Garriere. In 1969, he started painting under the tutelage of Haitian master painter, Philome Obin...
Category
Late 20th Century Abstract Landscape Paintings
Materials
Oil
You May Also Like
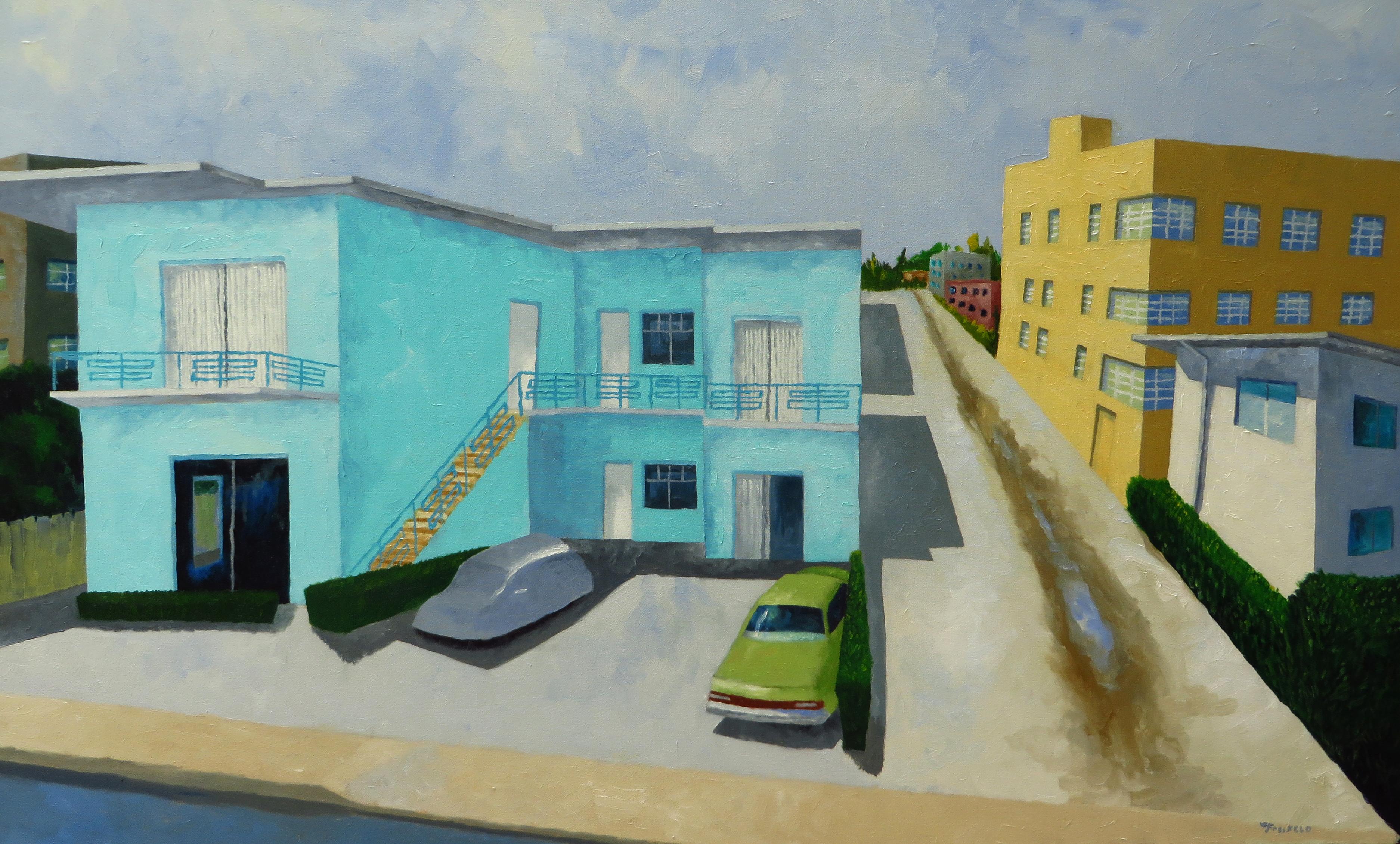
Turquoise Modern
By Mitchell Freifeld
Located in San Francisco, CA
Artist Comments
Even though this little turquoise apartment house is in Miami's Deco Town, it looks like it was either built or remodeled somewhere in the 1950s and luckily, ...
Category
21st Century and Contemporary Contemporary Interior Paintings
Materials
Oil
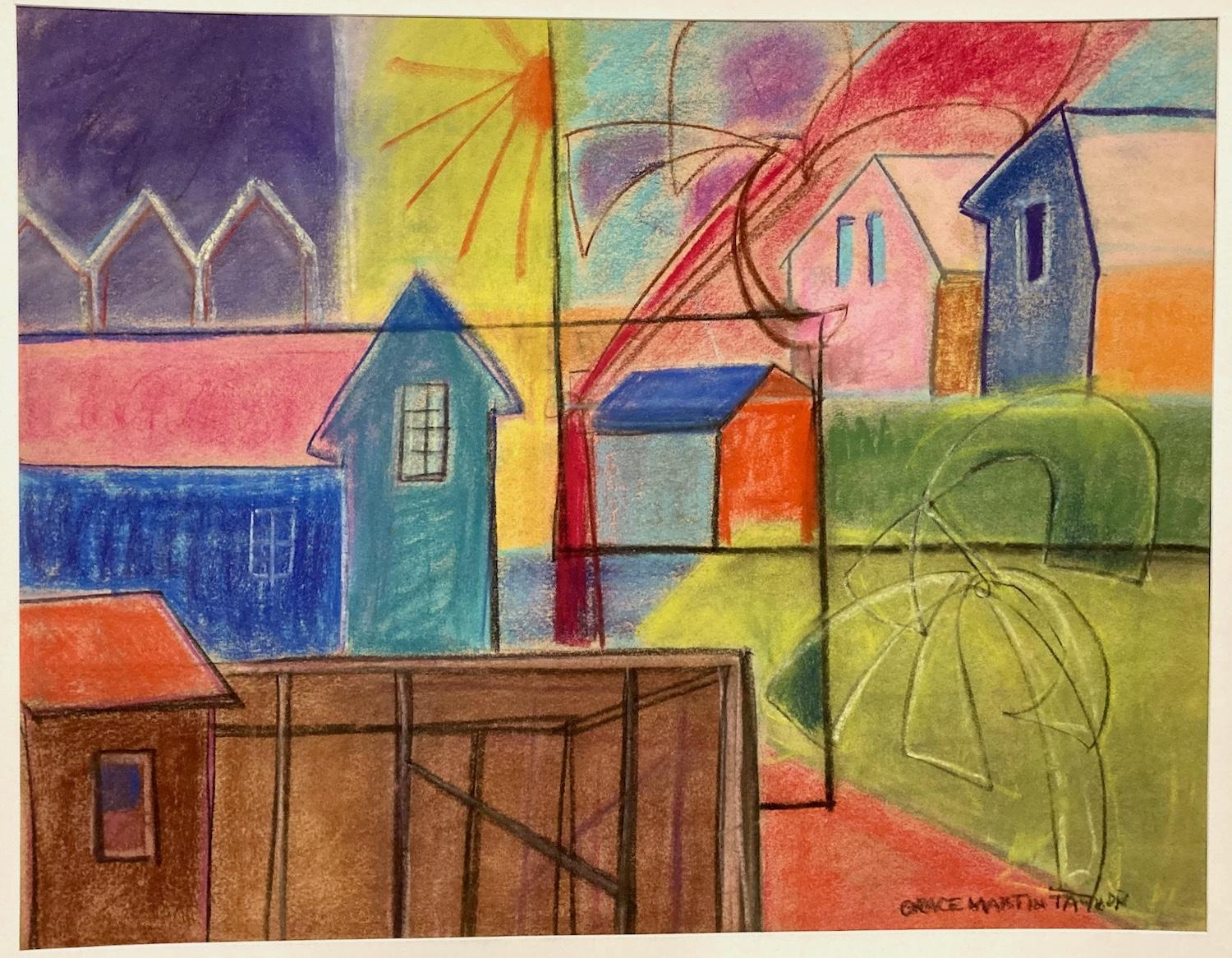
Grace Martin Taylor (Frame), (Town View), 1930, pastel, signed
Located in New York, NY
West Virginia native Grace Martin Taylor, artist for the brightly colored pastel (TownView), attended the Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts and the Art S...
Category
1930s American Modern Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Pastel
Metropolitan Landscapes #1, Painting, Pastels on Paper
By Christian Culver
Located in Yardley, PA
Pastel on heavy archival paper with architectural photographs mounted. Note - the size given is the actual size of the image. Comes in a traveling frame...
Category
Early 2000s Abstract Abstract Paintings
Materials
Pastel
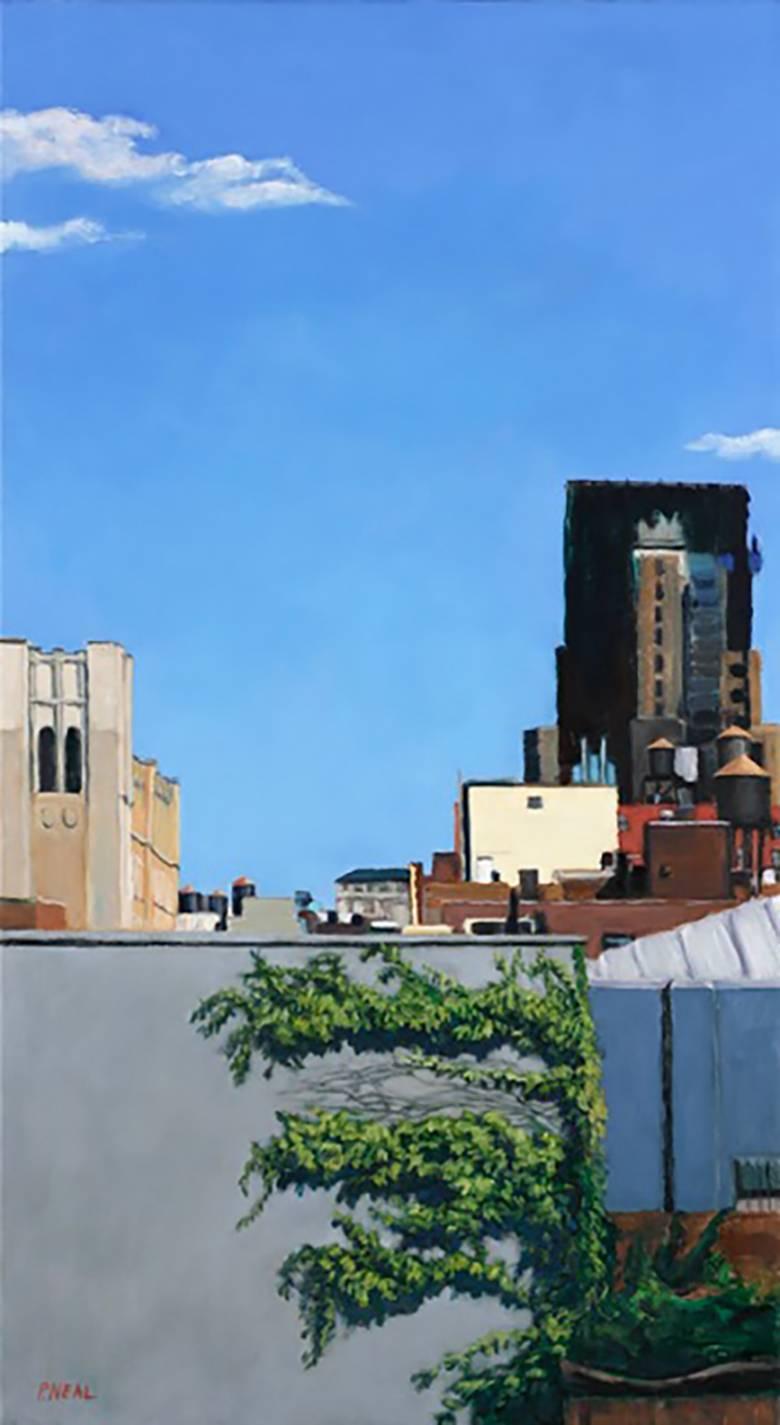
Blue Sky Green (Modern Cityscape Oil Painting of Brooklyn Rooftops)
By Patty Neal
Located in Hudson, NY
oil on linen on panel
23.5 x 13 inches
This modern cityscape oil painting was completed on linen and mounted on panel. Painted in a realistic style, the scene is of Brooklyn roofto...
Category
2010s Modern Landscape Paintings
Materials
Linen, Oil, Wood Panel
VILLAGE ON THE WATER - Modern Nature Oil Pastel Painting, Blue Tones, Light
By Janusz Kokot
Located in Salzburg, AT
Janusz Kokot was born in Kalisz in 1960. He studied at the Pedagogical University in Częstochowa at the Art Institute. He practices painting and drawing. In the years 1988 - 2020 he ...
Category
2010s Contemporary Landscape Paintings
Materials
Paper, Oil Pastel
"Around the Corner" by Frida Willis - Pastel Tone Constructivist Cityscape
Located in Carmel, CA
Frida Willis (Swedish, born 1971)
"Around the Corner" 2024
Oil Pastel, Paper
The artist signed the bottom right of the artwork.
Frida Willis’ Around the Corner presents an urban lan...
Category
2010s Contemporary Landscape Paintings
Materials
Paper, Oil Pastel
More Ways To Browse
Green Mid Century Art
Neighborhood Painting
Washington Green
Mid Century Catch All
Don Brown Drawing
Old California Watercolors
Mint Green Mid Century
Mid Century Modern Texas Art
Mid Century Fence
Don Winter
Used Doors Philadelphia
Park City Utah
St Petersburg Florida
Pastel 80s
Painting With Swimming Pools
Sausalito Painting
Scott Hill
Watercolor Utah