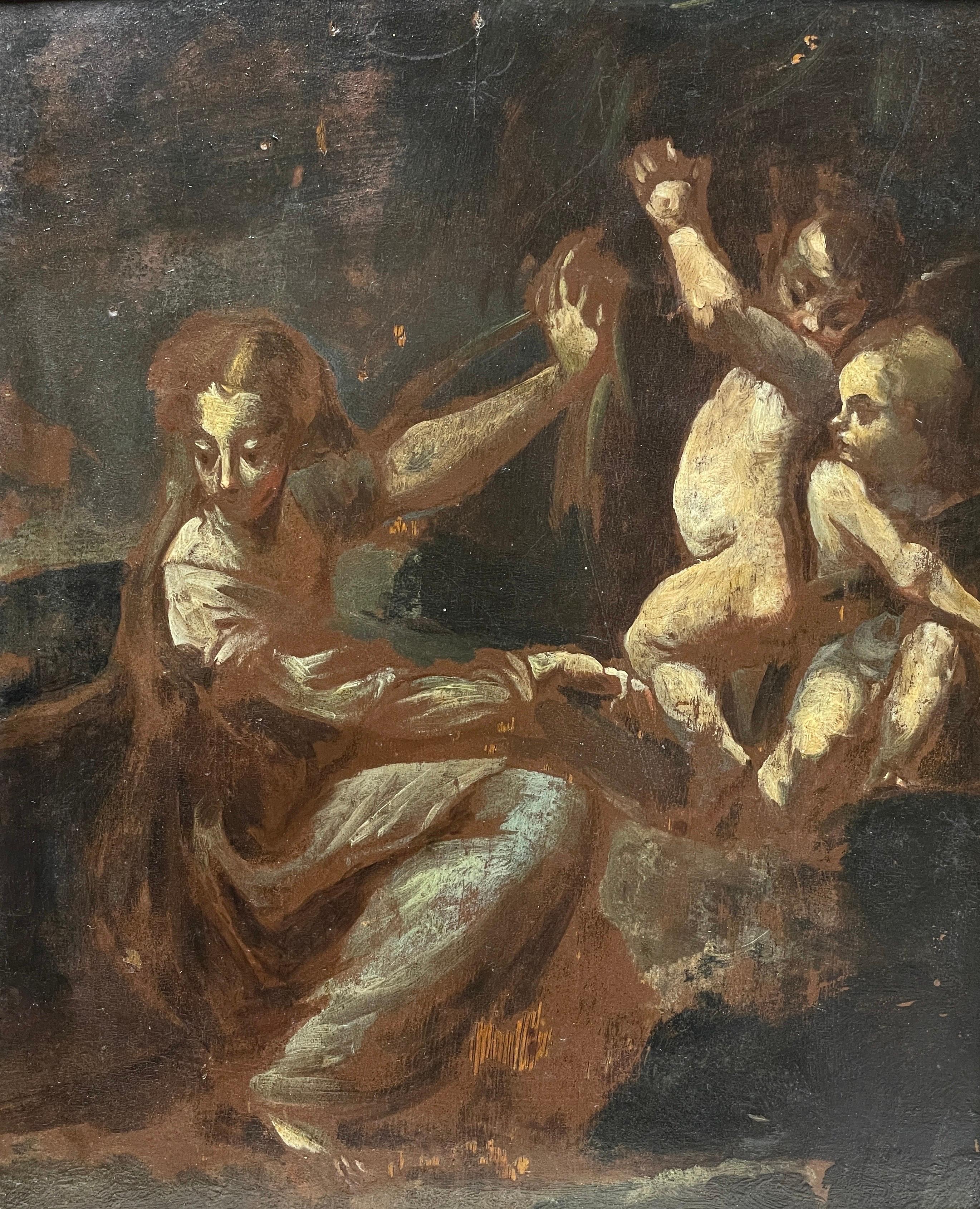Portrait of an Elizabethan Gentleman, Edmund Huddleston Dated 1562, oil on panel
View Similar Items
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 9
George GowerPortrait of an Elizabethan Gentleman, Edmund Huddleston Dated 1562, oil on panelDated 1562
Dated 1562
$10,615.98List Price
About the Item
- Creator:George Gower (1540 - 1596, British)
- Creation Year:Dated 1562
- Dimensions:Height: 23.63 in (60 cm)Width: 19.3 in (49 cm)Depth: 2.76 in (7 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:This painting has passed a strict quality and condition assessment by a professional conservator prior to going on sale. It can be hung and enjoyed immediately.
- Gallery Location:London, GB
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU1199115343882
About the Seller
5.0
Gold Seller
Premium sellers maintaining a 4.3+ rating and 24-hour response times
Established in 1998
1stDibs seller since 2019
44 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 5 hours
Authenticity Guarantee
In the unlikely event there’s an issue with an item’s authenticity, contact us within 1 year for a full refund. DetailsMoney-Back Guarantee
If your item is not as described, is damaged in transit, or does not arrive, contact us within 7 days for a full refund. Details24-Hour Cancellation
You have a 24-hour grace period in which to reconsider your purchase, with no questions asked.Vetted Professional Sellers
Our world-class sellers must adhere to strict standards for service and quality, maintaining the integrity of our listings.Price-Match Guarantee
If you find that a seller listed the same item for a lower price elsewhere, we’ll match it.Trusted Global Delivery
Our best-in-class carrier network provides specialized shipping options worldwide, including custom delivery.More From This Seller
View AllDutch Old Master Portrait of Maurits, Prince of Orange-Nassau, Oil on Panel
Located in London, GB
In 1607, the Delft city council decided to commission a portrait of Stadholder Maurits of Nassau for the town hall, with Michiel van Mierevelt as the chosen artist due to the passing...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Oil, Wood Panel
Portrait of a Gentleman, Doublet & White Ruff, Gloves Inscribed 1624, on panel
By Frans Pourbus the Younger
Located in London, GB
Titan Fine Art presents this exquisite oil on panel portrait depicting a handsome young gentleman in an exuberant black damask doublet. The pose, with one hand holding gloves and the other akimbo, was one that was well-established for gentleman of the upper echelons of society by the time this work was painted. The principle governing portraits at this time was the recording and defining in visual terms of the position of a sitter in society. In addition to brilliant and complex symbols of luxury, they often contained many symbolic elements too; the inclusion of gloves was often used in portraits that celebrated a betrothal as in ancient times gloves were used to seal a marriage contract.
The extraordinary costume of a black shimmering doublet, the brilliant white reticella ruff, and the cuffs edged with lace were immensely costly… this attire proclaims to every onlooker that this is a superior being. The rendering of the reticella lace ruff is exquisite and the artist has recorded the design that runs through the black damask fabric with meticulous attention to detail. The preservation of this black pigment is remarkable considering the age of the work. Black pigments are especially vulnerable to fade and wear over time partly due to environmental condition but also from unprofessional cleaning. This work is an exquisite example from the period.
According to the inscription in the upper right, the gentleman was in his 22nd year of age in 1624. The coat of arms, which is displayed without a crest, may be ‘blazoned’ in the language of heraldry, as: Sable on a Chevron between in chief two Roundels and in base a Billet [or possibly Square] Or three Martlets Sable. In plainer English this means a black (Sable) background, spanned by a gold (Or) chevron, above which are two golden solid circles (Roundels), and below which is a gold rectangle (Billet); on the chevron are three small black birds (Martlets). Martlets are a stylised form of heraldic bird, believed to be based on the swift, which are conventionally drawn with small tufts instead of feet. In Continental Europe it is also conventional for them to be drawn without beaks, as appears to be the case here. The birds in this instance also have a vaguely duck-like appearance.
Five families have been identified with very close armorial bearings to the one in our portrait. They are the (van) Houthem’s (of Brabant), the Prévinaire’s (of Flanders and Holland), and the Proveneer’s (of Liège) and it must be noted that the locations of these families also fit with the painting’s Flemish origins. However the French Grenières’s (of Île-de-France) and the Jallot’s (of Normandy) are the next closest matches and plausible matches, as Frans Pourbus had settled in Paris just a few years before our portrait was painted.
This painting has been assessed by a professional conservator prior to going on sale, and as thus, it can be hung and enjoyed immediately.
Frans Pourbus the Younger...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Oil, Wood Panel
Portrait of a Lady in an Elaborate Ruff & Lace Coif c.1610-20, Dutch Old Master
Located in London, GB
This magnificent oil on panel portrait, presented by Titan Fine Art, is a splendid example of the sumptuous female portraits that were painted for members of the upper echelons of society during the early part of the 1600’s. The artist has rendered this portrait with meticulous attention to detail and the surface effects of the fine materials. The elaborate lace coif and cuffs are painstakingly delineated, as is the bold black damask, and sumptuous gold decoration of her skirt and stomacher, which is wonderfully preserved and quite remarkable considering the age of the work and the fact that darker pigments are particularly vulnerable to fading and wear. This work with its spectacular depiction of costume is of absolute quality, it can be rated as one of the best works in the artist’s oeuvre and as such it is an important and splendid example of Dutch portraiture.
The Dutch Golden Age of painting was a period in Dutch history, roughly spanning the 17th century, in which Dutch trade, science, military, and art were among the most acclaimed in the world. Dutch explorers charted new territory and settled abroad. Trade by the Dutch East-India Company thrived, and war heroes from the naval battles were decorated and became national heroes. During this time, The Dutch Old Masters began to prevail in the art world, creating a depth of realistic portraits of people and life in the area that has hardly been surpassed. The Golden Age painters depicted the scenes that their discerning new middleclass patrons wanted to see. This new wealth from merchant activities and exploration combined with a lack of church patronage, shifted art subjects away from biblical genres.
Dress was a key component in portraits, and the exuberant attire reiterates the incredible wealth of this woman. The sitter will have visited the artist’s workshop and inspected examples on display. They would have chosen the size and the sort of composition and on that basis negotiated the price – which would have also been determined by the complexity of the clothing and the jewels that were to be depicted, and by the materials to be used. When all was considered, this portrait would have cost the sitter (or her husband) a substantial sum.
The colour black was regarded as humble and devout yet at the same time refined and sophisticated and the most expensive colour of fabric to dye and to maintain. Citizens spent fortunes on beautiful black robes. Such uniformity must also have had a psychological side-effect and contributed to a sense of middle-class cohesion; the collective black of the well-to-do burgess class will have given its members a sense of solidarity. The colour was always an exciting one for artists and when this portrait was painted there were at least fifty shades of it, and as many different fabrics and accoutrements. Artists went to great lengths to depict the subtle nuances of the colour and the fabrics and textures and how they reflected light and it was an ideal background against which gold and crisp white lace could be juxtaposed to dramatic effect.
The sitter is either a married women or a widower as is evident by the clothing that she wears and the position, toward her right, it is highly likely that this portrait was once a pendant that hung on the right-hand side of her husband’s portrait as was convention at the time. She wears a vlieger which was a type of sleeveless over-gown or cape worn by well-to-do married women in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. Variations with short sleeves or high shoulder rolls are known. Sometimes sleeves were attached with aiglets, and often slits were made to allow belts or the hands to pass through. Three-piece vlieger costumes of this kind were standard items of clothing in portraits of the women of the civic elite in the period 1600-40 and was a variant of the Spanish ‘ropa’ and served as a trademark of well-to-do married burgher women. Girls and unmarried woman, including beguines, wore a bouwen (a dress with a fitted bodice and a skirt that was closed all round) instead. This clear distinction between apparel for married and unmarried women is clear not only from inventories and trousseau lists, but also from contemporary sources such as the Dutch Spanish dictionary published by Juan Rodrigues in 1634. In it, a bouwen is described as a ‘ropa de donzella’ (over-gown worn by a virgin) and a vlieger as a ‘ropa de casada’ (overgown worn by a married woman). It is striking how few women are depicted wearing a bouwen, unless they are part of a group, family or children’s portrait and it can therefore be assumed that independent portraits of unmarried women were seldom commissioned. It is also believed that the clothing worn in these portraits existed and were faithfully reproduced when cross-referenced with the few exact documents. These sources also demonstrate that clients wanted their clothing to be depicted accurately and with this in mind precious garments and jewels were often left in the painter’s studio.
The prominent white lawn molensteenkraag (or millstone ruff) is held up by a wire supportasse and was reserved only for the citizens that could afford this luxurious item that often required 15 meters of linen batiste. The fabulous wealth of this sitter is also evident by the elaborate lace coif and cuffs which have been exquisitely depicted; lace was often literally copied by artists in thin white lines over the completed clothing.
The gold bracelet with jewels is a type that was evidently fashionable as it is seen in a number of portraits during the 1610s and 1620. Clothing and jewellery were prized possessions and were often listed in inventories of estates and passed down from generation to generation. There were a great number of jewellers of Flemish origin working at all the courts and cities of Europe, competing with the Italians, and then the French, adapting themselves to the tastes and positions of their patrons and the raw materials available in the country where they worked. The fashion for jewels “in the Flemish style” succeeded that of the Italian style.
Cornelis van der Voort, who was probably born in Antwerp around 1576, came to Amsterdam with his parents as a child. His father, a cloth weaver by trade, received his citizenship in 1592. It is not known who taught the young Van der Voort to paint, but it has been suggested that it was either Aert Pietersz or Cornelis Ketel. On 24 October 1598 Van der Voort became betrothed to Truytgen Willemsdr. After his first wife’s death he became betrothed to Cornelia Brouwer of Dordrecht in 1613. In addition to being an artist, Van der Voort was an art collector or dealer, or both. In 1607 he bought paintings from the estate of Gillis van Coninxloo, and after an earlier sale in 1610 a large number of works he owned were auctioned on 7 April 1614. Van der Voort is documented as appraising paintings in 1612, 1620 and 1624. In 1615 and 1619 he was warden of the Guild of St Luke. He was buried in Amsterdam’s Zuiderkerk on 2 November 1624, and on 13 May 1625 paintings in his estate were sold at auction.
Van der Voort was one of Amsterdam’s leading portrait painters in the first quarter of the 17th century. Several of his group portraits are known. It is believed that he trained Thomas de Keyser (1596/97-1667) and Nicolaes Eliasz Pickenoy (1588-1650/56). His documented pupils were David Bailly (c. 1584/86-1657), Louis du Pré...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Oil, Wood Panel
Portrait of a Lady in White Chemise, Russet & Blue Drapery c.1695, Oil Painting
By Harman Verelst
Located in London, GB
This lavish portrait, painted circa 1695, is an exquisite example of the type of portrait in vogue during the last quarter of the seventeenth century. It is evident that the artist ...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil
Portrait of a Lady in Green Dress & Pearl Jewellery c.1660 Painting John Wright
By John Michael Wright
Located in London, GB
In this exquisite work, painted around the time of the Great Fire of London in 1666, a beautiful young woman is wearing a green dress over a white chemise and a russet-coloured scarf...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil
Portrait of a Gentleman in Grey Coat & White Cravat, Oil on canvas Painting
Located in London, GB
This exquisite work, presented by Titan Fine Art, is by the notable artist Hans Hysing, who was a noteworthy painter in England; it is significant in its q...
Category
18th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil
You May Also Like
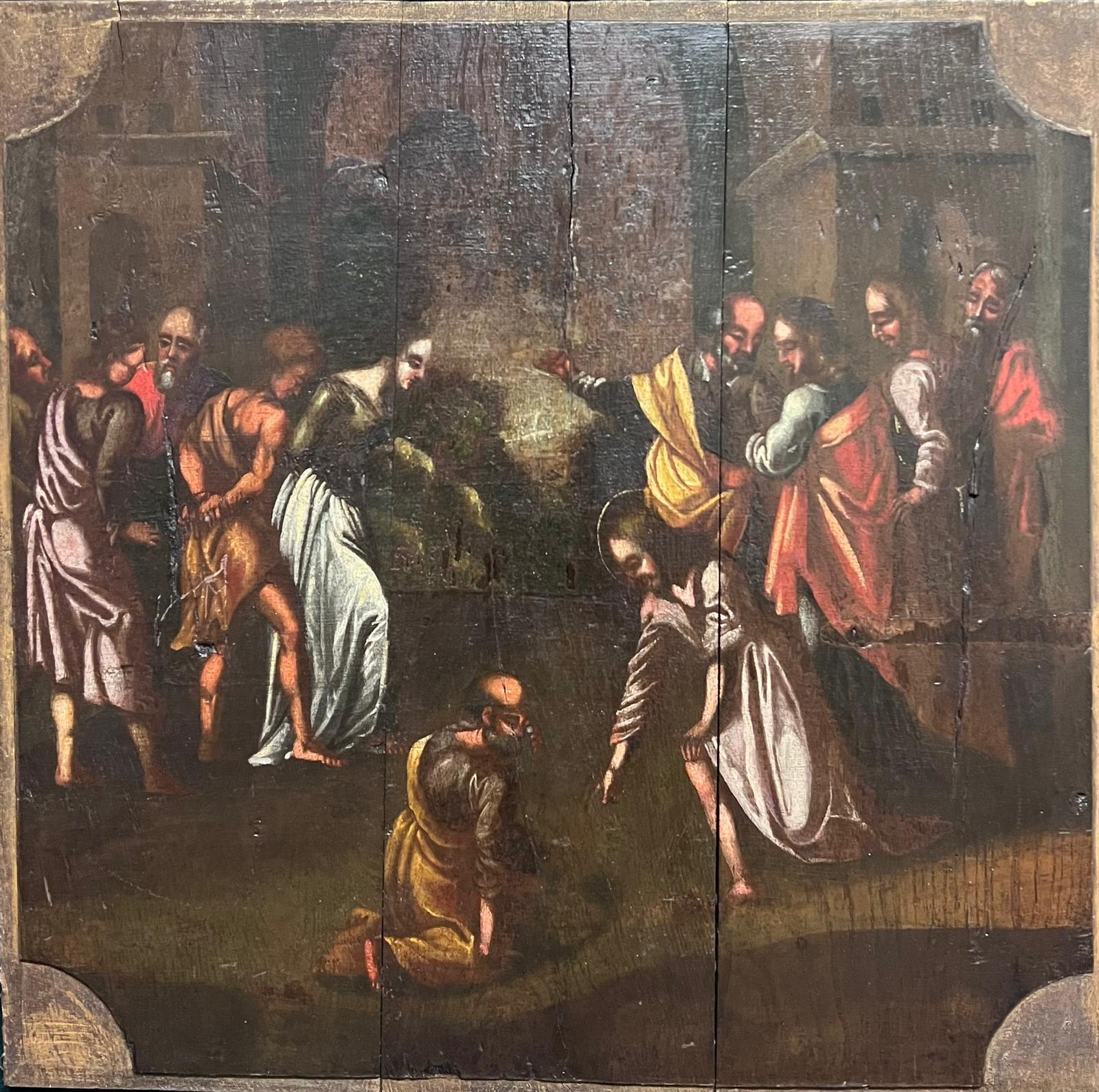
Large 17th Century Dutch Old Master Oil Painting on Wood Panel Biblical Scene
Located in Cirencester, Gloucestershire
Biblical Figures, Large Gathering around Christ?
Dutch Old Master, early 17th century
oil painting on wood panel, stuck on velvet backing board
velvet board: 27 x 29 inches
board: 25.5 x 26 inches
provenance: private collection, France
condition: good and sound condition, obvious old panel...
Category
Early 17th Century Old Masters Figurative Paintings
Materials
Oil, Wood Panel
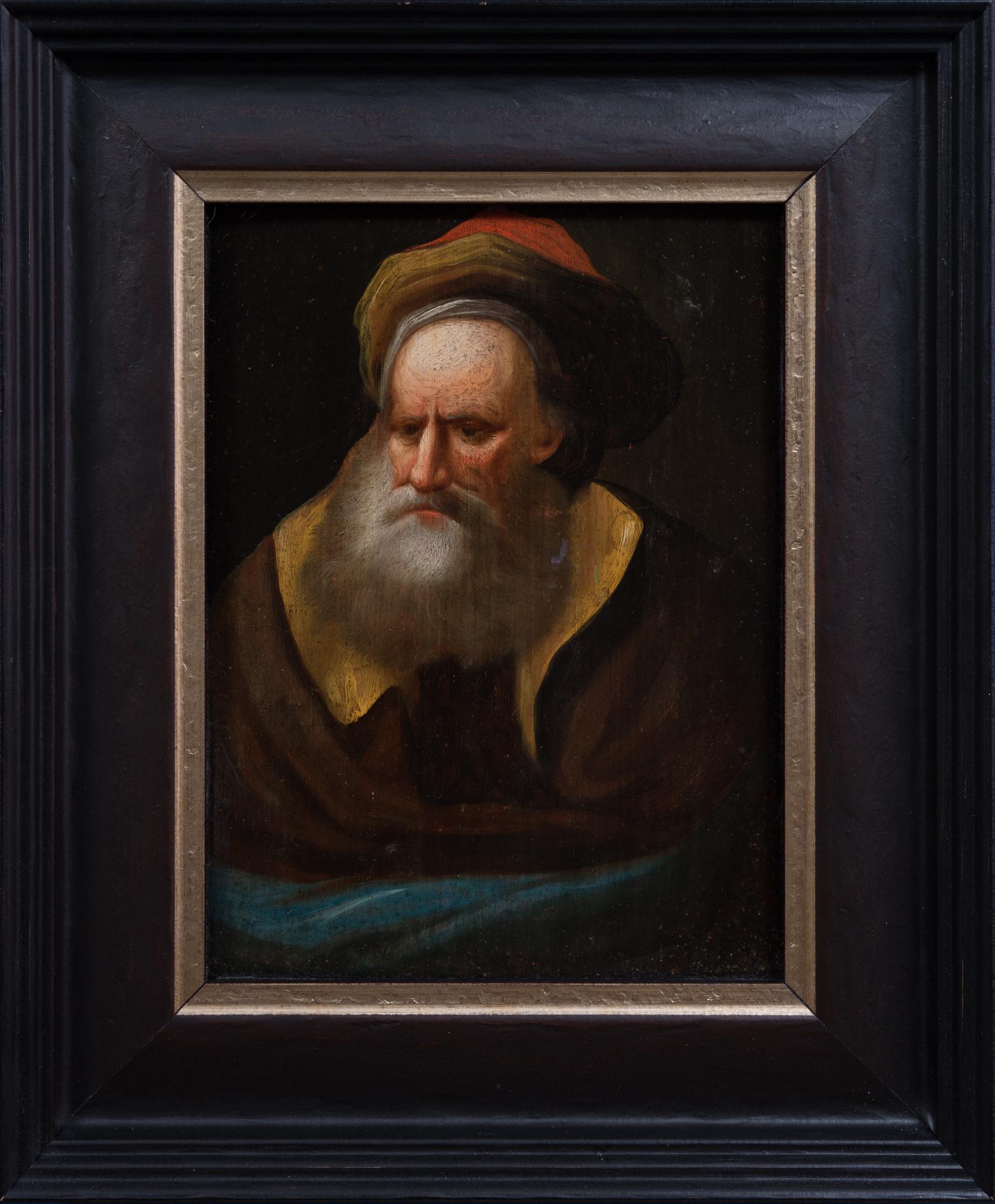
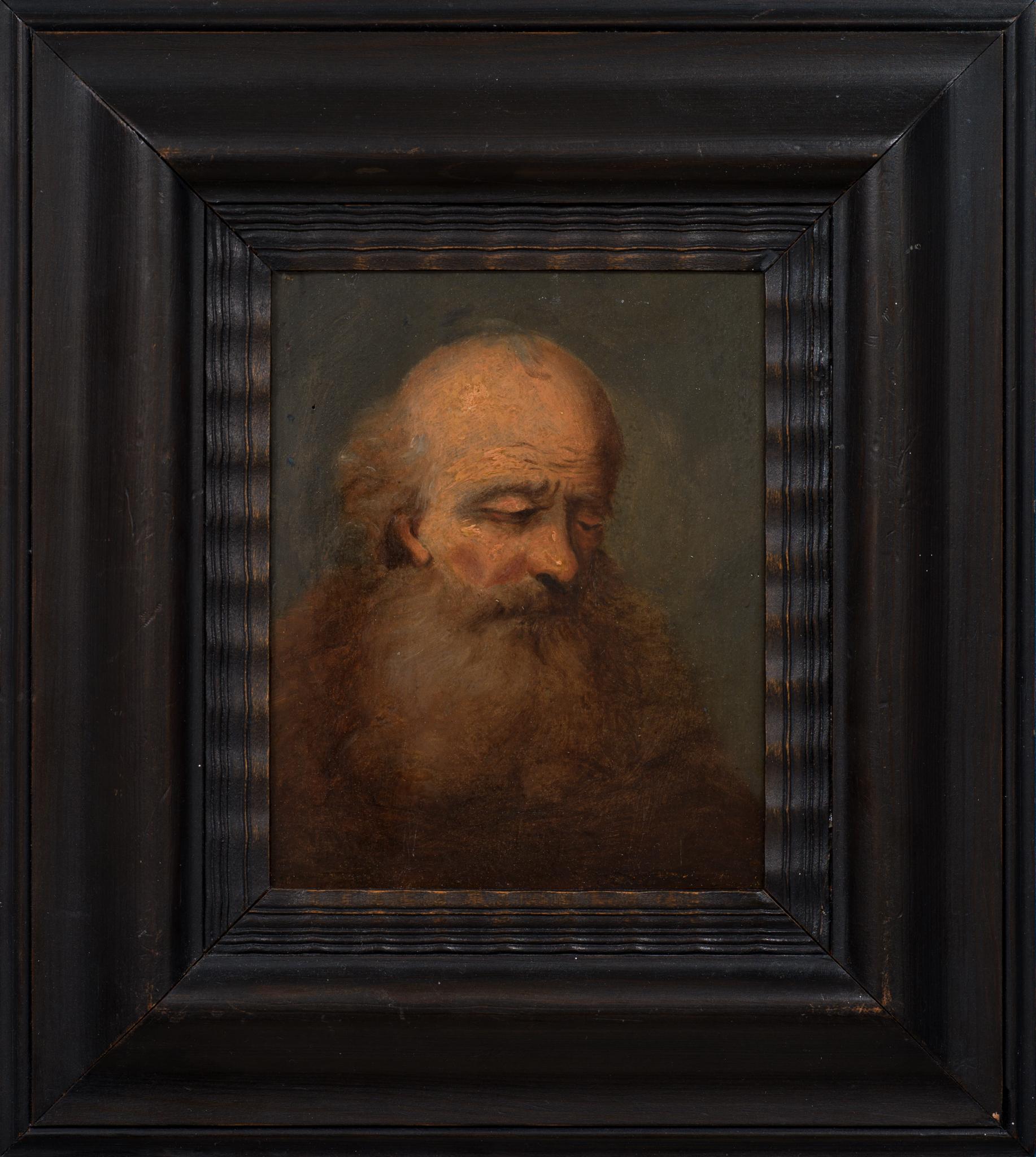
Portrait of an Old Bearded Man
Located in Stockholm, SE
We are pleased to offer a captivating portrait, most likely painted in the late 18th century, attributed to an artist within the circle of Christian Wilhelm Ernst Dietrich. This oil ...
Category
Late 18th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Oil, Wood Panel
Angelic Cherubs with Classical Figure in Wilderness Finely Painted Preparatory
Located in Cirencester, Gloucestershire
Figure with Cherubim in Wilderness
Italian School, 17th century
oil painting on wood panel
framed 13 x 11 inches
condition: overall for its age very good, though the work is most likely a preparatory...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Figurative Paintings
Materials
Oil, Wood Panel
17th Century by Giovanni Stefano Danedi Madonna and Child Crowned by Angels
Located in Milano, Lombardia
Giovanni Stefano Danedi, called Montalto (Treviglio, Italy, 1612 - Milan, Italy, 1690)
Title: Madonna and Child crowned by angels
Medium: Oil on panel
Dimensions: without frame 58 x ...
Category
17th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Oil, Panel
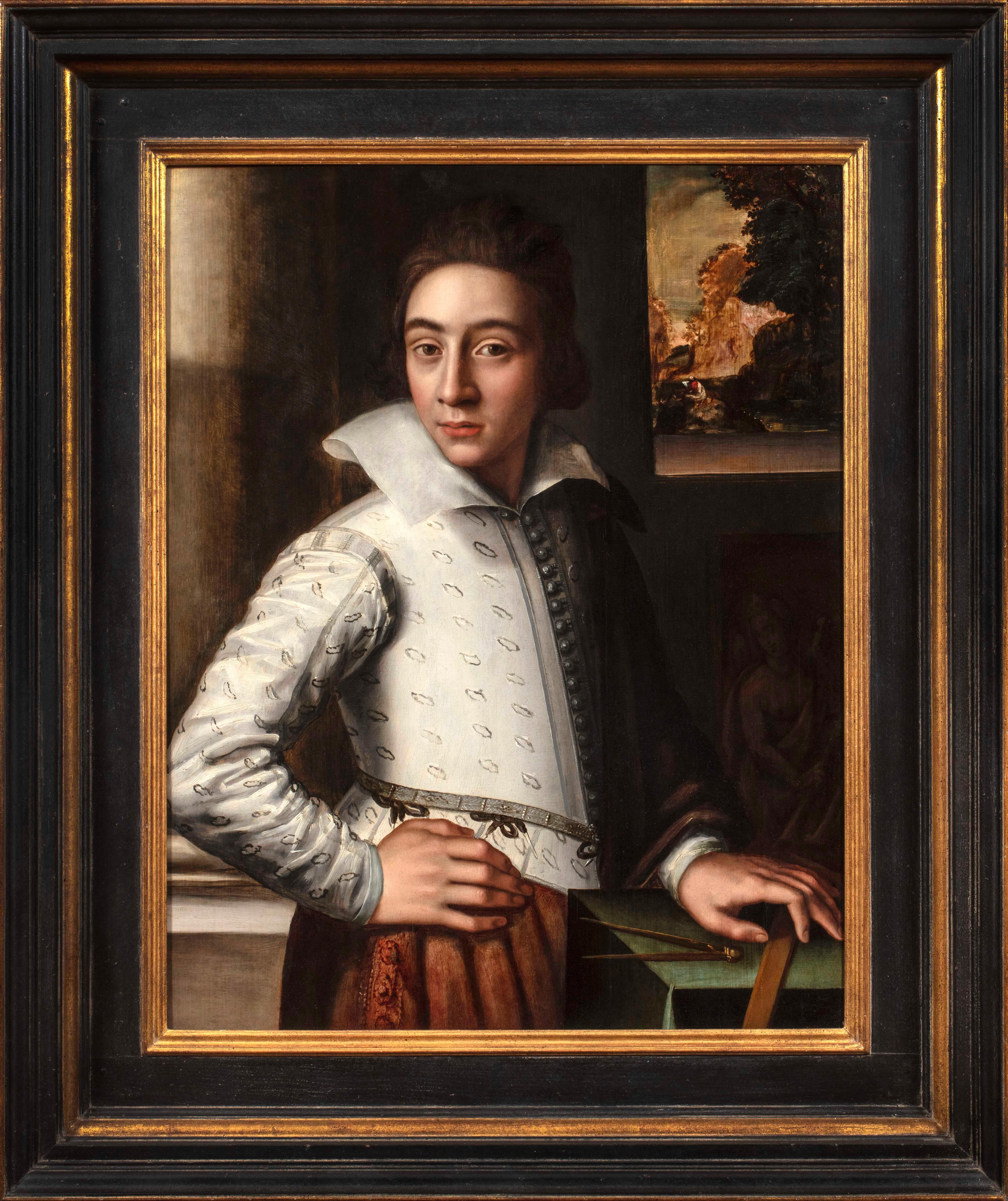
Portrait of an Artist (possibly a Self-Portrait)
Located in New York, NY
Provenance:
Bradley Collection.
Private Collection, Upperville, Virginia.
Literature:
Katlijne van der Stighelen and Hans Vlieghe, Rubens: Portraits of Unidentified and Newly Identified Sitters painted in Antwerp, Corpus Rubenianum Ludwig Burchard, vol. 19, pt. 3, London and Turnhout, 2021, under cat. no. 189, p. 161, and fig. 75.
This painting had previously been considered to be by an anonymous Tuscan painter of the sixteenth century in the orbit of Agnolo Bronzino. While the painting does in fact demonstrate a striking formal and compositional similarity to Bronzino’s portraits—compare the nearly identical pose of Bronzino’s Portrait of a Young Man in the Metropolitan Museum of Art (Fig. 1)—its style is completely foreign to Italian works of the period. That it is painted on an oak panel is further indication of its non-Italian origin.
This portrait can in fact be confidently attributed to the Antwerp artist Huybrecht Beuckelaer. Huybrecht, the brother of Joachim Beuckelaer, has only recently been identified as the author of a distinct body of work formerly grouped under the name of the “Monogrammist HB.” In recent studies by Kreidl, Wolters, and Bruyn his remarkable career has been delineated: from its beginnings with Joachim in the workshop of Pieter Aertsen; to his evident travels to Italy where, it has been suggested, he came into contact with Bronzino’s paintings; to his return to Antwerp, where he seems to have assisted Anthonis Mor in painting costume in portraits; to his independent work in Antwerp (where he entered the Guild of Saint Luke in 1579); and, later to his career in England where, known as “Master Hubberd,” he was patronized by the Earl of Leicester. Our painting was recently published by Dr. Katlijne van der Stighelen and Dr. Hans Vlieghe in a volume of the Corpus Rubenianum, in which they write that the painting “has a very Italian air about it and fits convincingly within [Beuckelaer’s] oeuvre.” Stighelen and Vlieghe compare the painting with Peter Paul Ruben’s early Portrait of a Man, Possibly an Architect or Geographer in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, in which the sitter holds a compass and wears a similarly styled doublet (Fig. 2).
Huybrecht both outlived and travelled further afield than his brother Joachim, who made his career primarily in Antwerp. Whereas Joachim was the main artistic inheritor of their uncle and teacher, Pieter Aertson, working in similar style and format as a specialist in large-scale genre and still-life paintings, Huybrecht clearly specialized as a painter of portraits and was greatly influenced by the foreign artists and works he encountered on his travels. His peripatetic life and his distinctly individual hand undoubtedly contributed to the fact his career and artistic output have only recently been rediscovered and reconstructed. His periods abroad seem to have overlapped with the mature phase of his brother Joachim’s career, who enrolled in the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke much earlier than his brother, establishing himself as an independent painter in 1560. Joachim’s activity was confined to the following decade and half, and his latest work dates from the last year of his life, 1574. Our portrait was likely produced in the late 1560s, a dating supported by the dendrochronological investigation performed by Dr. Peter Klein, which established that it is painted on an oak panel with an earliest felling date of 1558 and with a fabrication date of ca. 1566.
This painting presents a portrait of an artist, almost certainly Huybrecht’s self-portrait. The young sitter is confidently posed in a striking patterned white doublet with a wide collar and an abundance of buttons. He stands with his right arm akimbo, his exaggerated hands both a trademark of Huybrecht and his brother Joachim’s art, as well as a possible reference to the “hand of the artist.” The figure peers out of the painting, interacting intimately and directly with the viewer, as we witness him posed in an interior, the tools and results of his craft visible nearby. He holds a square or ruler in his left hand, while a drawing compass...
Category
16th Century Old Masters Paintings
Materials
Oil, Panel
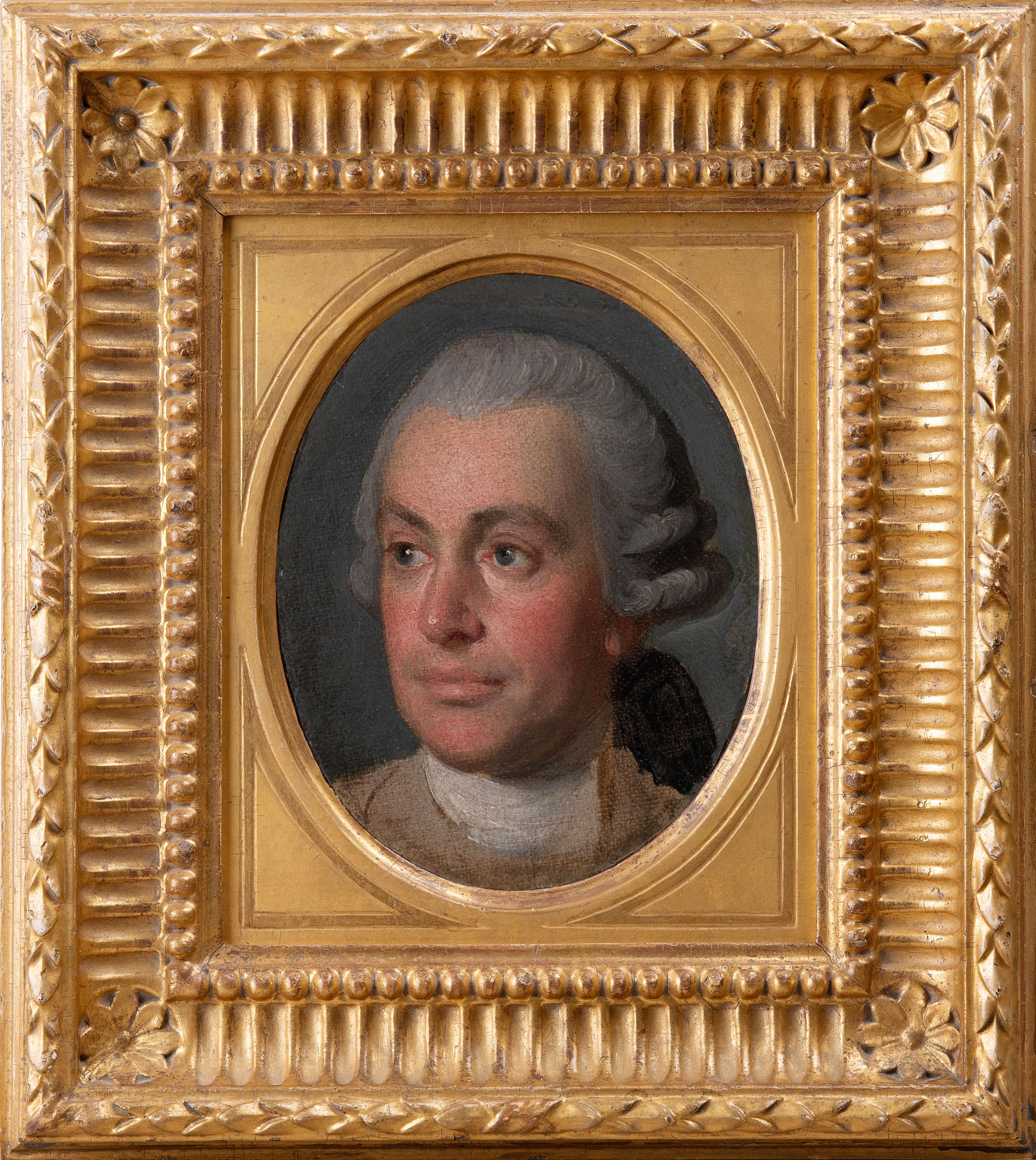
18th century portrait of the painter Nathaniel Dance
Located in London, GB
Collections:
Robert Gallon (1845-1925);
Private Collection, UK.
Oil on canvas laid down on panel
Framed dimensions: 11.5 x 10 inches
This highly engaging, previously unpublished portrait by Johan...
Category
18th Century Old Masters Portrait Paintings
Materials
Canvas, Oil, Wood Panel
Recently Viewed
View AllMore Ways To Browse
Henry Vi
Edward Vi
Antique Soldier Statues
18th Century Cannon
King Edward Viii
19th C British Woods Painting
William The Conqueror
Dior Men Coats
Spanish Cannons
God Save The Queen
18th Century Mens Coat
Robert Burns Antique
Antique Signal Cannon
Jane Seymour
George Gower
Anne Boleyn
Husband And Wife Statue
Elizabethan Oil Portrait