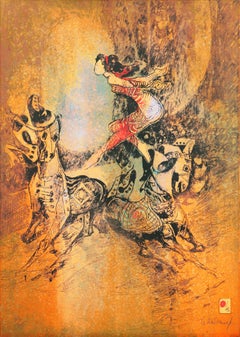Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
to
3,737
7,386
1,907
1,049
292
144
Overall Width
to
Overall Height
to
4,948
1,695
560
482
355
220
174
144
95
56
11
5
1
694
579
260
250
104
3,540
7,596
26,117
6,843
293
650
1,429
1,272
1,340
2,293
3,754
5,343
2,827
1,282
3,034
8,114
2,569
76
7,152
4,171
3,718
2,316
2,273
2,100
1,523
1,273
741
504
502
454
340
296
289
258
240
198
190
185
5,674
2,139
1,615
683
480
763
3,476
5,737
3,808
Period: Mid-20th Century
The Whore of Babylon
By Adolf Dehn
Located in Middletown, NY
A scarce impression by Dehn, the spirit of sedultive culture personified.
Lithograph on white wove paper with deckle edges, 13 1/2 x 17 1/8 inches (343 x 435 mm), full margins. Sign...
Category
American Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Handmade Paper, Lithograph
MATTA - 10 EROTIC ETCHINGS - New School Portfolio
Located in Santa Monica, CA
ROBERTO MATTA (Chilean 1911- 2002)
NEW SCHOOL PORTFOLIO (1943-5) (Sabatier 1-7, 4 prints not recorded by Sabatier)
Portfolio with complete set of 10 etch...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Etching
'Equestrian Actress', Modernism, Circus, Vietnamese, French, Horse, Acrobats
By Hoi Lebadang
Located in Santa Cruz, CA
Signed lower right, 'Lebadang' and with number and limitation, 163/215, lower left.
Also known as Dang Lebadang (Vietnamese-French, 1922-2015) this not...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Paper, Lithograph
La Tour Eiffel au ciel gris, Regards sur Paris, André Masson
By André Masson
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin d’Arches paper. Inscription: unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: from the folio, Regards sur Paris, 1963. Published by André Sauret, Paris;...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,036 Sale Price
20% Off
Chocolat Dancing in the Achille Bar afte H. de Toulouse-Lautrec
Located in Roma, IT
Chocolat Dancing in the Achille Bar is a modern artwork realized in the mid-20th century.
Mixed colored lithograph after H. de Toulouse-Lautrec.
Original title: Chocolat dansant da...
Category
Post-Impressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph, Paper
Toulouse-Lautrec, Composition, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Dessinateur (after)
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Paper size: 12.25 x 9.25 inches. Inscription: Signed in the plate and unnumbered, as issued. Notes: From the album, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Dessinateur,...
Category
Post-Impressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$716 Sale Price
20% Off
Harry Shokler, Island Harbor
Located in New York, NY
Harry Shokler used serigraphy to great advantage in this landscape. It's colorful and detailed.
It is signed in the image at the lower left. When printmakers began making serigraphs...
Category
American Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Screen
Picasso, Portrait of a Lady, Picasso: Fifteen Drawings (after)
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph and stencil on vélin paper. Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good Condition. Notes: From the folio, Picasso: Fifteen Drawings, 1946. Published by Pantheon Books, Inc., New York; rendered and printed by Albert Carman, City Island...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph, Stencil
$3,996 Sale Price
20% Off
original lithograph
Located in Henderson, NV
Medium: original lithograph. Printed in Paris in 1967 by Clot, Bramsen et Georges and issued in an edition of 2500 for "Les Temps Situationistes" (The Situationist Times -- a radical...
Category
Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
General Dynamics, Convair 880, World's Fastest Jetliner – Original Poster
By Erik Nitsche
Located in Zurich, CH
A poster belonging to Erik Nitsche's third series for General Dynamics, promoting its Convair Company.
Founded 1952, General Dynamics hired Nitsche a...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Paper
Original SAS One Giant Leap vintage travel poster / Un Pas de Geant
Located in Spokane, WA
Original 1950s SAS Scandinavian Airline System travel by air vintage poster. Linen backed in B+ condition. This poster was restored to the top and bottom left corners. Ready t...
Category
Conceptual Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Picasso, étude pour la céramique, Céramiques de Picasso (Orozco 105) (after)
Located in Fairfield, CT
Medium: Collotype and lithograph on vélin gloss finish paper (to resemble the finish of ceramic), archivally hinged on vélin paper
Year: 1948
Paper Size: 11.25 x 15 inches
Catalogue ...
Category
Cubist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,436 Sale Price
20% Off
Le Purgatoire IX (Field 189-200; M/L 1039-1138), La Divine Comédie
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Woodcut in colors on vélin pur chiffon de Rives paper. Paper size: 13 x 10.375 inches. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Catalogue raisonné reference: Michler & Löpsin...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Woodcut
$796 Sale Price
20% Off
The Three Women - Héliogravure by Marc Chagall - 1960
By Marc Chagall
Located in Roma, IT
Héliogravure on brown-toned paper, so signature.
On bot sheets, recto and verso.
Edition of 6500 unsigned copies. Printed by Mourlot and published by Tériade, Paris.
Ref. Mourlot,...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Photogravure
Ansicht Von Rothenburg
By Hans Figura
Located in San Francisco, CA
Artist: Hans Figura
Title: Ansicht Von Rothenburg
Year: Circa 1930
Medium: Color etching on silk
Paper: Wove
Image size: 9.25 x 4.75 inches
Framed size: 16.5 x 12.5 inches
Signa...
Category
Realist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Etching
A Handsome 1930s Rockwell Kent Lithograph on Paper, Titled "Canterbury Tales"
Located in Chicago, IL
A handsome 1930s Rockwell Kent lithograph on paper, titled "Canterbury Tales". Nicely matted and framed in a gold-toned frame. Image size: ...
Category
American Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Paper, Lithograph
Composition (Field 69-3; M/L. 1600), VI tavole dal ciclo della, Biblia Sacra
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph in colors on vélin Fabriano charta ex meris pannis "ab alveo" manu fabricata, perlucidis figuris intexta paper. Paper size: 19 x 13.75 inches. Inscription: Signed in the p...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,116 Sale Price
20% Off
Rita - Lithograph by Bernard Buffet - 1960
Located in Roma, IT
Color lithograph realized by Buffet in 1960.
Hand signed in pencil lower right.
Edition of 59/125; numbered in pencil.
Burnishing of the sheet on edges.
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,244 Sale Price
25% Off
Chagall, Tribe of Asher, Vitraux pour Jérusalem (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the album, Chagall, Vitraux pour Jérusalem. Published by Musée des Arts Décora...
Category
Expressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
20% Off
Composition, Alternance, Jean Cocteau
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Etching on Rives BFK paper. Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the folio, Alternance, 1946. Published by Le Gerbier, Paris; printed by atelier Quesnevill...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Engraving
$1,436 Sale Price
20% Off
Ubac, Composition, Derrière le miroir (after)
By Raoul Ubac
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From Derrière le miroir, N° 105-106, 1958. Published by Aimé Maeght, Éditeur, Paris...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$716 Sale Price
20% Off
Composition, Verve: Revue Artistique et Littéraire
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin des Papeteries du Marais paper. Paper Size: 14 x 10.25 inches. Inscription: Signed in the plate and unnumbered, as issued. Notes: From the album, Verve: Revue Art...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$716 Sale Price
20% Off
Chagall, Composition, Couleur amour (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph and stencil on vélin papier a la cuve du Moulin Richard de Bas spécialement filigrané pour cette édition paper. Signed in the plate and unnumbered, as issued. Good conditi...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph, Stencil
$7,196 Sale Price
20% Off
God and Eve - Lithograph by Marc Chagall - 1960
By Marc Chagall
Located in Roma, IT
Color lithograph realized by Marc Chagall in 1960 to illustrate "The Bible".
Edition of 6500, published by Tériade in no. 33 and 34 of the Art Magazine Verve.
Printed by Mourlot a...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Vuillard, Intérieur aux tentures roses, L'œuvre gravé de Vuillard (after)
Located in Fairfield, CT
Medium: Lithograph on grand vélin Renage paper
Year: 1948
Paper Size: 12.375 x 9.5 inches; image size: 11.81 x 9.05 inches
Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued
Notes: From...
Category
Post-Impressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$716 Sale Price
20% Off
Couple : The Argument - Original Lithograph
By Le Corbusier
Located in Paris, IDF
Le Corbusier (1887-1965)
Couple : The Argument, 1938
Original lithograph
Signature printed in the plate
Dated in the plate
On light vellum 21 x 27 cm (c. 8 x 11 inch)
Very good con...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Miró, Composition (Cramer 103; Mourlot 382-383), Miró Cartones 1956-1965 (after)
By Joan Miró
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph and stencil on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the album, Miró: Cartones, 1959-1965, October - November 1965, 196...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,436 Sale Price
20% Off
Chagall, Composition, Couleur amour (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph and stencil on vélin papier a la cuve du Moulin Richard de Bas spécialement filigrané pour cette édition paper. Signed in the plate and unnumbered, as issued. Good conditi...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph, Stencil
$7,196 Sale Price
20% Off
3 Biennale Internationale de L'estampe, France 1968 Miss American Indiana poster
Located in New York, NY
Richard Lindner
3 Biennale Internationale de L'estampe (International Biennale of Graphic Arts), Miss American Indian, 1968
Silkscreen on wove paper
Unnumbered
35 1/2 × 23 1/2 inches...
Category
Pop Art Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Screen
Sundial - Woodcut by Maurits Cornelis Escher - 1931
Located in Roma, IT
Woodcut print realized by Escher for the series "Emblemata", and published in 1931.
On Hollande van Gelder paper.
Edition of 300.
Unsigned, as issued. Excellent condition, matted....
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Woodcut
The Lady and the Jester - Lithograph by Umberto Brunelleschi - 1930s
Located in Roma, IT
The revelation is a color lithograph on ivory paper, created by the Italian artist Umberto Brunelleschi(Montemurlo 1879- Paris 1949).
Illustration for “Tales and Short Stories” by L...
Category
Art Nouveau Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Deux Femmes Nues - Etching by Pablo Picasso - 1930
Located in Roma, IT
Etching on wove Arches paper.
Hand signed and numbered in ink. Edition of 125 prints.
Published by Editions Albert Skira, Paris, in 1930.
Very good condition.
Catalogue Bloch no. 132.
Category
Cubist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Paper, Etching
Renoir, Le Chemin tournant, Seize Aquarelles et Sanguines de Renoir (after)
Located in Fairfield, CT
Medium: Lithograph and stencil on vélin d’Arches Johannot paper
Year: 1948
Paper Size: 10.75 x 15 inches
Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued
Notes: From the folio, Seize ...
Category
Impressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,436 Sale Price
20% Off
The Japanese landscape After Utagawa Hiroshige - Mid 20th Century
Located in Roma, IT
The Japanese landscape is a modern artwork realized in the Mid-20th Century.
Mixed colored lithograph after a woodcut realized by the great Japanese artist Utagawa Hiroshige in the ...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
"Juges" from the suite "Les Fleurs du Mal""
Located in San Francisco, CA
This artwork titled "Juges" from the suite "Les Fleurs du Mal" created in 1937/38, is an original color aquatint on Montval paper by renown French artist Georges Rouault, 1871-1958....
Category
Expressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Aquatint
La Mère et les Enfants
Located in New York, NY
Signed by Picasso in pencil lower left. Numbered 32/50 in pencil lower right.
Catalogue raisonne references: Bloch 739; Mourlot 239; Reuße 625.
Framed print. Framed dimensions ...
Category
Cubist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Inferno, Canto VII (Field 189-200; M/L. 1039-1138), La Divina Commedia
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Woodcut in colors on vélin pur chiffon de Rives paper. Paper size: 13 x 10.375 inches. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Catalogue raisonné reference: Michler & Löpsin...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Woodcut
Chagall, Tribe of Zebulun, Vitraux pour Jérusalem (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the album, Chagall, Vitraux pour Jérusalem. Published by Musée des Arts Décora...
Category
Expressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
20% Off
Composition (Field 69-3; M/L. 1600), VI tavole dal ciclo della, Biblia Sacra
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph in colors on vélin Fabriano charta ex meris pannis "ab alveo" manu fabricata, perlucidis figuris intexta paper. Paper size: 19 x 13.75 inches. Inscription: Signed in the p...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,116 Sale Price
20% Off
La Vache et la Chaise - Lithograph after Fernand Léger - 1959
Located in Roma, IT
Lithograph realized after Fernand Léger in 1959, on Richard de Bas paper.
Monogrammed in the plate.
It belongs to the suite "Contrastes", printed by Daniel Jacomet and published by...
Category
Cubist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Diurnes : Portrait with Tall Nose - Original Collotype and Stencil (Cramer #115)
Located in Paris, IDF
Pablo PICASSO (1881-1973)
Diurnes : Portrait with Tall Nose , 1962
Original collotype and stencil (Jacomet workshop)
Unsigned
Limited to 1000 copy
On paper 40 x 30 cm (c. 15.7 x 11...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Stencil
Girls with Dachshund, Impressionist Lithograph by Constantin Terechkovitch
Located in Long Island City, NY
Constantin Terechkovitch, Russian (1902 - 1978) - Girls with Dachshund, Medium: Lithograph, signed and numbered in pencil, Edition: 91/150, Image Size: 25.5 x 19.75 inches, Size: 28....
Category
Impressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Composition, Histoire d'O, Léonor Fini
By Leonor Fini
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin d’Arches pur chiffon paper. Inscription: signed in the plate and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: from the folio, L'Histoire d'O, 1962. Published and...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
20% Off
Chagall, Composition, Le Dur Désir de Durer (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin bouffant d'Alfa paper. Inscription: unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the volume, Le Dur Désir de Durer, illustré par Marc Chagall, ...
Category
Expressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$796 Sale Price
20% Off
Chagall, Tribe of Dan, Vitraux pour Jérusalem (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the album, Chagall, Vitraux pour Jérusalem. Published by Musée des Arts Décora...
Category
Expressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
20% Off
Miró, Composition (Cramer 69; Dupin 292; Mourlot 286-294) (after)
By Joan Miró
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good Condition, with centerfold, as issued. Notes: From folio, Miró 1959-1960, 1961. Published by Pierre M...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,596 Sale Price
20% Off
Tribute to Toulouse Lautrec : Lovers, the Kiss - Lithograph - Printed Signature
Located in Paris, IDF
Pablo PICASSO (1881-1973)
Tribute to Toulouse Lautrec : Lovers, the Kiss
Lithograph enhanced with stencil (Jacomet process) after a pastel by the artist
Printed signature in the pla...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Cinderella - Original 1950 Lobby Card.
Located in London, GB
Cinderella - Original 1950 Lobby Card
Vintage 1950 Lobby Card:
When Cinderella's cruel stepmother prevents her from attending the Royal Ball, she gets some unexpected help from the lovable mice Gus and Jaq and from her Fairy Godmother.
Directors: Clyde Geronimi Wilfred Jackson Hamilton Luske
Writers: Charles Perrault Bill Peet...
Category
Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Paper, Cardboard
Purgatorio, Canto XXXII (Field 189-200; M/L. 1039-1138), La Divina Commedia
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Woodcut in colors on vélin pur chiffon de Rives paper. Paper size: 13 x 10.375 inches. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Catalogue raisonné reference: Michler & Löpsin...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Woodcut
Miró, Composition (Mourlot 1722), Derrière le miroir (after)
By Joan Miró
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition, with bifold, as issued. Notes: From volume, Derrière le miroir, N° 125-126, 1961. Publishe...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
20% Off
The Creole Dancer - PhotoLithograph after Henri Matisse - 1993
Located in Roma, IT
The Creole Dancer is a photolithograph realized in 1993 after Henri Matisse.
On Milano handmade paper.
Very good conditions.
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Matisse, Mlle H.D. Femme devant un aquarium, Portraits par Henri Matisse (after)
Located in Fairfield, CT
Medium: Lithograph on vélin paper, mounted on vélin paper backing sheet, as issued.
Year: 1954
Paper Size: 12 x 9.25 inches; image size: 6.69 x 8.27 inches
Inscription: Signed in the...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$716 Sale Price
20% Off
Jesus Scourged by Salvador Dali from Biblia Sacra porfolio
Located in Paonia, CO
Jesus Scourged, 1967 is a colored lithograph from the original gouache on heavy rag paper from Salvador Dali’s five volume Biblia Sacra Suite published in Rome by Rizzoli , 1...
Category
Surrealist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Chagall, Tribe of Asher, Vitraux pour Jérusalem (after)
By Marc Chagall
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the album, Chagall, Vitraux pour Jérusalem. Published by Musée des Arts Décora...
Category
Expressionist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
20% Off
MOCA Chicago Lithograph, first North American building Christo wrapped Signed/N
By Christo
Located in New York, NY
This is a truly historic limited edition hand signed museum print from the 1960s - of the first North American building the legendary artists Christo ever wrapped:
Christo
Wrap In Wr...
Category
Pop Art Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Offset, Lithograph, Laid Paper, Pencil
Composition, Cirque (Saphire, N° 44-106)
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph on vélin d’Arches paper. Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the folio, Cirque, Lithographies Originales. Published by Les Éditions Verve, Paris, under the direction of Tériade, éditeur, Paris; printed by Mourlot Frères, Paris, October 5, 1950. Excerpted from the folio (translated from French), "Cirque" is entirely composed, handwritten text and illustrations, of original lithographs by Fernand Léger. This album was produced by Fernand Léger with the collaboration of Tériade and Marguerite Lang. It was completed printing on the presses de Mourlot Frères, on October 5, 1950, for Les Éditions Verve, Paris. The edition of this album includes two CCLXXX examples numbered from I to CCLXXX and XX hors-commerce examples. Numbered from I to XX. All examples, on vélin d'Arches, are signed by the artist [on the colophon].
Catalogue raisonné reference: Léger, F., & Saphire, L. (1978). Fernand Léger : the complete graphic work. Blue Moon Press, 44-106.
History of the edition: Cirque was originally conceived as a collaboration between Fernand Léger and the novelist Henry Miller. At a time when the two were interested in working together, the publisher Efstratios Tériade Léger approached Leger to make prints for an artist’s book. Tériade hoped to publish a series of such books with the circus as the theme. Léger was a circus enthusiast who often used circus images in his paintings. He often went to the Cirque Médrano in Paris and the Ringling Brothers and Barnum and Bailey Circus...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
$1,996 Sale Price
37% Off
Rodin, Composition, La Varende, Rodin (after)
Located in Auburn Hills, MI
Lithograph and stencil on vélin pur fil paper. Inscription: unsigned and unnumbered, as issued. Good condition. Notes: From the folio, La Varende, Rodin, 1944. Published by Éditions ...
Category
Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph, Stencil
$716 Sale Price
20% Off
Selected Tales of Guy de Maupassant, the complete portfolio
By Adolf Dehn
Located in Middletown, NY
Twenty hand-signed, numbered, and titled images based on the selected work of Maupsassant.
Portfolio containing 20 lithographs based on selected tales by de Maupassant, printed on h...
Category
American Modern Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Handmade Paper, Lithograph
Abel Pann Israeli Bezalel School Lithograph Judaica Biblical Print Jewish Art
By Abel Pann
Located in Surfside, FL
Abel Pann (1883–1963) was a European Jewish painter who settled in the Talpiot neighborhood of Jerusalem in the early twentieth century and taught at the Bezalel Academy of Art under...
Category
Symbolist Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Seascape - Oil Paint by Athos Brioschi - Mid-20th Century
Located in Roma, IT
Seascape is a modern artwork realized by Athos Brioschi in mid-20th Century
Mixed colored oil on canvas.
Hand signed on the lower margin.
Includes frame: 54x44 cm
Category
Contemporary Mid-20th Century Figurative Prints
Materials
Canvas, Oil
Recently Viewed
View AllMore Ways To Browse
Kim Tschang Yeul
Tom Blackwell On Sale
Tom Everhart Lithograph
Torii Kotondo
Victor Richardson
Vintage Boulangerie Signs
Vintage Les Nereides
Vintage Meat Scales
Vintage Multiplier Reel
Warhol Northwest Mask
Whistler Fumette
Yoko Ono Lithograph Harold Town
Zeno Giglietti
Ak47 Lotus
Alex Katz Bicycle
Alex Katz Christy
Alex Katz Twilight
Alex Katz Wedding Dress