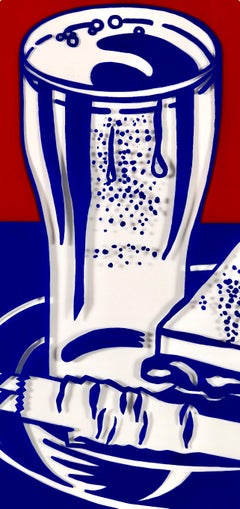
By Roy Lichtenstein
Located in Southampton, NY
This exquisite silkscreen by Roy Lichtenstein (1923–1997), titled Sandwich and Soda, originates from the landmark 1964 folio X + X (Ten Works by Ten Painters). Published by the Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art, Hartford, and printed by Sirocco Screenprints, Inc., North Haven, in Sandwich and Soda, Lichtenstein translates his signature Pop Art vocabulary—bold outlines, flat commercial color, and Ben-Day dot structure—into a crisp, iconic composition that reimagines everyday consumer imagery with graphic intensity and conceptual clarity.
Executed as a silkscreen on Mylar over Mohawk Superfine Bristol paper, this work measures 20 x 24 inches. Unsigned and unnumbered as issued. Printed by Sirocco Screenprints, Inc., North Haven, one of the most capable American screenprinting ateliers of the mid-20th century.
Artwork Details:
Artist: Roy Lichtenstein (1923–1997)
Title: Sandwich and Soda, from X + X (Ten Works by Ten Painters), 1964
Medium: Silkscreen on Mylar over Mohawk Superfine Bristol paper
Dimensions: 20 x 24 inches (50.8 x 60.96 cm)
Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered as issued
Date: 1964
Publisher: Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art, Hartford
Printer: Sirocco Screenprints, Inc., North Haven
Edition: D
Catalogue raisonne reference: Corlett, Mary Lee, and Roy Lichtenstein. The Prints of Roy Lichtenstein: A Catalogue Raisonne 1948–1997. 2nd rev. ed., Hudson Hills Press in association with the National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.; Distributed in the U.S. by National Book Network, 2002, No. 35.
Condition: Well preserved, consistent with age and medium
Provenance: From the 1964 folio X + X (Ten Works by Ten Painters), published by the Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art, Hartford
Notes:
Excerpted from the folio, This portfolio was commissioned and printed in an attempt to extend as much of the visual impact as possible of ten artists to paper and to make these prints available to collectors who might not otherwise have such a vivid slice of the artist. The dry surface of screening seemed to be most apt to translate the effect of their painting, both the flatness which is the unifying bond between the ten, and the insistance of paint on the surface of canvas so like the visible heft of ink on paper here. Samuel J. Wagstaff, Jr., Curator of Printings.
About the Publication:
X + X (Ten Works by Ten Painters), published in 1964 by the Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art in Hartford, stands as one of the most ambitious and influential printmaking endeavors of postwar American art. Conceived under the direction of curator Samuel J. Wagstaff, Jr., the project sought to capture and translate the defining visual languages of ten leading American painters of the era—Stuart Davis, Ellsworth Kelly, Robert Indiana, Adolph Gottlieb, George Ortman, Larry Poons, Richard Anuszkiewicz, Frank Stella, Andy Warhol, and Roy Lichtenstein—into original silkscreens. Each artwork was created as an autonomous work that embodied the formal, chromatic, and conceptual principles of its respective artist. The choice of silkscreen printing, executed by Sirocco Screenprints, Inc., was central to the portfolio’s purpose: its dry, matte surface and capacity for crisp, saturated color allowed for a faithful translation of the painters’ flatness, surface tension, optical effects, and graphic precision. Organized and published by a major American museum at a moment of seismic change in contemporary art, X + X marked a turning point in institutional engagement with editioned works, representing one of the first concerted efforts by a museum to commission an ensemble of original graphics from the leading figures of its time. The portfolio captured the pulse of 1960s American painting—from Hard-Edge abstraction to Pop, Op, and Color Field—offering both a curated snapshot of artistic innovation and an accessible format that expanded the audience for contemporary art. Today, X + X is widely regarded as a landmark in American printmaking, celebrated for its curatorial vision, technical accomplishment, and its role in defining the dialogue between museum patronage and the burgeoning print culture of the 1960s.
About the Artist:
Roy Lichtenstein (1923–1997) was an American painter, printmaker, and sculptor whose revolutionary elevation of comic-book graphics, Ben-Day dots, commercial illustration, and mass-media visual language into the realm of fine art made him one of the founding giants of Pop Art, drawing on the breakthroughs of Pablo Picasso, Alexander Calder, Alberto Giacometti, Salvador Dali, Joan Miro, Wassily Kandinsky, Marcel Duchamp, and Man Ray to synthesize Cubist fragmentation, Surrealist wit, Modernist experimentation, and Duchampian conceptualism into an unmistakable style defined by bold outlines, flat industrial color, graphic reduction, and the now-iconic Ben-Day dot technique; emerging in the 1960s alongside Andy Warhol, Claes Oldenburg, James Rosenquist, Jasper Johns, and Robert Rauschenberg, Lichtenstein shifted American art away from Abstract Expressionism toward a cool, analytical investigation of consumer culture, mass reproduction, advertising, and the manufactured image, creating paintings, prints, sculptures, and monumental public works that reimagined romance comics, war scenes, cartoons, brushstroke parodies, landscapes, and art-historical citations while offering a humorous yet incisive commentary on how images shape contemporary life; his influence is immense, shaping artists such as Jeff Koons, Takashi Murakami, Damien Hirst, Julian Opie, KAWS, Banksy, and numerous contemporary painters, designers, fashion houses, and digital creators, while his works are held in major institutions including the Museum of Modern Art, the Whitney Museum of American Art, the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, the Art Institute of Chicago, the National Gallery of Art, Tate, Centre Pompidou, SFMOMA, the Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden, and LACMA, with his highest auction record achieved when Nurse (1964) sold for 95,365,000 USD at Christie's New York on November 9, 2015.
Roy Lichtenstein silkscreen...
Category
1960s Pop Art Roy Lichtenstein