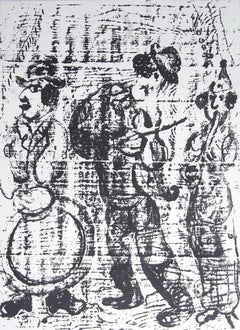For collectors of lithographs and other vintage fine art prints, interest in original Marc Chagall signed lithographs has deepened over the years.
Marc Chagall lithographs as well as his other prints and paintings widely influenced the fantastic imagery of Surrealism and other movements of the 20th century. Known for his dreamlike creations inspired by folk art, Chagall drew on the colors and forms introduced by Cubism and Fauvism for a distinctive style all his own.
Chagall was born into an Orthodox Jewish family in Liozna, Belarus, and one of his earliest teachers was painter Yehuda Pen, who ran a school of drawing and painting in nearby Vitebsk in western Russia. In 1907, Chagall went to St. Petersburg to continue his art studies, including with painter Léon Bakst with whom he would later collaborate on set designs for the Ballets Russes.
Chagall relied on the patronage of the Jewish community to get past the restrictions on Jewish people in Russia, like Maxim Vinaver, who in 1911 supported Chagall in traveling to Paris to study. There, he found a studio in the maze of Montparnasse ateliers nicknamed “La Ruche” (“The Hive”) alongside many fellow Jewish artists from around Europe, such as Expressionist painter Chaïm Soutine and painter and sculptor Amedeo Modigliani. He also began a long friendship with abstract colorist Robert Delaunay and his wife, artist Sonia Delaunay-Terk, with Chagall bringing some of their ideas of vivid color into his subsequent work.
That first stay in Paris lasted four prolific years, with Chagall absorbing the ideas of French Impressionism and Fauvism, leading to complex and enigmatic pieces, including the 1913 Self-Portrait with Seven Fingers depicting the artist at work in his studio, a glimpse of the Eiffel Tower through the window, and the 1911 I and the Village evoking memories of his Jewish community in Belarus with the face of a goat and a man gazing at each other, enveloped by intersecting colors and shapes.
The outbreak of World War I, which unfolded when Chagall had returned to Russia for his fiancée Bella Rosenberg, cut off his return to Paris. During those years in Russia, he became extremely enthusiastic about the Russian Revolution, in particular its promise to grant full citizenship to Jewish people like him, and was named the Commissar for Art in Vitebsk, although he became disenchanted with its ideology and eventually resigned.
Chagall left the Soviet Union in 1922, living in Berlin and Paris again in 1923. The outbreak of World War II and the Nazi invasion of France compelled him to flee to the United States. (His monographs had been destroyed in Nazi book burnings and some of his works confiscated from museums and displayed as part of a “Degenerate Art” exhibition.) After the war, he returned to France, and throughout the rest of his life, he continued to expand his practice.
Chagall had created etchings of Russian life during the 1920s but would explore printmaking later more deeply, during the 1950s, when he sought guidance from veteran lithographer Charles Sorlier, who became a friend and collaborator.
Chagall’s vibrant and densely colorful prints are known around the world. There are rare single lithographs from the artist’s largest print portfolios that contain over two dozen colors. In 1960, he was commissioned to paint a new ceiling for the Opéra Garnier in Paris and stained-glass windows for the cathedrals in Metz and Reims around the same time. Chagall’s windows are celebrated today both for their narrative depth and rich swaths of color, and he granted permission to his printmaking associate Sorlier to create lithographs based on his works in stained glass.
Shop Marc Chagall signed lithographs, numbered Chagall lithographs and more of the artist's kaleidoscopic original prints, including figurative prints and landscape lithographs, on 1stDibs.
Described by art critic Robert Hughes as "the quintessential Jewish artist of the twentieth century," the Russian-French modernist Marc Chagall worked in nearly every artistic medium. Influenced by Symbolism, Fauvism, Cubism and Surrealism, he developed his own distinctive style, combining avant-garde techniques and motifs with elements drawn from Eastern European Jewish folk art.
Born Moishe Segal in 1887, in Belarus (then part of the Russian empire), Chagall is often celebrated for his figurative paintings, but he also produced stained-glass windows for the cathedrals of Reims and Metz, in France; for the United Nations, in New York; and for the Hadassah Hospital in Jerusalem, as well as book illustrations, stage sets, ceramics, tapestries and fine-art prints. Characterized by a bold color palette and whimsical imagery, his works are often narrative, depicting small-village scenes and quotidian moments of peasant life, as in his late painting The Flight into Egypt from 1980.
Before World War I, Chagall traveled between St. Petersburg, Paris and Berlin. When the conflict broke out, he returned to Soviet-occupied Belarus, where he founded the Vitebsk Arts College before leaving again for Paris in 1922. He fled to the United States during World War II but in 1947 returned to France, where he spent the rest of his life. His peripatetic career left its mark on his style, which was distinctly international, incorporating elements from each of the cultures he experienced.
Marc Chagall remains one of the past century’s most respected talents — find his art on 1stDibs.