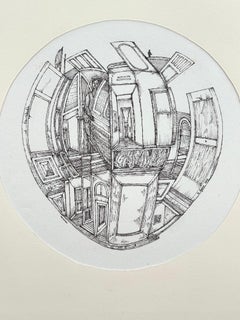
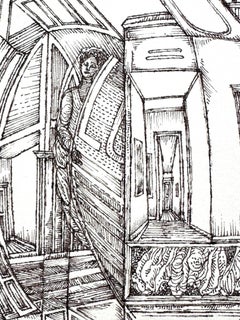
Roland AyersUntitled, 1982
$960Sale Price|20% Off
Untitled
By Roland Ayers
Located in Wilton Manors, FL
Roland Ayers (1932-2017). Untitled, 1983. Ink on paper, measures 17 x 23 inches. Unframed and unmounted. Signed and dated lower left. Ayers holds the distinction of having participated in the first important survey of African-Americans, Contemporary Black Artists in America, a 1971 show at The Whitney. Biography: Artist and art educator, Roland Ayers was born on July 2, 1932, the only child of Alice and Lorenzo Ayers, and grew up in the Germantown district of Philadelphia. Ayers served in the US Army (stationed in Germany) before studying at the Philadelphia College of Art (currently University of the Arts). He graduated with a BFA in Art Education, 1954. He traveled Europe 1966-67, spending time in Amsterdam and Greece in particular. During this period, he drifted away from painting to focus on linear figurative drawings of a surreal nature. His return home inaugurated the artist’s most prolific and inspired period (1968-1975). Shorty before his second major trip abroad in 1971-72 to West Africa, Ayers began to focus on African themes, and African American figures populated his work almost exclusively. In spite of Ayers’ travel and exploration of the world, he gravitated back to his beloved Germantown, a place he endowed with mythological qualities in his work and literature. His auto-biographical writing focuses on the importance of place during his childhood. Ayers’ journals meticulously document the ethnic and cultural make-up of Germantown, and tell a compelling story of class marginalization that brought together poor families despite racial differences. The distinctive look and design of Germantown inform Ayers’ visual vocabulary. It is a setting with distinctive Gothic Revival architecture and haunting natural beauty. These characteristics are translated and recur in the artist’s imagery. During his childhood, one of the only books in the Ayers household was an illustrated Bible. The images within had a profound effect on the themes and subjects that would appear in his adult work. Figures in an Ayers’ drawing often seem trapped in a narrative of loss and redemption. Powerful women loom large in the drawings: they suggest the female role models his journals record in early life. The drawings can sometimes convey a strong sense of conflict, and at other times, harmony. Nature and architecture seem to have an antagonistic relationship that is, ironically, symbiotic. A critical turning point in the artist’s career came in 1971 when he was included in the extremely controversial Whitney Museum show, Contemporary Black Artists in America. The exhibition gave Ayers an international audience and served as a calling card for introductions he would soon make in Europe. Ayers is a particularly compelling figure in a period when black artists struggled with the idea of authenticity. A questioned often asked was “Is your work too black, or not black enough?” Abstractionists were considered by some peers to be sell-outs, frauds or worse. Figurative* work was accused of being either sentimental or politically radical depending on the critical source. Ayers made the choice early on to be a figurative artist, but considered his work devoid of political content. Organizations such as Chicago’ s Afri-Cobra in the late 1960‘s asserted that the only true black art of any relevance must depict the black man and woman...
1980s Abstract Roland Ayers Art
Paper, Ink