Items Similar to Palatial Sculpture of Henri Robert-Marcel Duchamp by Ursula Meyer
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 21
Palatial Sculpture of Henri Robert-Marcel Duchamp by Ursula Meyer
About the Item
Palatial bust of Henri Robert-Marcel Duchamp by Ursula Meyer. The sculpture itself measures 47" in height, 27.5" in width, and 21.5" depth acquired from the home of the most prolific American conceptual artist. Signed and dated.
Provenance:
From the Estate of Ann Pollon Re: The Collection of Ursula Meyer. Descendant.
Acquired from the artist.
Henri-Robert-Marcel Duchamp French: (28 July 1887-2 October 1968) was a French-American painter, sculptor, chess player, and writer whose work is associated with Cubism, Dada, and conceptual art He was careful about his use of the term Dada and was not directly associated with Dada groups. Duchamp is commonly regarded, along with Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse, as one of the three artists who helped to define the revolutionary developments in the plastic arts in the opening decades of the 20th century, responsible for significant developments in painting and sculpture. Duchamp has had an immense impact on twentieth-century and twenty first-century art, and he had a seminal influence on the development of conceptual art. By the time of World War I he had rejected the work of many of his fellow artists (such as Henri Matisse) as "retinal" art, intended only to please the eye. Instead, Duchamp wanted to use art to serve the mind.
Ursula Meyer was a German-born American sculptor, art-focused academician, and fine art
critic, who proved an influential player in the transmission of and appreciation for European born Modernism to the United States in the post-World War II era. At first a ceramicist beholden to the teachings of 1930s Germany’s Bauhaus and Italy’s Futurists, she eventually became a creator and exponent of a crisp, geometry-focused sculptural lexicon in ceramics, and later wood and metal sculpture. Her legacy includes a decades-long exploration of Minimalism, as well as experimentations in creating and deciphering Conceptual and
Expressive genres.
Born in Hanover, Germany in 1915 to Ernst Josef Meyer and Elsa Katzenstein, Ursula Meyer is
recorded as having “studied with former Bauhaus masters after the Bauhaus itself had closed
under threat of National Socialism” in 1933. Spanning the years 1934 through 1937, Ursula’s
Bauhaus tutorial is not fully documented, but it may well have included at least brief study with
the French-born Marguerite Friedlaender Wildenhain (1896-1985), the first woman to earn the
Master Potter certification in Germany, and who worked with Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky,
Max Kehan and Gerhard Marcks (1889-1981). Meyer is recorded as having directly worked
with Marcks, as well as with Otto Lindig (1895-1966) and the Dutch-born Jan Bonjes Van Week
(1899-1969). In 1937, she began formal study at the Reggia Scuola in Faenza, Italy. Here, she
further developed her skills as a potter, presumably bridging the organic forms and glazes
identified with the pre-Dessau Bauhaus and the more architectonic and heroically Classical
models associated with Italy’s Futurist movement that paralleled the reign of Italian dictator
Benito Mussolini. As she noted later in life, “art is an inevitable part of the larger order of
society, its language and world shared and interdependent with the…’vision’…of its specific
Time, Life, place…”
Ursula Meyer emigrated to the United States on the British passenger ship Georgic in June
1939, the manifest of which listed her as “Hebrew,” “Stateless,” and a “Potterer.” A year later,
she married Austrian-émigré musician and academician Michael Pollon (1913-1996) in New
York. In 1944, she gave birth to the couple’s only child, Ann Caroline Pollon, and in January of
the following year, she became a citizen of the United States.
With her marriage and the subsequent birth of her daughter, Ursula Meyer seemed to step
away — if only temporarily — from her established career path. But Meyer’s artistic ambitions
were not left dormant. Following her 1954 divorce from Pollon, she returned to academic
study. She exhibited a group of imposing ceramic vases at the international Expo ‘58 (1958
Brussel’s World’s Fair) — an impressive feat representing a strong commitment to studio
productivity that obviously garnered regional and national critical notice. Her work of this time
has been assessed by curators as “an interesting link to her slightly later metal and wood
sculptures. Though geometric and abstract, the ceramics appear rough and uneven, with
deliberately unfinished, expressive surfaces” no doubt beholden to her early Bauhaus
influences. Ursula completed her Bachelor of Arts degree at New York’s New School in 1960,
and received her Master of Arts degree from Columbia University two years later, at the age of
47. In the fall of 1963, Ursula Meyer’s recognized skill and talent led to her appointment as a
professor of sculpture at New York City’s Hunter College. While at Hunter, she participated in
numerous landmark exhibitions celebrating Minimalism in art and sculpture, including the serial
“Artist-Craftsmen of New York,” organized by New York’s Cooper Union Museum, in 1963,
1964, and 1965. Additional exhibition venues included: the National Design Center (1964;
1965); Artists for CORE (Gallery of American Federation of the Arts — New York; 1967); Artists
for SEDF (1967); “Cool Art” (Aldrich Contemporary Art Museum — Ridgefield, Connecticut;
1967); “Schemata 7” (Finch College Museum of Art — New York; 1967). Of these exhibitions,
Meyer included works representing a refinement of her evolving design lexicon. At this point,
she resisted the application or integration of texture to her favored geometric forms —
particularly the square. And scale became less restrictive or suppressed, with her works taking
on a greater monumentality and importance. Her “Homage to Tiny Alice” — presumably a
reference to Edward Albee’s controversial 1965 three act play, “Tiny Alice,” which addressed
financial corruption in religion — (1967) was among her most celebrated works, and it was
included in the Newark Museum’s 1968 exhibition “Cool Art: Abstraction Today,” where it was
showcased beside the works of Sol LeWitt and Robert Smithson.
From 1968 through the 1980 academic year, Meyer served as Associate Professor of Art at
Herbert Lehman College, City University of New York. Here, she had her greatest influence as
an artist and academician. She perfected her Minimalist, Euclidean-based vocabulary,
concentrating on unadorned, precise manipulations of squares, triangles, and other geometric
forms. Whether as initial sketches, maquettes, or full-scale sculptures, her works at this time
conveyed an even greater monumentality that appealed to Modern Art museum curators and
then contemporary architects designing new, multi-purpose public gathering spaces, alike.
Meyer exhibited in a number of group shows, and her work was also honored with a series of
solo exhibitions at the Hunter College Art Gallery (1968), the Herbert H. Lehman College Art
Gallery (1971), and the City University of New York’s Graduate Center (1974). Long-term
installations of her sculpture on the campuses of CUNY paralleled these exhibitions, while her
work entered into the permanent collections of the Finch College Museum (no longer extant),
The Brooklyn Museum, The Newark Museum, and the Aldrich Contemporary Art Museum.
As an art critic in a volatile era of war protests and cultural revolution, Meyer became
increasingly political, participating in such important demonstrations and reform efforts as the
short-lived but influential Art Workers’ Coalition, which was formed in 1969 in protest of the
restrictive policies of institutions like New York’s Museum of Modern Art. The AWC
successfully secured the establishment of free admission days at MoMA and other New York
museums, as well as the public identification of shortcomings regarding the celebration of work
by women and other minorities.
As a writer on art, Ursula Meyer is probably best known for her 1972 book, “Conceptual Art” —
an exploration of the then burgeoning genre whereby the idea presented by the artist is viewed
as more important than a finished product, if there is, indeed, one. Through a thoughtful and
dense text, Meyer explored the works of such artists as Vito Acconci, Terry Atkinson, David
Bainbridge, as well as others. This is perhaps her best remembered contribution to the art
world, and it still remains a pertinent introduction to the genre that she, herself would explore
following her 1980 retirement from the City University of New York.
Following her retirement, Ursula Meyer continued to create in her studio and at her desk —
expressing her artistic vision, while also serving as a critic, consultant, and lecturer. Meyer died
in 2003, leaving a remarkable body of work, spanning nearly six decades. She is counted as
an influential voice of the American Minimalist movement of the 1960s — a promoter of the
“interplay of transiency and stability” in art.
James Archer Abbott
Art Historian, Curator, and Museum Director
Author Jansen Furniture
Designing Camelot.
- Creator:Ursula Meyer (Sculptor)
- Dimensions:Height: 62.5 in (158.75 cm)Width: 33 in (83.82 cm)Depth: 31.5 in (80.01 cm)
- Style:Mid-Century Modern (Of the Period)
- Materials and Techniques:
- Place of Origin:
- Period:
- Date of Manufacture:1971
- Condition:Wear consistent with age and use. Minor fading.
- Seller Location:Stamford, CT
- Reference Number:
About the Seller
4.9
Platinum Seller
These expertly vetted sellers are 1stDibs' most experienced sellers and are rated highest by our customers.
Established in 1975
1stDibs seller since 2009
1,597 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: <1 hour
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Ships From: Stamford, CT
- Return PolicyA return for this item may be initiated within 1 day of delivery.
More From This SellerView All
- Black Geometric Sculpture by Ursula Meyers Conceptual ArtistBy Ursula MeyerLocated in Stamford, CTBlack geometric sculpture by Ursula Meyers conceptual Artist. Ursula Meyer (1915-2003) American sculpture signed and dated. This monumental geometric form sculpture is one the first work of art ever offered for sale, only at Greenwich Living, by renowned artist Ursula Meyer. Provenance: From the Estate of Ann Pollon Re: The Collection of Ursula Meyer. Descendant. Acquired from the Artist Studio. Ursula Meyer was a German-born American sculptor, art-focused academician, and fine art critic, who proved an influential player in the transmission of and appreciation for European born Modernism to the United States in the post-World War II era. At first a ceramicist beholden to the teachings of 1930s Germany’s Bauhaus and Italy’s Futurists, she eventually became a creator and exponent of a crisp, geometry-focused sculptural lexicon in ceramics, and later wood and metal sculpture. Her legacy includes a decades-long exploration of Minimalism, as well as experimentations in creating and deciphering Conceptual and Expressive genres. Born in Hanover, Germany in 1915 to Ernst Josef Meyer and Elsa Katzenstein, Ursula Meyer is recorded as having “studied with former Bauhaus masters after the Bauhaus itself had closed under threat of National Socialism” in 1933. Spanning the years 1934 through 1937, Ursula’s Bauhaus tutorial is not fully documented, but it may well have included at least brief study with the French-born Marguerite Friedlaender Wildenhain (1896-1985), the first woman to earn the Master Potter certification in Germany, and who worked with Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky, Max Kehan and Gerhard Marcks (1889-1981). Meyer is recorded as having directly worked with Marcks, as well as with Otto Lindig...Category
Late 20th Century American Modern Abstract Sculptures
MaterialsWood
- Gilt Bronze Figure of a Lady Playing a Flute SculptureLocated in Stamford, CTAn exquisite bronze sculpture of a lady with music instrument.Category
Vintage 1940s Neoclassical Sculptures
MaterialsBronze
- Mid-Century Modern, Sheep Sculpture, Resin, Wool, 2000Located in Stamford, CTLarge Mid-Century Modern Francois Lalanne Style Sheep Sculpture, Wool / Resin One large wool / resin sheep. Finely detailed in authentic shearling. ...Category
Early 2000s American Mid-Century Modern Animal Sculptures
MaterialsResin, Sheepskin
- Midcentury Brutalist Abstract Sculpture, Patinated Bronze Decorative Art ObjectLocated in Stamford, CTMid-Century Brutalist Abstract Sculpture, Patinated Bronze Decorative Art Object Unique brutalist relief sculpture labeled Miquel-Dumeny on the underside. Titled '143 bi'Category
Vintage 1960s American Mid-Century Modern Abstract Sculptures
MaterialsBronze
- Solid Bronze Abstract Sculpture / Statue, Organic Form Mid-Century ModernLocated in Stamford, CTOrganic Form Mid-Century Modern Solid Bronze Abstract Sculpture / Statue on Base A large and impressive bronze sculpture on a wooden base. Thi...Category
Vintage 1970s Mid-Century Modern Abstract Sculptures
MaterialsBronze
- 'Venus De Milo' Nude Murano Glass Sculpture / Statue, Italian Mid-Century ModernBy Loredano Rosin, Archimede SegusoLocated in Stamford, CT'Venus De Milo' Nude Murano Glass Sculpture / Statue, Italian Mid-Century Modern A solid murano glass sculpture of a female nude on a pedestal by Loredano Rosin (1936-91) for Archime...Category
Vintage 1950s Italian Mid-Century Modern Figurative Sculptures
MaterialsMurano Glass
You May Also Like
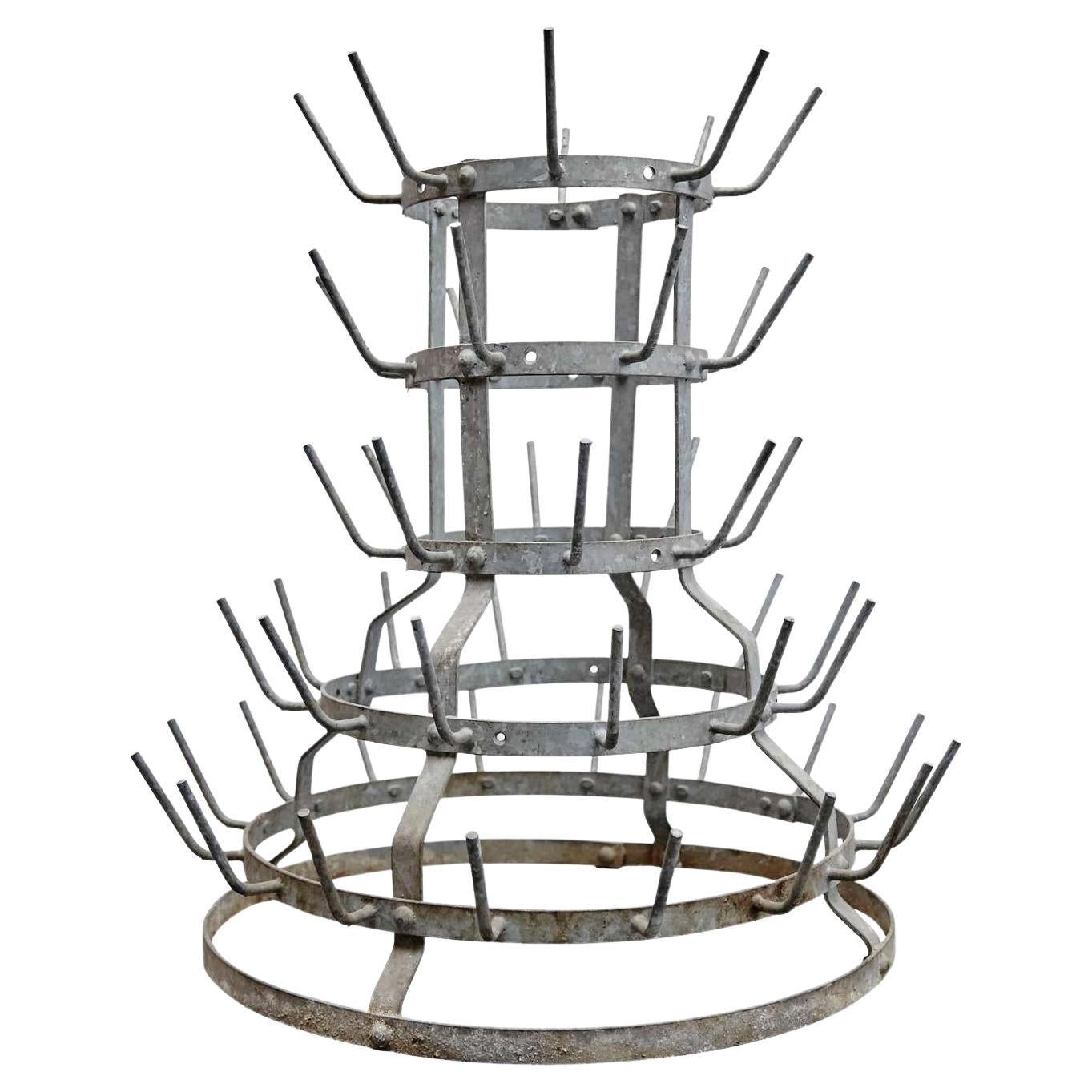
- Marcel Duchamp Thonet Readymade "Porte Chapeau"By Marcel DuchampLocated in Sharon, CTThonet manufactured this object (11022) around the turn of the century and was illustrated in their 1904 catalog (see photo). In 1917 Duchamp hung one from the ceiling of his New Yor...Category
Early 20th Century French Modern Mobiles and Kinetic Sculptures
MaterialsWood
- Bottle Holder After Marcel Duchamp ReadymadeBy Marcel DuchampLocated in Barcelona, BarcelonaBottle holder as the ones used by Marcel Duchamp for his readymade, Not signed. In good original condition, with minor wear consistent with age and use. Preserving a beautiful ...Category
Vintage 1950s French Modern Abstract Sculptures
MaterialsMetal
- Art Deco Dancer Sculpture in Copper by Henri Lautier Cast by Robert ThewBy Henri LautierLocated in Philadelphia, PAThis listing is for a Classic and striking Art Deco copper sculpture depicting a dancing nude by Henri Lautier who was a French Sculpture. The sculpture stands at approx 12.25 inches tall, 6" wide, and 6" deep. The figure is mounted on a round copper base. The underside of the base is marked with the year 1928 and the initials of the foundry G. Thew, for Robert Garrett Thew. The condition of the piece is very nice, with no damage, and a great patina on the copper which only age will produce. Robert Garrett Thew (1892-1964) was born in Sharon, CT and studied at Syracuse University under Edward Penfield (1866-1925), Walter Biggs...Category
20th Century American Art Deco Figurative Sculptures
MaterialsCopper
- 20th Century Bottle Dryer, in the Style of Porte-Bouteilles by Marcel DuchampLocated in Dusseldorf, DEOriginal vintage bottle dryer or bottle holder in the style of the well-known "Readymade" with the name "Porte-Bouteille" by the French Artist Mar...Category
Mid-20th Century French Modern Abstract Sculptures
MaterialsMetal
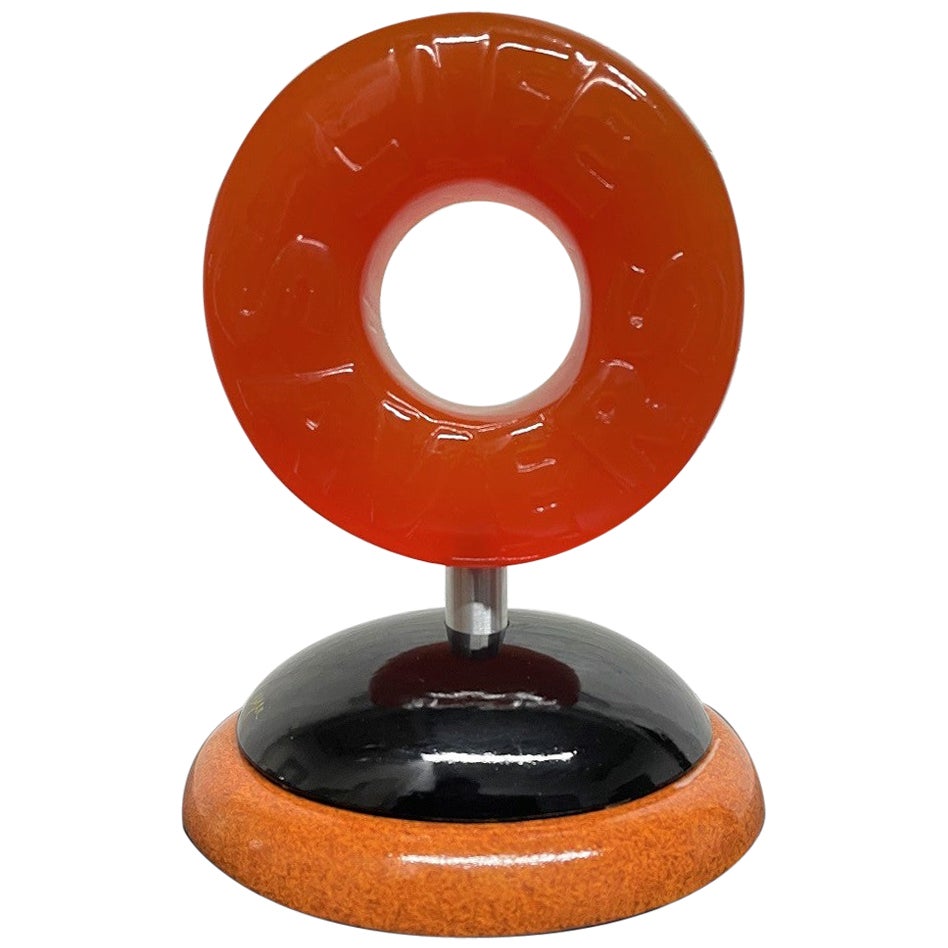
- Lifesaver Candy Sculpture by Daniel Meyer, SignedBy Daniel MeyerLocated in New York, NYSigned, Lifesaver Candy Sculpture by Daniel Meyer. The sculpture is wood, resin and acrylic. Lifesaver is orange.Category
21st Century and Contemporary Modern Figurative Sculptures
MaterialsResin, Acrylic, Wood
- One of Kind Sculpture by Marcel-André BouraineLocated in Bois-Colombes, FR1930s sculpture by famous French artist Marcel André Bouraine Documented.Category
Vintage 1930s French Busts
MaterialsTerracotta
Recently Viewed
View AllMore Ways To Browse
Palatial Furniture
Modernism Decorative Objects
Robert Holland
Midcentury Ship Sculpture
Josef Of Italy
Henri Ii Furniture
Early 20th Century German Ceramic
Mid Century Modern Still Life Sculpture
Wood Book Desk
Early European Figurative Sculpture
Brown Wassily
School Desk Wood
Book Sculpture Italian
Record Player Vintage Record Player
Record Player Vintage Vintage Record Players
Bust Of David
French Palatial
Palatial French