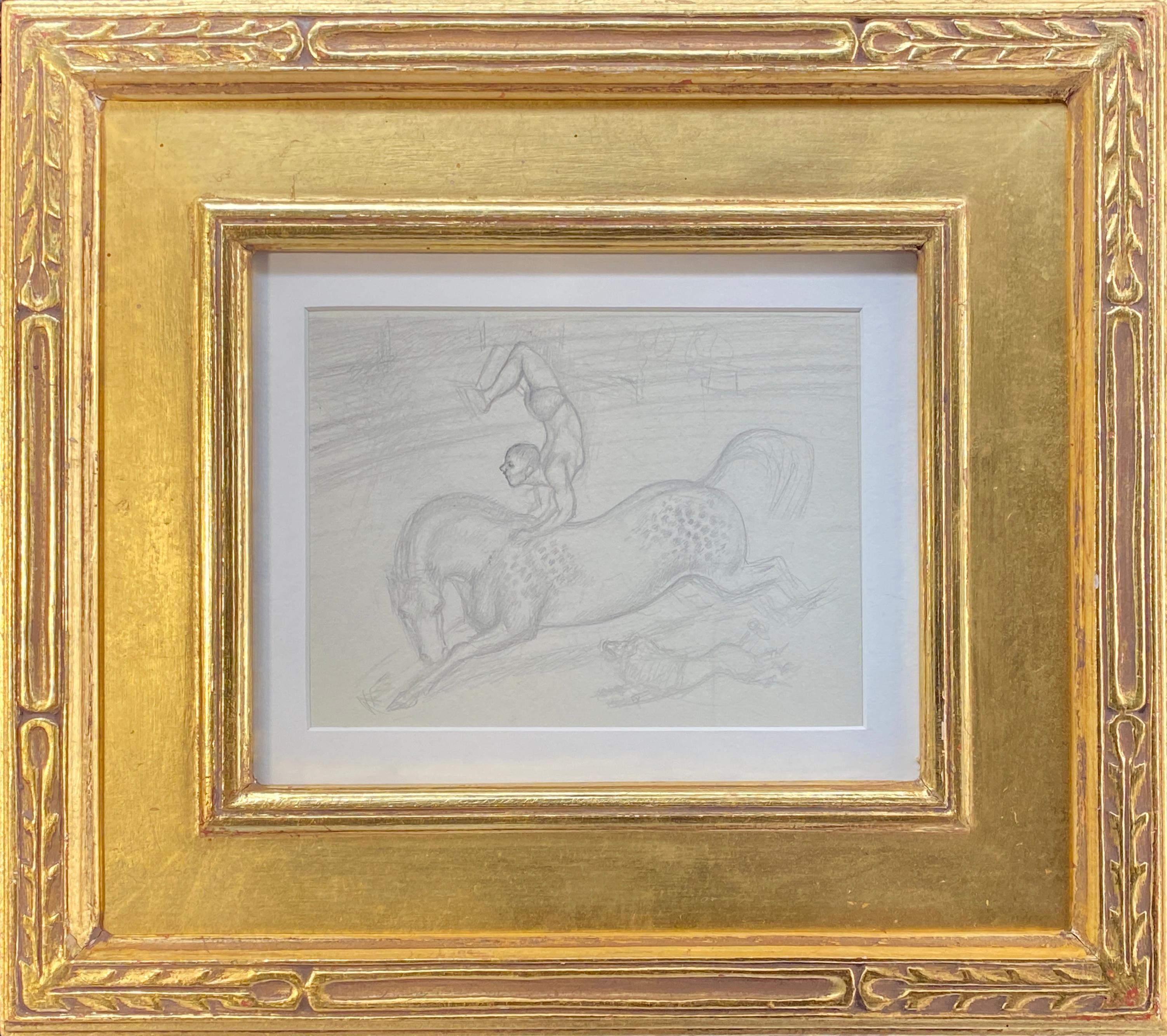
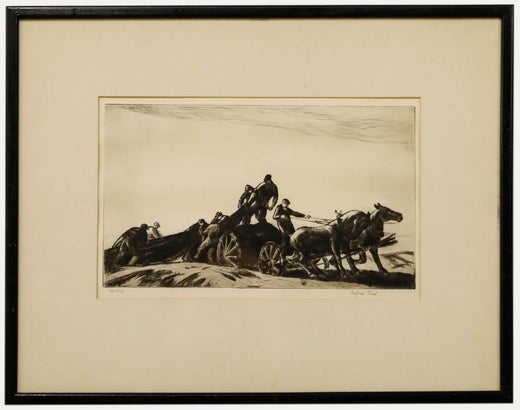
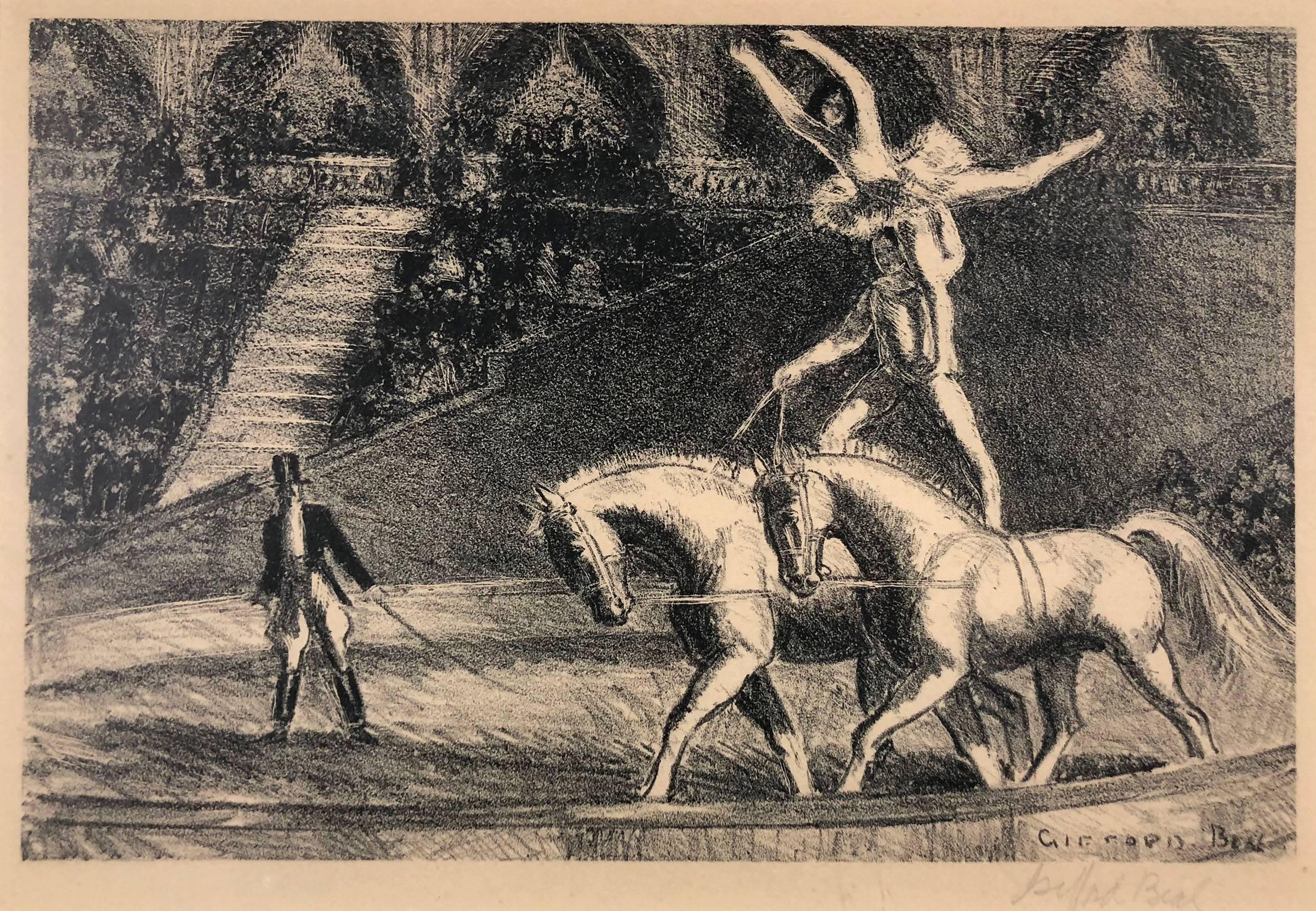Gifford BealBareback Act, Old Hippodrome
About the Item
- Creator:Gifford Beal (1879-1956, American)
- Dimensions:Height: 6.5 in (16.51 cm)Width: 9.5 in (24.13 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Missouri, MO
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU747310910962
Gifford Beal
Gifford Beal, painter, etcher, muralist and teacher, was born in New York City in 1879. The son of landscape painter William Reynolds Beal, Beal began studying at William Merritt Chase's Shinnecock School of Art (the first established school of plein air painting in America) at the age of 13, when he accompanied his older brother, Reynolds, to summer classes. Beal remained a pupil of Chase's for 10 years also studying with him in New York City at the artist's private studio in the Tenth Street Studio Building. Later at his father's behest, Beal attended Princeton University from 1896–1900 while continuing his lessons with Chase. Upon graduation from Princeton, Beal took classes at the Art Students' League, studying with impressionist landscape painter Henry Ward Ranger and Boston academic painter Frank Vincent DuMond. Beal ended up as President of the Art Students League for 14 years, "a distinction unsurpassed by any other artist." Beal’s student days were spent entirely in this country. Given the opportunity to visit Paris en route to England in 1908, Beal chose to avoid it, he stated, "I didn't trust myself with the delightful life in ParisIt all sounded so fascinating and easy and loose." His subjects were predominately American and it has been said stylistically "his art is completely American." Beal achieved early recognition in the New York Art World. Beal became an associate member of the National Academy of Design in 1908 and was elected to full status as an academician in 1914. Beal was known for garden parties, circuses, landscapes, streets, coasts, flowers and marines. This diversity in subject matter created "no typical or characteristic style to his work." Beal's style was highly influenced by Chase and Childe Hassam, a long time friend of the Beal family who used to travel about the countryside with Beal in a car sketching local sights. Both Hassam and Chase were famous for their impressionist views of New York City and Connecticut and Long Island coastlines. Beal's early work reflects his acquaintance with these painters and focused on the city's commercial and industrial growth. Beal's major influence, however, remained Chase, whose "greatness" Beal attributed to the "sheer fullness of his nature, his store of energy" and his dedication to the profession of painting. "When the story of American art is finally told," Beal predicted, "Chase's name will be high on the list of the great." Regarding his use of color, one art critic wrote: "On the whole, he is inclined toward color that is rich and strong. The garden scenes have masses of deep and gleaming foliage over the gay scenes below. The circus pictures are resplendent in hue. He takes the rich green that crowns the cliffs at Montauk and with it gives depth and richness to their tawny sides. The ocean in Sword Fisherman is an intense blue, neither light nor dark and full of almost imperceptible shadings." Beal found early success with his views of the Hudson Valley where his family had an estate called Willellen in Newburgh, overlooking the Hudson River. A gifted technician and draftsman, Beal did considerable mural painting including seven panels portraying the life of scientist John Henry; North Country and Tropical Country, Department of the Interior building, Washington, D.C and others. Renewing an early interest for the sea, a subject he had favored during his student years, Beal started to achieve recognition for his marine landscapes. In 1921, Beal began spending most of his summers on the Massachusetts coast, first at Provincetown and then at Rockport. Both Beal and his brother Reynolds had a strong attraction to the sea. In the 1940s, Beal, never one to rest on his laurels made a dramatic stylistic change, his painting technique became freer as he replaced naturalistic perspective with an intricately patterned and flattened picture plane. These more decorative works echoed ancient Persian paintings as well as the work of Maurice and Charles Prendergast whose art Beal greatly admired. In the end, Beal adopted a "less objective" style that was high key and "utilizing softer edges." This new work was said to be influenced by Raoul Dufy. However many influences one may choose to cite in Beal's work this is secondary to the fact that Beal throughout his artistic career derived a strong personal statement in his art that was "fundamentally sound and aesthetically pleasing." Beal was a member of the American Academy of Arts and Letters, the American Institute of Arts and Letters, the Architectural League of America and the National Society of Mural Painters. His work can be found in numerous museums and public collections across the country. Beal passed away on Feb. 5th, 1956 at the age of 75 in New York City.
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Shipping from: Missouri, MO
- Return Policy
More From This Seller
View All1950s American Realist Figurative Prints
Lithograph
1930s American Modern Figurative Prints
Woodcut
Early 20th Century American Modern Animal Drawings and Watercolors
Paper, Pencil, Color Pencil
Early 20th Century American Modern Landscape Paintings
Oil, Panel
1920s Realist Figurative Prints
Aquatint
1920s Realist Figurative Prints
Engraving, Aquatint
You May Also Like
1920s American Realist Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Paper, Graphite
Late 20th Century Modern Figurative Prints
Lithograph
1950s Prints and Multiples
Lithograph
1930s American Modern Figurative Prints
Etching
1910s Abstract Figurative Prints
Lithograph
Mid-20th Century Abstract Impressionist Figurative Paintings
Oil