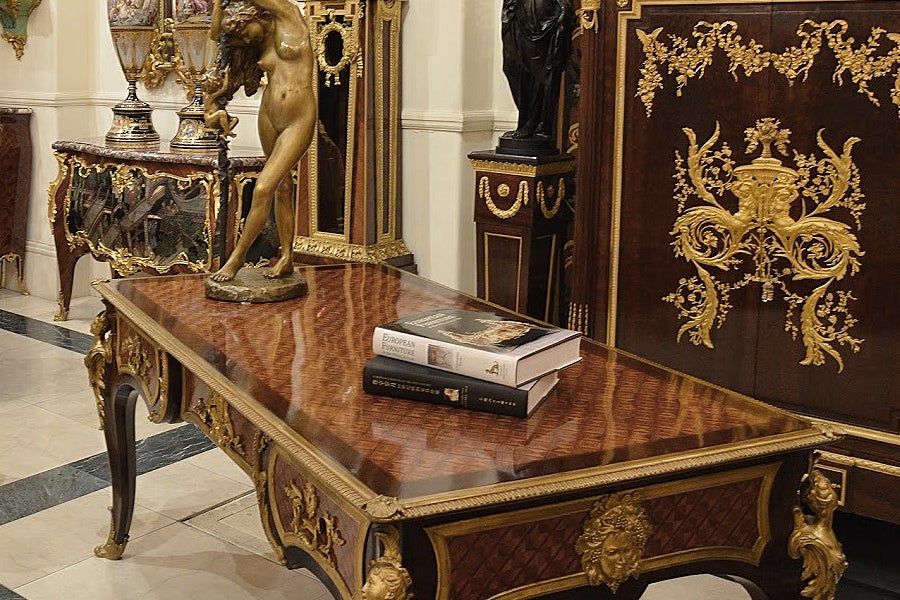
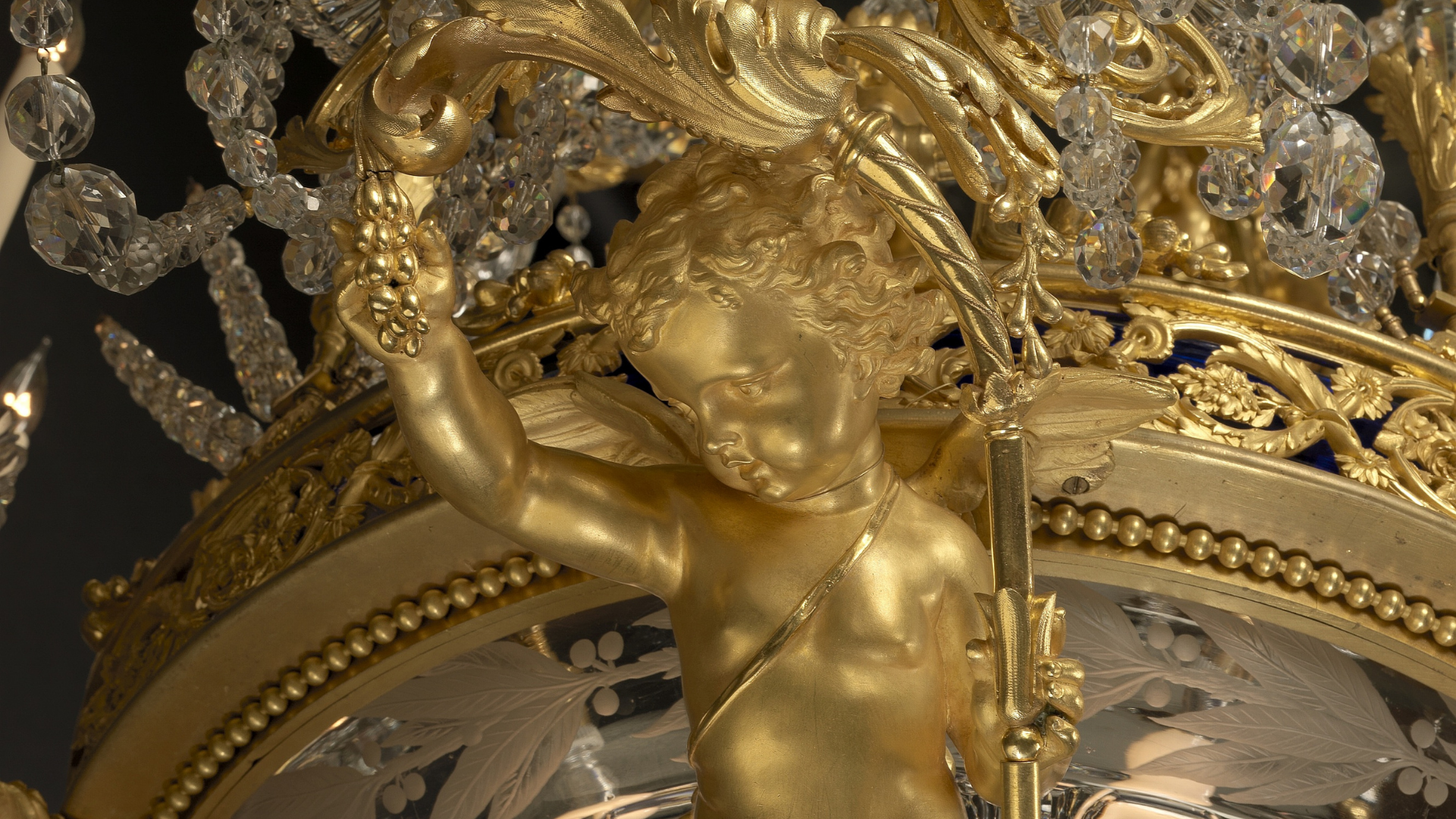
A Large and Important Louis Philippe Period Gilt-Bronze Three-Piece Clock Garniture.
Attributed to the Feuchère family. The clock movement by Hémon.
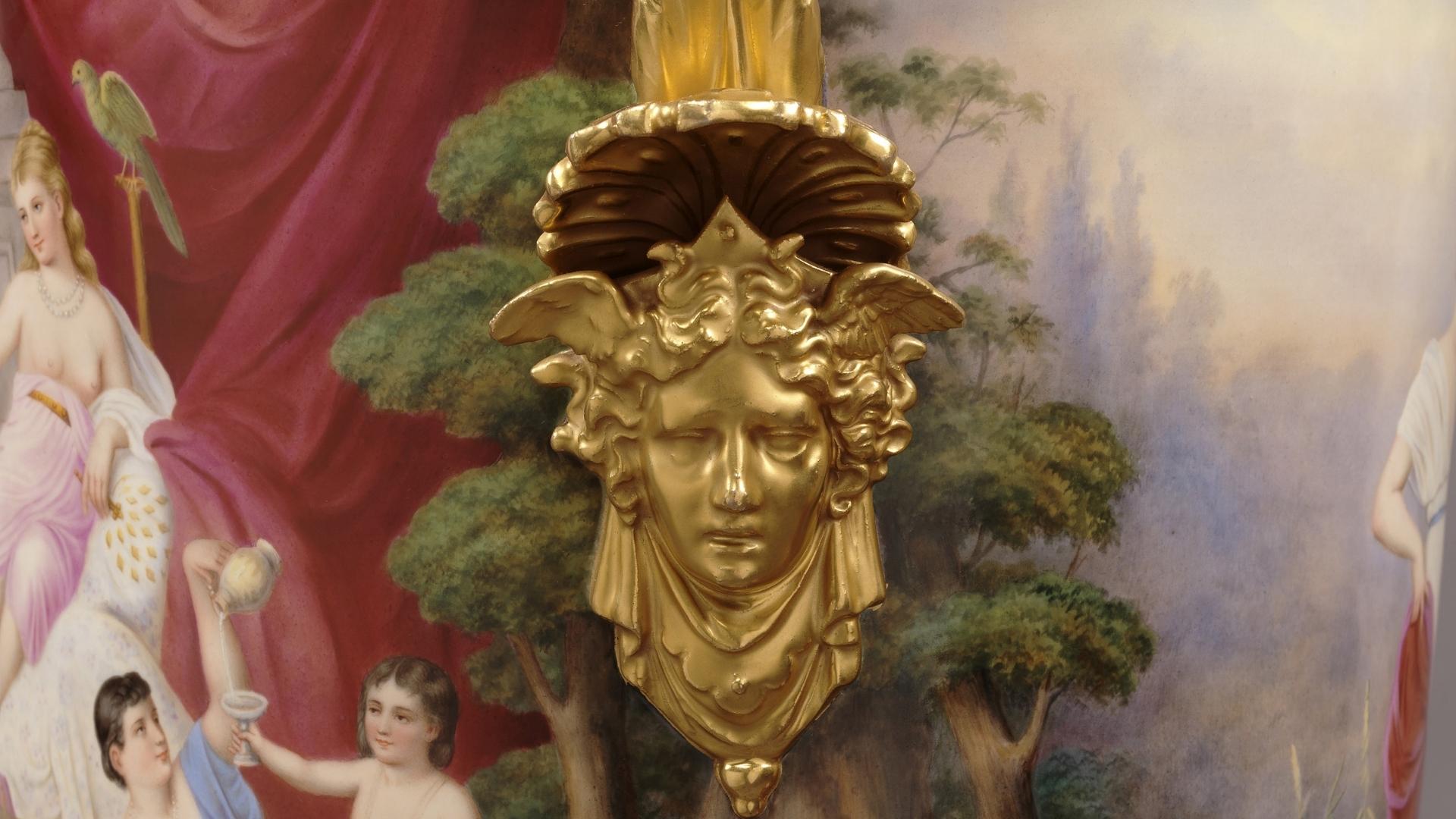
In the Renaissance revival style. Comprising a clock and a pair of nine-light candelabra. The clock case of architectural out-shape with cherubic term figures supporting a rectangular pediment centred by an urn. The sides of the clock tower cast in relief with strapwork and foliage. The dial inset with enamel Roman numeral chapters. The twin-barrel clock movement with tic-tac escapement, silk suspension and countwheel strike to bell. Pendulum and winding key.
The candelabra as twin-handled vases supporting tiered branches with candle nozzles. Modelled en suite with naturalistic scrolls and foliage. Surmounted by finials modelled as an eagle toying with a serpent. The scrolled handles flanked by cherubic figures and serpents. The bodies fronted by bacchic masks and supported on socles bearing angels.
France, Circa 1835.
The clock movement signed ‘HEMON A PARIS’. The clockmaker Claude Hémon was established at rue de St. Martin circa 1810-1820.
Dimensions, the clock:
Height : 106 cm 42 inches
Width : 58 cm 23 inches
Depth : 38 cm 15 inches
Weight : 72 kg
Dimensions, the candelabra:
Height : 104 cm 41 inches
Width : 36 cm 14 inches
Depth : 36 cm 14 inches
Weight : 28 kg (each)
This magnificent clock garniture of palatial size is designed in the Renaissance revival style and dates to the Louis Philippe period. Executed in sculptural gilt-bronze with leaves, scrolls, masks and exotic birds, the naturalistic ornament represents an elaborate system of allegories and mythological iconography which recall the influence of Italian Mannerist art in France.
The distinctive design reflects a new style which replaced the neoclassism of the French Empire period. With the fall of Napoleon Bonaparte, artists and designers sought a new decorative vocabulary with which to aggrandise the Bourbon restoration. With the French revolution and Louis XVI’s execution still within living memory, it seemed too soon for a revival of the style of the Grand Siècle. Instead they looked further back to the time of François I, whose patronage of Italian artists had brought the Renaissance to France. The idea of a renaissance revival appealed to the new Bourbon monarchs and their patronage ignited great creativity in the arts.
The reigns of Louis XVIII and Charles X, who were brothers of the late King, Louis XVI, and later of Louis Philippe I, nicknamed the Citizen King, coincided with the enlightenment and the dawn of the industrial age. Great technical progress was made in metallurgy and casting which raised the art of bronze making to new heights in the hands of great masters such as Pierre-Philippe Thomire (1751-1843) and Pierre- Jean-François Denière (1774-1866).
The renaissance provided a rich and varied source book in architecture, furniture and other decorative arts for designers such as Claude Aimé Chenavard (1798-1838) whose Album de l’ornemaniste (1835) became a reference work. Léon Feuchère (1804-1857) also produced drawings of interiors, silver, bronzes and furniture and was a scion of the prominent family of bronze castors established by his grandfather Pierre-François Feuchère (1737-1823) who had worked as a gilder for the bronze caster Pierre Gouthière before setting up a bronze foundry that would become one of the largest in Paris under the management of his son Lucien-François (d. 1841) and grand-son Armand (1797-1866). A number of drawings by Léon Feuchère have recently been discovered by the Rijksmuseum and probably belonged to the collection of Louis-Philippe-Albert, duc d’Orléans, comte de Paris (1838-1894). Louis-Philippe-Albert was the grandson of the French king, Louis-Philippe I (1773-1850), who granted him the title of comte de Paris, and the son of Ferdinand-Philippe, duc d’Orléans (1810-1842). Ferdinand-Philippe was an important collector and sponsored many young artists to create metalwork objets d’art, notably a celebrated surtout de table made by Claude-Aimé Chenavard and Jean-Jacques Feuchère (1807-1852), a cousin of Armand and Léon. Principally remembered as a sculptor, Jean-Jacques Feuchère trained in the family foundry and designed small objects, cigar
boxes...