Items Similar to Lithograph Screenprint Male Heroic Figures
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 8
Ernst NeizvestnyLithograph Screenprint Male Heroic Figures
$1,100
£856.40
€973.87
CA$1,581.49
A$1,736.78
CHF 906.98
MX$20,729.19
NOK 11,490.55
SEK 10,709.65
DKK 7,273.53
About the Item
Ernst Iosifovich Neizvestny (Russian: Эрнст Ио́сифович Неизве́стный) (born 1925) is a Russian sculptor. He lives and works in New York City.
Non Conformist Post Soviet Avant Garde
Neizvestny was born 9 April 1925 in Sverdlovsk (now Yekaterinburg). In 1942, at the age of 17, he joined the Red Army as a volunteer. At the close of World War II, he was heavily wounded and sustained a clinical death. Although he was awarded the Order of the Red Star and his mother received an official notification that her son had died, Neizvestny managed to survive.
In 1947, Neizvestny was enrolled at the Art Academy of Latvia in Riga. He continued his education at the Surikov Moscow Art Institute and the Philosophy Department of the Moscow State University. His sculptures, often based on the forms of the human body, are noted for their expressionism and powerful plasticity. Although his preferred material is bronze, his larger, monumental installations are often executed in concrete. Most of his works are arranged in extensive cycles, the best known of which is The Tree of Life, a theme he has developed since 1956.
Art career
Although Nikita Khrushchev famously derided Neizvestny's works as "degenerate" art at the Moscow Manege exhibition of 1962 ("Why do you disfigure the faces of Soviet people?"), the sculptor was later approached by Khruschev's family to design a tomb for the former Soviet leader at the Novodevichy Cemetery. Other well-known works he created during the Soviet period are Prometheus in Artek (1966).
During the 1980s, Neizvestny was a visiting lecturer at the University of Oregon and at UC Berkeley. He also worked with Magna Gallery in San Francisco, and had a number of shows which were well-attended in the mid 1980s. This gallery also asked him to create his "Man through the Wall" series to celebrate the end of Communism at the end of the 1980s. Magna Gallery closed at the end of 1992
In 1996, Neizvestny completed his Mask of Sorrow, a 15-meter tall monument to the victims of Soviet purges, situated in Magadan. The same year, he was awarded the State Prize of the Russian Federation. Although he still lives in New York City and works at Columbia University, Neizvestny frequently visits Moscow and celebrated his 80th birthday there. A museum dedicated to his sculptures was established in Uttersberg, Sweden. Some of his crucifixion statues were acquired by John Paul II for the Vatican Museums. In 2004 Neizvestny became an honorary member of the Russian Academy of Arts.
Museum and Public Collections
Museum of Modern Art, New York
The Jewish Museum, New York
Kennedy Center for Performing Arts, Washington, D.C.
Duke University Museum of Art, Durham, North Carolina
Museum of Art, University of California, Berkeley, California
Jane Voohrees Zimmerli Museum, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey
United Nations, New York
The State Russian Museum, St. Petersburg
The State Tretyakov Gallery, Moscow
The State Pushkin Museum, Moscow
Dostoevsky Museum, Moscow
ART4.RU Contemporary Art Museum, Moscow
Museum of Fine Arts, Kursk
Museum of Fine Arts,Vologda
Museum of Fine Arts,Volgograd
Museum of Modern Ecclesiastical Art, Vatican, Rome
Moderna Museet, Stockholm, Sweden
Tree of Life Museum, Uttersberg, Sweden
Sven-Olov Anderson’s Torg, Koping, Sweden
Thielska Galleriet, Stockholm, Sweden
Oslo Municipal Art Collection, Norway
Municipality of Oslo Art Collection, Norway
Israel Museum, Jerusalem
Tel Aviv Museum of Modern Art, Tel Aviv
Lvov Gallery, Lvov, Ukraine
Museum of Modern Art, Belgrade, Serbia
Yerevan Gallery, Yerevan, Armenia
Monuments and Public Commissions
Lotus Blossom, Aswan Dam, Egypt
Tree of Life II, United Nations, New York
Bust of Dmitri Shostakovich for the Kennedy Center, Washington, D.C.
Tree of Life, Moscow
Prometheus, 15m stainless steel sculpture for Electro-Expo 72 exhibition, Moscow
Wings for the Institute of Light Alloys, Moscow
Rebirth (Archangel Michael), Moscow
Nikita Khrushchev’s tombstone at Novodevichiy Cemetery, Moscow
Mask of Mourning, Memorial to the Victims of Stalinism, Magadan, Russia
Exodus and Return, Monument to The Kalmykian Deportation, Elista, Kalmykia, Russia
970-meter decorative relief for Institute of Electronics and Technology, Zelenograd, Russia
Monument to the Coal Miners, Kemerovo, Russia
Monument to Sergei Diaghilev, Perm, Russia
Monument to World’s Children, 150-meter decorative relief for Artek Pioneer Camp in the Crimea, Ukraine
Golden Child, Odessa, Ukraine
Great Centaur, United Nations, Geneva
Centaur and Stone Tears, Belgrade, Serbia
Mask of Grief, Tombstone for Centaur, Milan, Italy
Fragment of Centaur, Vasteras, Sweden
- Creator:Ernst Neizvestny (1926 - 2016, Russian)
- Dimensions:Height: 24.5 in (62.23 cm)Width: 17.5 in (44.45 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Surfside, FL
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU38217267322
About the Seller
4.9
Platinum Seller
Premium sellers with a 4.7+ rating and 24-hour response times
Established in 1995
1stDibs seller since 2014
1,837 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 1 hour
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Shipping from: Surfside, FL
- Return Policy
More From This Seller
View AllThe Rabbi 1977 Soviet Non Conformist Avant Garde Print
By Alek Rapoport
Located in Surfside, FL
Dimensions w/Frame: 25 3/4" x 20 3/4"
Alek Rapoport (November 24, 1933, Kharkiv, Ukraine SSR – February 4, 1997, San Francisco) was a Russian Nonconformist artist, art theorist and teacher.
Alek Rapoport spent his childhood in Kiev (Ukraine SSR). During Stalin's "purges" both his parents were arrested. His father was shot and his mother spent ten years in a Siberian labor camp. Rapoport lived with his aunt. At the beginning of World War II, he was evacuated to the city of Ufa (the Bashkir Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic). A time of extreme loneliness, cold, hunger and deprivation, this period also marked the beginning of Rapoport's drawing studies.
After the war, Rapoport lived in Chernovtsy (Western Ukraine), a city with a certain European flair. At the local House of Folk Arts, he found his first art teacher, E.Sagaidachny (1886–1961), a former member of the nonconformist artist groups Union of the Youth (Soyuz Molodyozhi) and Donkey's Tail, popular during the 1910s–1920s. His other art teacher was I. Beklemisheva (1903–1988). Impressed by Rapoport's talent, she later (1950) organized his move to Leningrad, where he entered the famous V.Serov School of Art (the former School of the Imperial Society for the Promotion of Arts, OPKh, later the Tavricheskaya Art School).
His association with this school lasted eight years, first as a student, and then, from 1965 to 1968, as a teacher. With "Socialist realism" the only official style during this time, most of the art school's faculty had to conceal any prior involvement in non-conformist art movements. Ya.K.Shablovsky, V.M.Sudakov, A.A.Gromov introduced their students to Constructivism only through clandestine means.
(1959–1963) Rapoport studied stage design at the Leningrad Institute of Theater, Music and Cinema under the supervision of the famous artist and stage director N.P.Akimov. Akimov taught a unique course based on theories of Russian Suprematism and Constructivism, while encouraging his graduate students to apply their knowledge to every field of art design. Despite differences in personal artistic taste with Akimov, who was drawn to Vermeer and Dalí, Rapoport was influenced by Akimov's personality and liberalism, as well as the logical style of his art.
In 1963, Rapoport graduated from the institute. His highly acclaimed MFA work involved the stage and costume design for I.Babel's play Sunset. In preparation, he traveled to the southwest regions of the Soviet Union, where he accumulated many objects of Judaic iconography from former ghettos, disappearing synagogues and old cemeteries. He wandered Odessa in search of Babel's characters and the atmosphere of his books.
He organized a new liberal course in technical aesthetics, introducing his students to Lotman's theory of semiotics, the Modulor of Le Corbusier, the Bauhaus school, Russian Constructivism, Russian icons and contemporary Western art. As a result of his "radicalism," Rapoport was fired for "ideological conspiracy."
He sought to cultivate himself as Jewish artist. This became particularly noticeable after the Six-Day War, when the Israeli victory led intellectuals, including the Jewish intelligentsia, to feel a heightened interest in Jewish culture and its Biblical roots. Rapoport's works of this period include Three Figures, a series of images of Talmudic Scholars, and works dealing with anti-Semitism. In the 1970s Rapoport joined the non-conformist movement, which opposed the dogmas of "Socialist realism" in art, along with Soviet censorship. The movement sought to preserve the traditions of Russian iconography and the Constructivist/Suprematist style of the 1910s. Despite the authorities' persecutions of nonconformist artists (including arrests, forced evictions, terminations of employment, and various forms of routine hassling), they united in a group, "TEV – Fellowship of Experimental Exhibitions." TEV's exhibitions proved tremendously successful.
In the same period, Rapoport became one of the initiators of another anti-establishment group, ALEF (Union of Leningrad's Jewish Artists). In the United States this group was known as "Twelve from the Soviet Underground." Rapoport's involvement with this group increased tension with the authorities and attracted KGB scrutiny, including "friendly conversations," surveillance, detentions and house arrests. It became increasingly dangerous for him to live and work in the USSR. In October 1976, Rapoport with his wife and son were forced to leave Russia.
In Italy, Rapoport exhibited at the Venice Biennale, "La Nuova Arte Sovietica-Una prospettiva non-ufficiale" (1977), participated in television programs about nonconformist art in the Soviet Union, and created lithographic works continuing his theme of Jewish characters from Babel's play Sunset.
In 1977, Rapoport's family was granted U.S. immigration status and settled in San Francisco. a significant event in Rapoport's life occurred in his meeting with San Francisco gallery owner Michael Dunev, who became his friend and representative, organizing all his exhibitions until the artist's death.
Toward the end of the 1980s and beginning of the 1990s, Rapoport completed his most ambitious works on the theme of the Old Testament prophets: Samson Destroying the House of the Philistines (1989), Lamentation and Mourning and Woe (1990), the four paintings Angel and Prophets (1990–1991) and Three Deeds of Moses (1992).
In 1992, the artist's friends in St. Petersburg organized the first exhibition of his works there since his departure into exile, with works patiently gathered from collectors and art museums. This exhibition, held in the City Museum of St. Petersburg and accompanied by headlines such as "A St. Petersburg artist returns to his town," was followed by much larger ones in 1993 (St. Petersburg and Moscow), organized in collaboration with Michael Dunev Gallery under the name California Branches – Russian Roots.
He Exhibited in "Soviet Artists, Jewish Themes...
Category
1970s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
The Talmudists Post Soviet Non Conformist Avant Garde Judaica Lithograph
By Alek Rapoport
Located in Surfside, FL
Dimensions w/Frame: 18.5 X 14.5
Alek Rapoport (November 24, 1933, Kharkiv, Ukraine SSR – February 4, 1997, San Francisco) was a Russian Nonconformist artist, art theorist and teacher.
Alek Rapoport spent his childhood in Kiev (Ukraine SSR). During Stalin's "purges" both his parents were arrested. His father was shot and his mother spent ten years in a Siberian labor camp. Rapoport lived with his aunt. At the beginning of World War II, he was evacuated to the city of Ufa (the Bashkir Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic). A time of extreme loneliness, cold, hunger and deprivation, this period also marked the beginning of Rapoport's drawing studies.
After the war, Rapoport lived in Chernovtsy (Western Ukraine), a city with a certain European flair. At the local House of Folk Arts, he found his first art teacher, E.Sagaidachny (1886–1961), a former member of the nonconformist artist groups Union of the Youth (Soyuz Molodyozhi) and Donkey's Tail, popular during the 1910s–1920s. His other art teacher was I. Beklemisheva (1903–1988). Impressed by Rapoport's talent, she later (1950) organized his move to Leningrad, where he entered the famous V.Serov School of Art (the former School of the Imperial Society for the Promotion of Arts, OPKh, later the Tavricheskaya Art School).
His association with this school lasted eight years, first as a student, and then, from 1965 to 1968, as a teacher. With "Socialist realism" the only official style during this time, most of the art school's faculty had to conceal any prior involvement in non-conformist art movements. Ya.K.Shablovsky, V.M.Sudakov, A.A.Gromov introduced their students to Constructivism only through clandestine means.
(1959–1963) Rapoport studied stage design at the Leningrad Institute of Theater, Music and Cinema under the supervision of the famous artist and stage director N.P.Akimov. Akimov taught a unique course based on theories of Russian Suprematism and Constructivism, while encouraging his graduate students to apply their knowledge to every field of art design. Despite differences in personal artistic taste with Akimov, who was drawn to Vermeer and Dalí, Rapoport was influenced by Akimov's personality and liberalism, as well as the logical style of his art.
In 1963, Rapoport graduated from the institute. His highly acclaimed MFA work involved the stage and costume design for I.Babel's play Sunset. In preparation, he traveled to the southwest regions of the Soviet Union, where he accumulated many objects of Judaic iconography from former ghettos, disappearing synagogues and old cemeteries. He wandered Odessa in search of Babel's characters and the atmosphere of his books.
He organized a new liberal course in technical aesthetics, introducing his students to Lotman's theory of semiotics, the Modulor of Le Corbusier, the Bauhaus school, Russian Constructivism, Russian icons and contemporary Western art. As a result of his "radicalism," Rapoport was fired for "ideological conspiracy."
He sought to cultivate himself as Jewish artist. This became particularly noticeable after the Six-Day War, when the Israeli victory led intellectuals, including the Jewish intelligentsia, to feel a heightened interest in Jewish culture and its Biblical roots. Rapoport's works of this period include Three Figures, a series of images of Talmudic Scholars, and works dealing with anti-Semitism. In the 1970s Rapoport joined the non-conformist movement, which opposed the dogmas of "Socialist realism" in art, along with Soviet censorship. The movement sought to preserve the traditions of Russian iconography...
Category
1970s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Cabaret Dancer (ala Toulouse Lautrec)
By Marcel Vertès
Located in Surfside, FL
This is an original hand signed (I believe it is also hand colored but i am not positive) Artists Proof Lithograph of a Circus scene. This depicts a Cabaret Dancer.
This came from a...
Category
1940s Art Deco Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
1970s Surrealist Pop Art Nude Angel Lithograph Print Psychedelic Color
Located in Surfside, FL
Hand Signed verso D. Herbert and numbered 1 of 20. (possibly Don Herbert)
Category
20th Century Pop Art Abstract Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Surrealist Dream Lithograph Belgian Master Magritte Pencil Signed by Mourlot
By (after) René Magritte
Located in Surfside, FL
Artist: Rene Magritte (after), Belgian (1898 - 1967)
Title: (from les Enfants Trouvés) Les Claires-Voies d'un Jeune Regard Embaument La Fête d'un Vieil Arbre
Year of original paintin...
Category
1960s Surrealist Landscape Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Rare Palestine Antique Hebrew Judaica Yahrzeit Synagogue Sign Memorial Plaque
Located in Surfside, FL
Circa 1890-1920. This Neoclassical, Judaic, Egyptian revival, Orientalist Mizrach sign, was produced in British Mandate Palestine by the chromolithograph process at the beginning of the 20th century. It pictures vignettes of holy places. with a hand written memorial. It was for the Tzedakah charity fund for the century-old institutions in Jerusalem: The great "Torah Center Etz Chaim"; a Free Kitchen for poor children and orphans; the famous Bikur Cholim Hospital with its dispensaries and clinics and the only Home for Incurable Invalids in Eretz Israel. They also worked with Arthur Szyk and Alfred Salzmann.. The A.L. Monsohn Lithographic Press (Monzon Press, Monson Press, דפוס אבן א"ל מאנזאהן, דפוס מונזון) was established in Jerusalem in 1892 by Abraham-Leib (or Avrom-Leyb) Monsohn II (Jerusalem, c.1871-1930) and his brother Moshe-Mordechai (Meyshe-Mordkhe). Sponsored by members of the Hamburger family, the brothers had been sent to Frankfurt, Germany in 1890 to study lithography. Upon returning to Jerusalem in 1892 with a hand press, they established the A.L. Monsohn Lithographic Press in the Old City of Jerusalem. According to the Information Center for Israeli Art A.L. Monsohn "created complex decorations for documents and oriental calendars that combined the tradition of Jewish art with modern printing techniques such as photographic lithography, raised printing and gilding."
The founders of the Monsohn press produced Jewish-themed color postcards, greeting cards, Jewish National Fund stamps, and maps documenting the evolution of the Jewish settlement in Eretz Israel in the nineteenth-twentieth centuries; religious material such as decorative plaques for synagogues, portraits of Old Yishuv rabbis such as Shmuel Salant, Mizrah posters indicating the direction of prayer for synagogues, memorial posters, and posters for Sukkot booths; color frontispieces for books such as Pentateuch volumes and the early song collections of Abraham Zvi Idelsohn (e.g., Shire Zion, Jerusalem 1908); artistic wedding invitations; and labels, packaging and advertisements for the pioneering entrepreneurs of Eretz Israel. The texts appearing in the Monsohn products were in several languages: Hebrew, Arabic, Yiddish, English, German (e.g., a c1920 trilingual Hebrew-English-Arabic "Malaria Danger" broadside warning the public of mosquitoes spreading malaria). Many of the brilliantly colored postcards and maps can be seen online as can the artistic invitations to his children's weddings which Monsohn published in the Jerusalem Hebrew press.
For years, the Monsohn (later, Monson/Monzon) Press was considered the best and most innovative in the country—pioneering in such techniques as gold-embossing and offset printing, among others. Early items for tourists included collections of Flowers of the Holy Land (c. 1910–1918)—pressed local flowers accompanied by scenes from the Eretz Israel countryside and relevant verses from the Bible, edited by Jsac Chagise (or Itzhak Haggis), an immigrant from Vitebsk, and bound in carved olive wood boards. Shortly after World War I Monsohn (now spelled מונזון) used zincography to produce the prints included in the Hebrew Gannenu educational booklets for young children illustrated by Ze'ev Raban of the Bezalel Academy of Art and Design and printed in Jerusalem by Hayim Refael Hakohen (vol. 1, 1919; vols. 2–3, 1920). In 1934 Monsohn moved into the new, western part of Jerusalem, in a shop with four presses and 30 workers, including Abraham-Leib's sons, David, Yosef, Moshe and Shimon, and his daughter Raytse's husband, Abraham Barmacz. The concern did business with all sectors of the city's population, including Arabs, for whom they printed in Arabic. Among their clients were members of the Ginio, Havilio, and Elite families, and Shemen, Dubek, and other renowned national brands, manufacturing products such as wine, candies, oil, and cigarettes. They also printed movie and travel posters, and government posters, postcards and documents, hotel luggage labels...
Category
Early 20th Century Aesthetic Movement More Art
Materials
Lithograph
You May Also Like
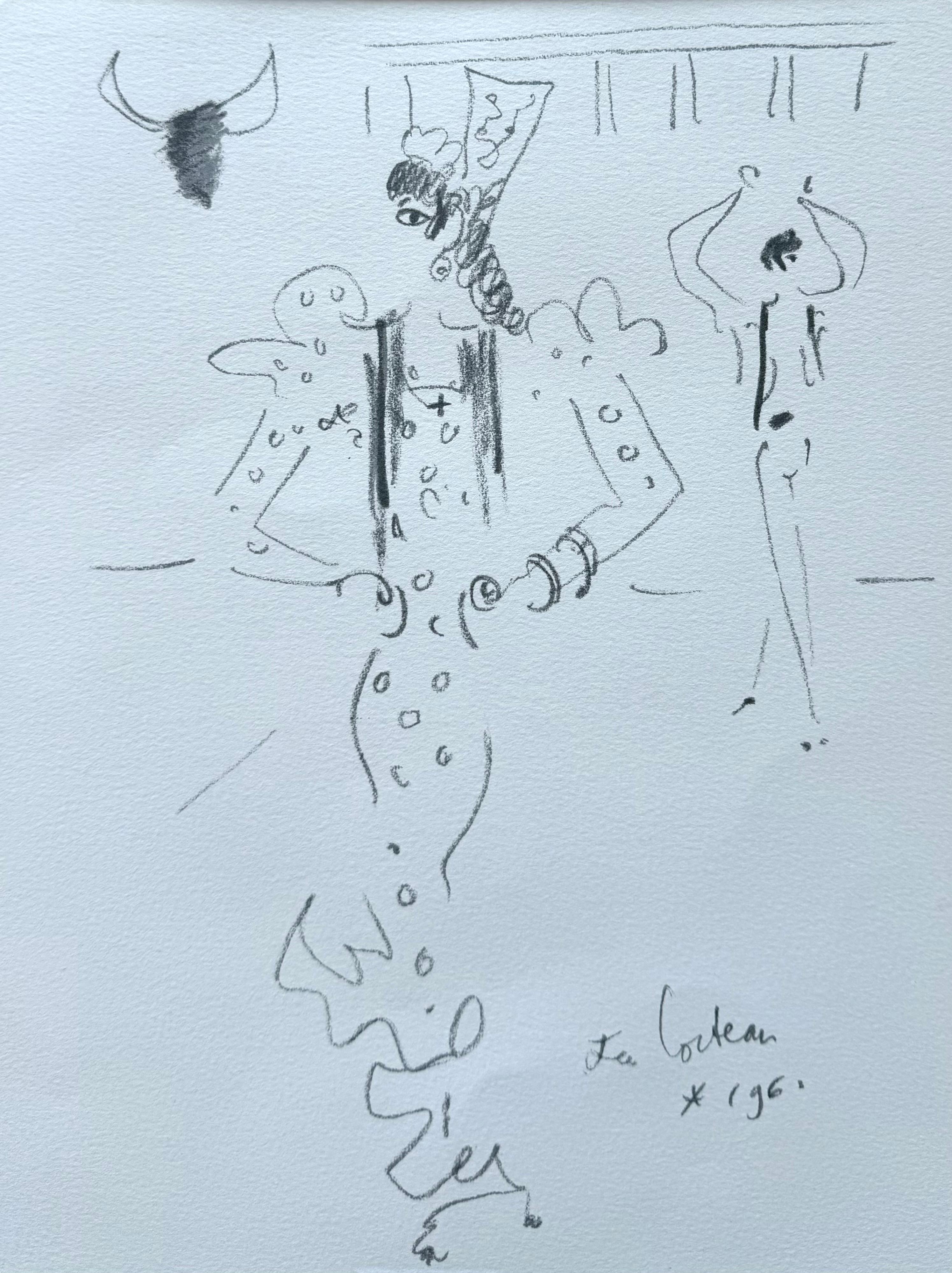
“ Spain, Captivating Flamenco”
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Southampton, NY
Jean COCTEAU (1889-1963)
Spain, Captivating Flamenco, 1971
Original Lithograph
Signed in the plate
Limited edition of 200 unnumbered copies
INFORMATION: Original lithograph publis...
Category
1960s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Archival Paper, Lithograph
Wifredo Lam - Knight - Original Lithograph
By Wifredo Lam
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Wifredo Lam - Knight - Original Lithograph
Published in the deluxe art review, XXe Siecle
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
Publisher: G. di San Lazzaro.
Unsigned and unumbered as issued
Category
1960s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Wifredo Lam - Original Handsigned Lithograph -El ultimo viaje del buque fantasma
By Wifredo Lam
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original lithograph, hand-signed and hand-numbered in pencil by the artist.
Edition: 56/99
Excellent Conditions
Dimensions: 76 x 56 cm
Reference : Catalogue raisonné Tonneau-Ryckely...
Category
1970s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
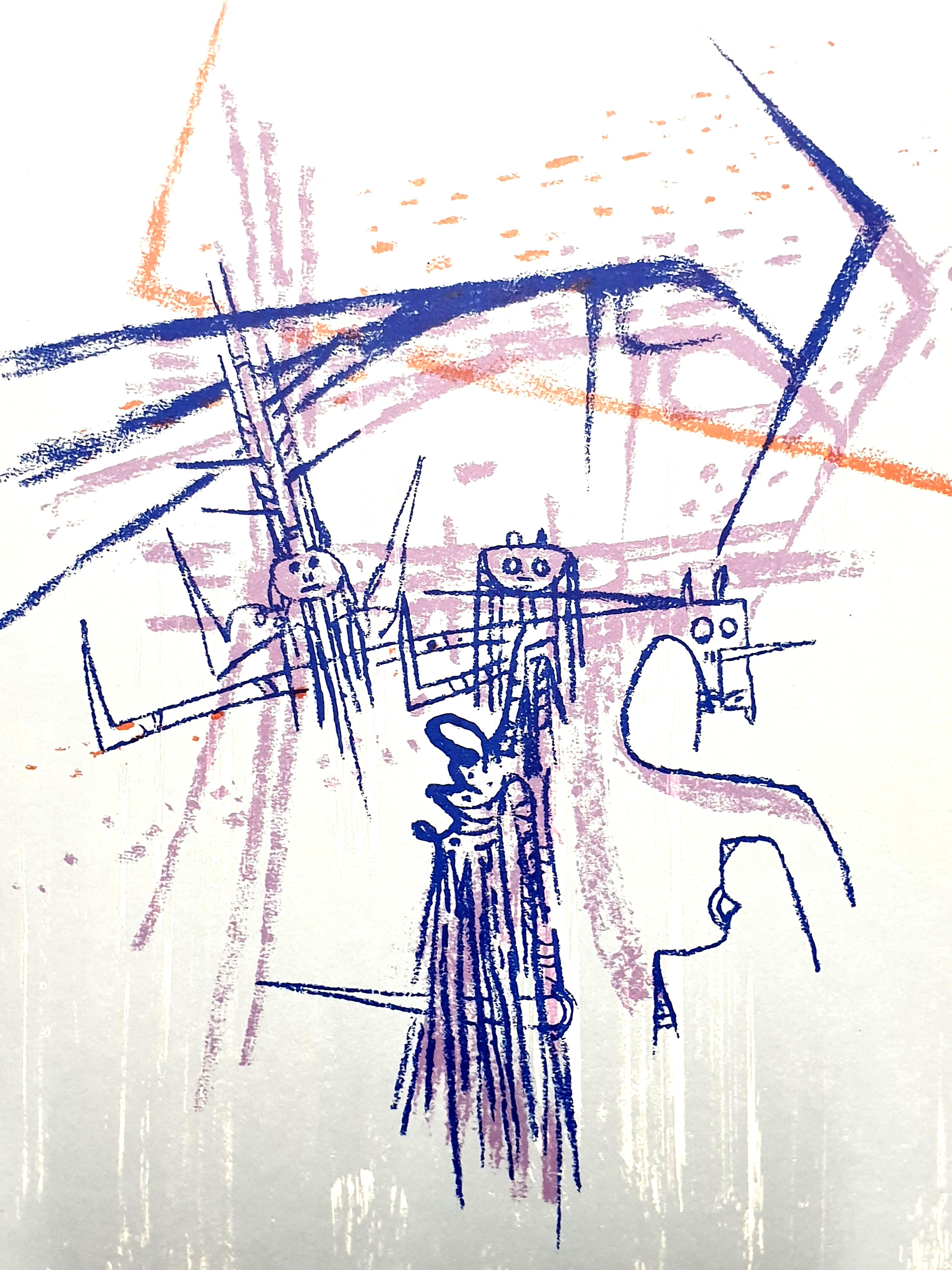
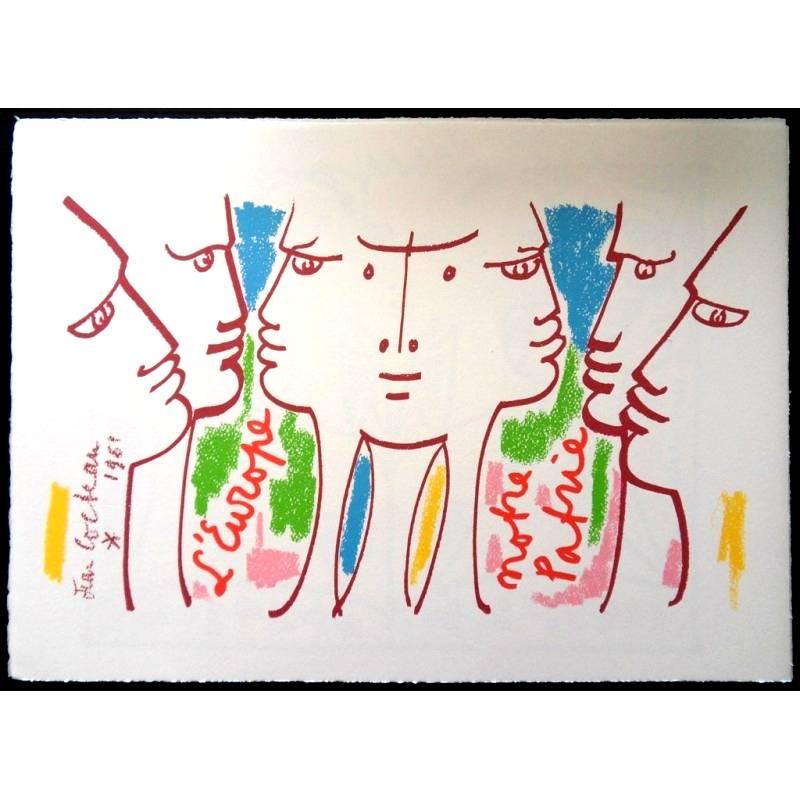
Jean Cocteau - Europe Our Homeland - Original Lithograph
By Jean Cocteau
Located in Collonge Bellerive, Geneve, CH
Original Lithograph by Jean Cocteau
Title: Europe Our Homeland
Signed in the plate
Dimensions: 33 x 46 cm
Edition: 200
Luxury print edition from the portfolio of Sciaky
1961
Jean Co...
Category
1960s Post-Modern More Prints
Materials
Lithograph
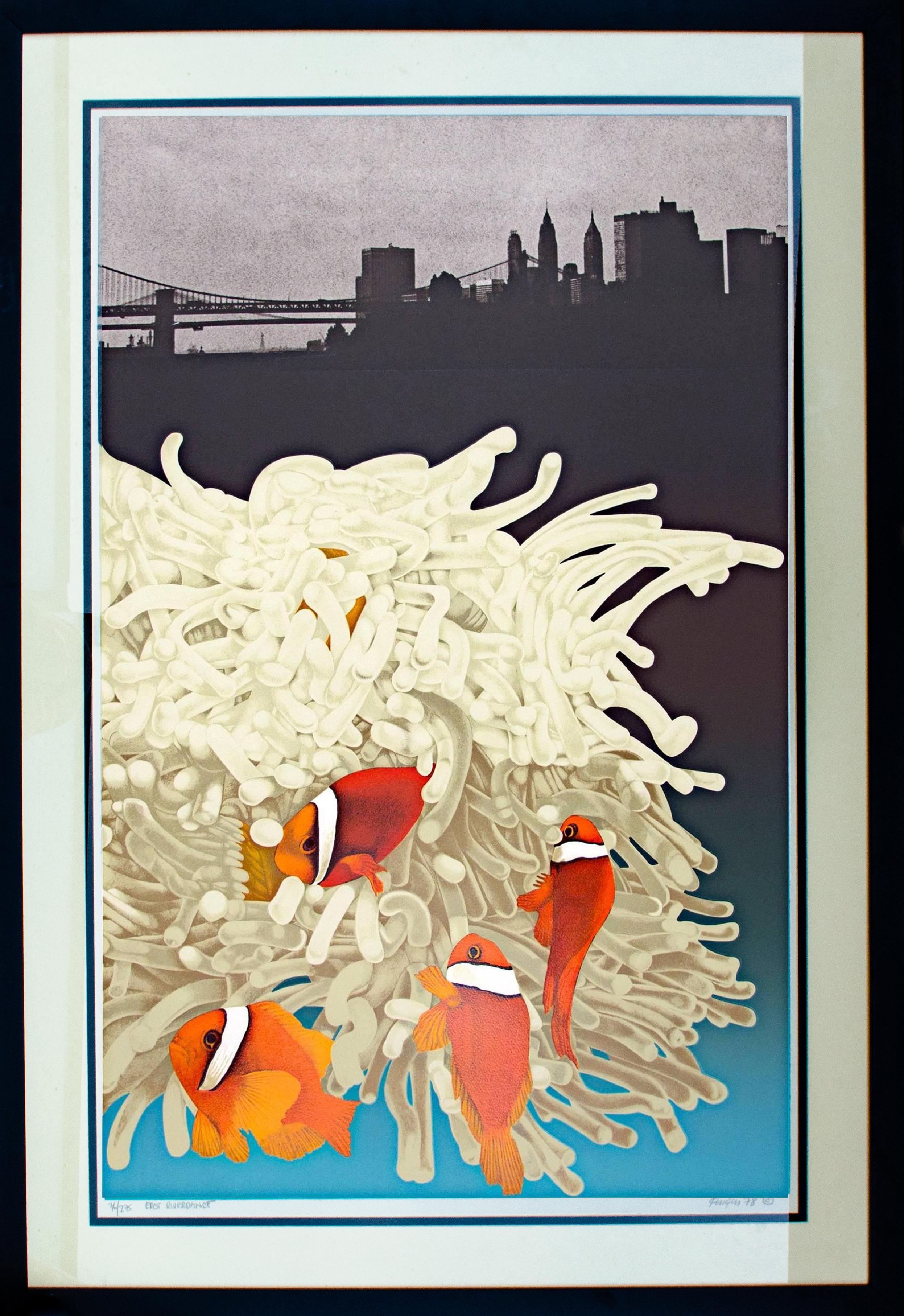
1978 Michael Knigin Manhattan Skyline Print
By Michael Knigin
Located in New York, NY
Michael Knigin (American, b. 1942)
East Riverdance, 1978
Lithograph (?)
Sight: 33 x 21 1/2 in. (image)
Framed: 41 1/8 x 29 x 3/4 in.
Signed, titled, dated, and numbered bottom
Editio...
Category
1970s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
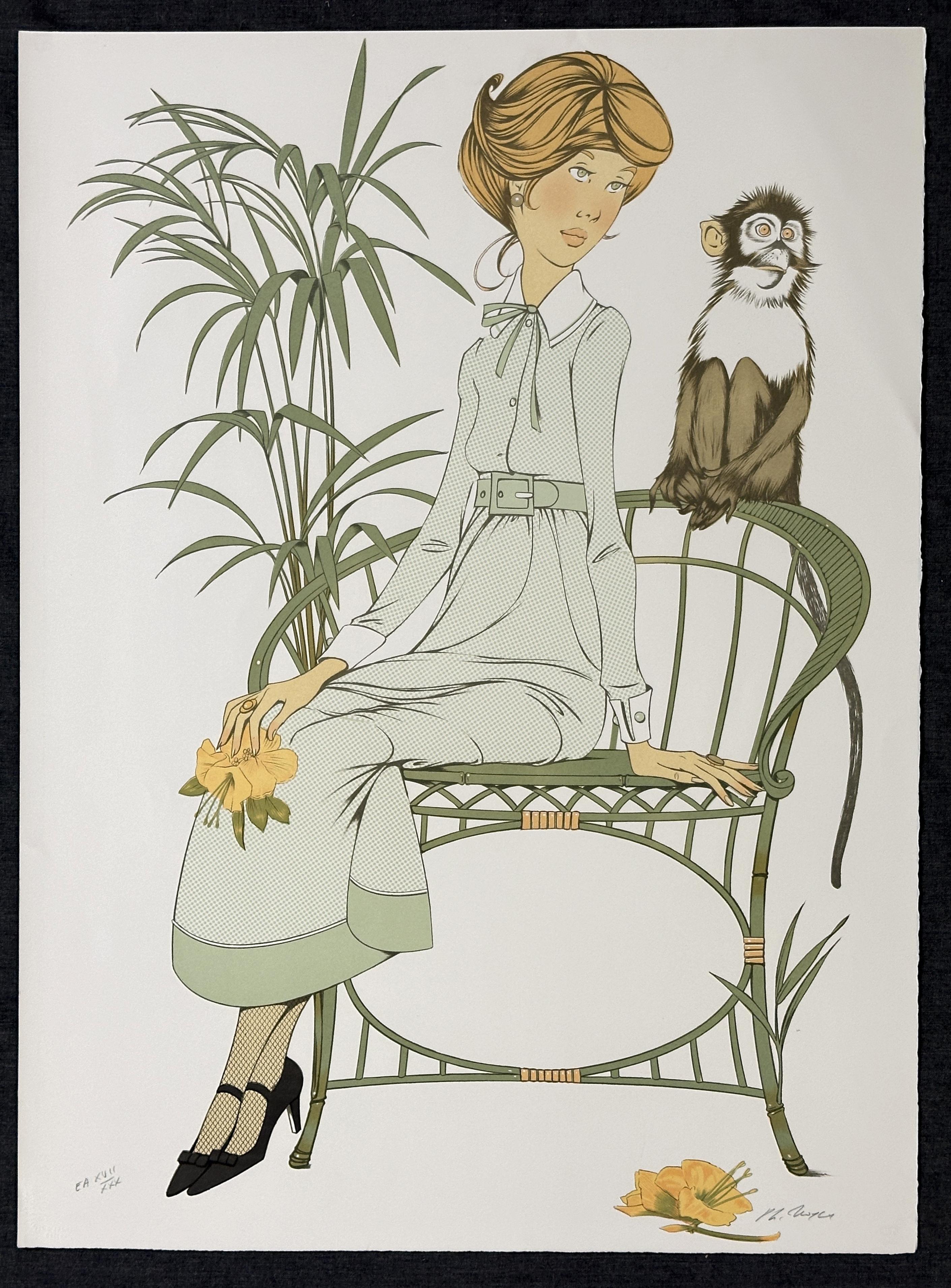
Philippe Noyer Le Singe 1980 A Signed Limited Edition
By Philippe Henri Noyer
Located in Rochester Hills, MI
Artist Name: Philippe Noyer
Title: Le Singe:
Medium Type: Lithograph
Size-Width Size-Height: 35" x 25"
Signed Edition Size: signed in pencil and marked EA XVII/XXX
Unframed in...
Category
1980s Post-Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph