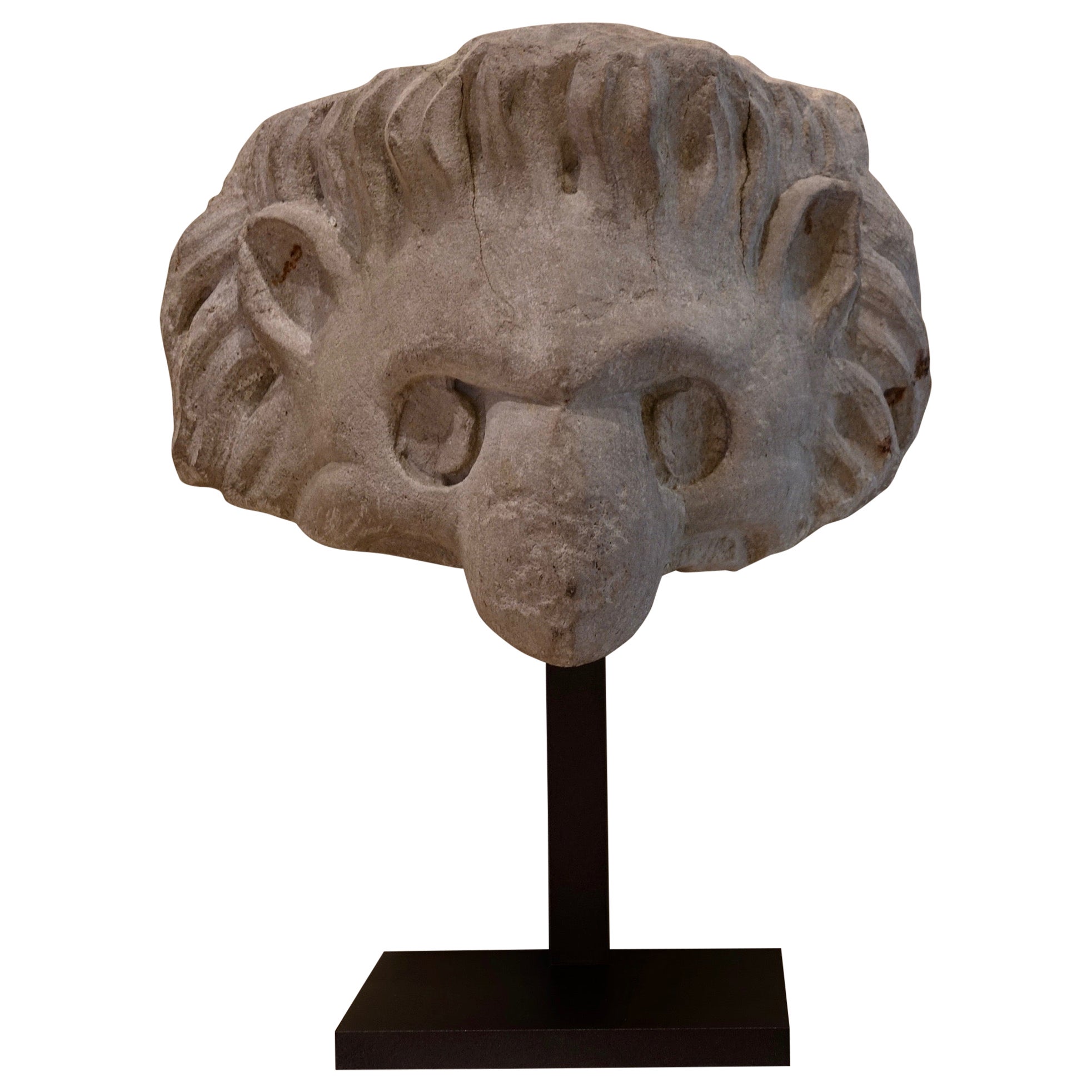
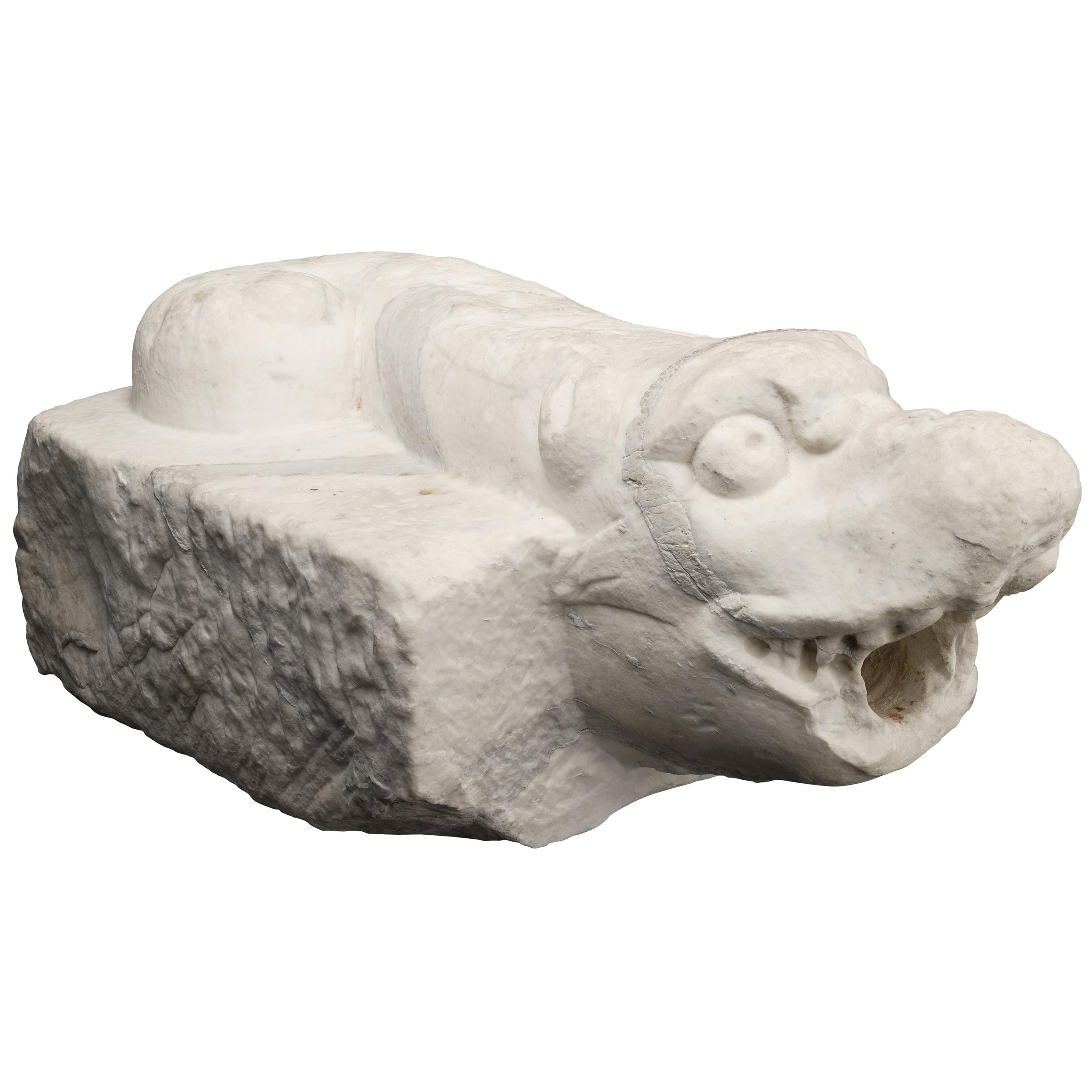
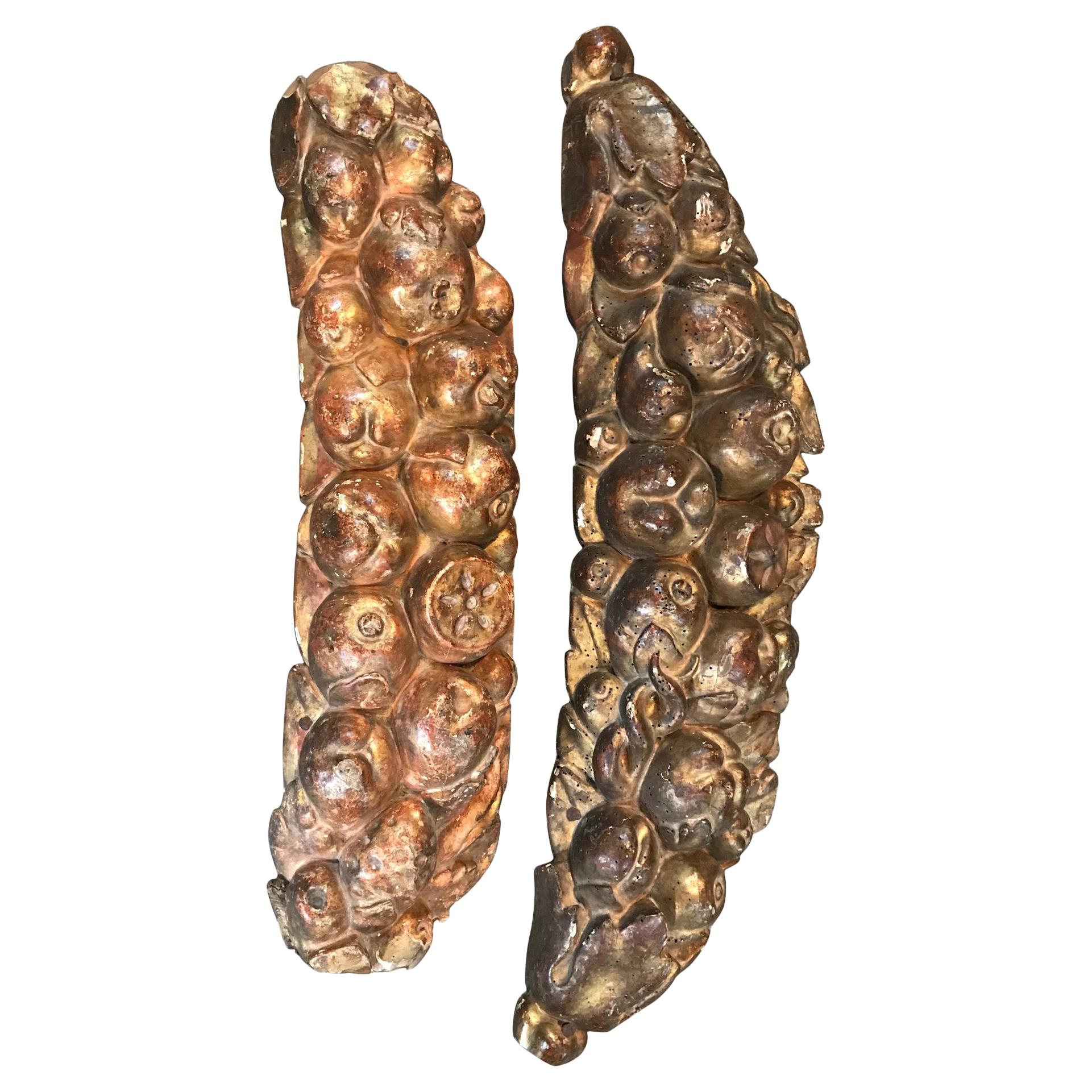
Marble Cherub Head, Late 16th-Early 17th Century, Italian, circa 1600-1620
View Similar Items
1 of 8
Marble Cherub Head, Late 16th-Early 17th Century, Italian, circa 1600-1620
About the Item
- Dimensions:Height: 8 in (20.32 cm)Width: 5.5 in (13.97 cm)Depth: 5.5 in (13.97 cm)
- Style:Renaissance (Of the Period)
- Materials and Techniques:
- Place of Origin:
- Period:Early 17th Century
- Date of Manufacture:1600-1620
- Condition:Wear consistent with age and use. Minor losses. The marble head of the Cherub is in good condition, with normal wear and weathering, some loss to the nose.
- Seller Location:Matlock, GB
- Reference Number:Seller: 33741stDibs: LU4228113100981
You May Also Like
- Christ in Boxwood, France, late 16th-early 17th century".Located in PARIS, FRChrist in Boxwood, France, late 16th-early 17th century Beautiful corpse of Christ with missing arms. He must have been on the Cross, arms in a horizontal position. Great expressiv...Category
Antique Early 17th Century French Renaissance Figurative Sculptures
MaterialsBoxwood
- French Late 16th Century Grand Scale Trunk FacadeLocated in Atlanta, GAA stunning, early 17th century trunk facade of grand scale. Dated 1621. Soundly constructed from richly stained oak with beautiful carvings of grapes on the vine, birds and other dec...Category
Antique Early 17th Century French Architectural Elements
MaterialsOak
- Pair of 17th/ 18th Century Italian White Marble Baroque OrnamentsLocated in Buisson, FRUnique and very beautiful pair weathered white marble baroque ornaments. They most likely once adorned a church altar. Original period pieces, Italy, ci...Category
Antique 17th Century Italian Baroque Architectural Elements
MaterialsMarble
$983 Sale Price / set52% Off - Griffin Head, Italy, 16th CenturyLocated in Bruxelles, BEGriffin head Italy, 16th century On a modern metal stand Measures: 20 x 29 x 21 cm (without the stand) The griffin is a legendary creature with the body of a lion, the head an...Category
Antique 16th Century Italian Renaissance Animal Sculptures
MaterialsMarble
$4,393 Sale Price20% Off - Italian Ancient Marble Sculpture Fountain, Late 16th CenturyLocated in Milano, ITSea monster Carrara marble mouth fountain Italy, late 16th century It measures 13.8 x 31.5 x 18.9 in (35 x 80 x 48 cm) State of conservation: some small evident gaps and widespread signs of wear due to outdoor exposure. The gray marks crossing it do not come from restoration, but are rather the natural veins of the marble. This work has some morphological characteristics typically associated with the iconography of the sea monster: an elongated muzzle, sharp teeth, protruding eyes, elongated ears, and a coiled serpent's tail. An in-depth series of studies on artistic depictions of the sea monster attempted to verify how this symbol evolved in antiquity in the European and Mediterranean contexts and how it gradually changed its image and function over time. The iconography itself is mutable and imaginative and its history is rich with cultural and artistic exchange, as well as the overlapping of ideas. This occurred so much that it is difficult to accurately pinpoint the "types" that satisfactorily represent its various developments. However, we can try to summarize the main figures, starting from the biblical Leviathan and the marine creature that swallowed Jonah (in the Christian version, this figure was to become a whale or a "big fish", the “ketos mega”, translation of the Hebrew “dag gadol”). Other specimens ranged from the dragons mentioned in the Iliad (which were winged and had legs) to "ketos” (also from Greek mythology), the terrifying being from whose Latinized name (“cetus”) derives the word "cetacean". See J. Boardman, “Very Like a Whale” - Classical Sea Monsters, in Monsters and Demons in the Ancient and Medieval Worlds, in Papers presented in Honor of Edith Porada, Mainz am Rhein 1987, pp. 73-84). In Italy the monster underwent yet further variations: it can be found in Etruscan art on the front of some sarcophagi representing the companion of souls, while among the Romans we find the “Pistrice” (cited by Plinio in Naturalis Historia PLIN., Nat., II 9, 8 and by Virgilio in Eneide: VERG., Aen., III, 427), which appeared in the shape of a stylized hippocampus or a very large monstrous cetacean and evolved into a hideous being with a dragon's head and long webbed fins. During the Middle Ages, the sea monster was the object of new transformations: at this time, it is often winged, the head is stretched like a crocodile, the front legs are often very sharp fins - sometimes real paws - until the image merges with dragons, the typical figures of medieval visionary spirituality widely found throughout Europe (on this topic and much more, see: Baltrušaitis, J., Il Medioevo fantastico. Antichità ed esotismi nell’arte gotica, Gli Adelphi 1997). In Italy during the 15th and 16th centuries, the revival of classicism - representative of the humanistic and Renaissance periods - led to a different reading of these "creatures". Indeed, the sea monster was also to find widespread use as an isolated decorative motif, especially in numerous fountains and sculptures where dolphins or sea monsters were used as a characterizing element linked to water (on this theme see: Chet Van Duzer, Sea Monsters on Medieval and Renaissance Maps, London, The British library, 2013). From the morphological point of view, the "sea monsters" of this period are mostly depicted as hybrid figures, in which the body of a mythological or real being (a hippocampus, a sea snake, a dolphin), is joined to a head with a rather indistinct appearance. It was usually characterized by large upright ears, an elongated snout, sharp teeth and globular, protruding eyes; a complex and indefinite figure, both from the symbolic point of view and from that of its genesis. The work we are examining is placed as a cross between the medieval sea serpent and the Renaissance dolphin, with stylistic features which recall the snake as often used in heraldry (such as the "snake" depicted in the coat of arms of the Visconti - the lords and then dukes of Milan between 1277 and 1447 - and which, for some, may be derived from the representations of the “Pistrice” that swallowed Jonah). In the search for sources, Renaissance cartography and in particular woodcuts should not be neglected. See for example the monsters of Olaus Magnus, from the editions of the “Historia de gentibus septentrionalibus” (“History of the peoples of the north”) and the natural histories of Conrad Gesner, Ulisse...Category
Antique 16th Century Italian Renaissance Animal Sculptures
MaterialsCarrara Marble
- Spanish 16th Century High Relief Limestone Bust from a BuildingLocated in Marbella, ES16th century high relief limestone bust that topped a stone arch. Side heraldic decorations indicate a patron Saint. The face is weathered but the general condition is good.Category
Antique 16th Century Spanish Renaissance Architectural Elements
MaterialsLimestone
Recently Viewed
View AllMore Ways To Browse
17th Century Wooden Sculpture
Carved Wooden Bust
Wooden Cherub
Small Marble Bust
Wooden Base Relief
Antique Wooden Cherub
Carved Marble Cherub
Cherub Bust
Carved Wooden Cherubs
17th Century Italian Cherub
16th Century Wooden Sculpture
Italian Wooden Cherubs
Small Marble Bust Head
Cherub Bust Marble
17th Century Wooden Cherub
16th Century Carved Cherub
Sculpture Midcentury Bust
Antique Bust French