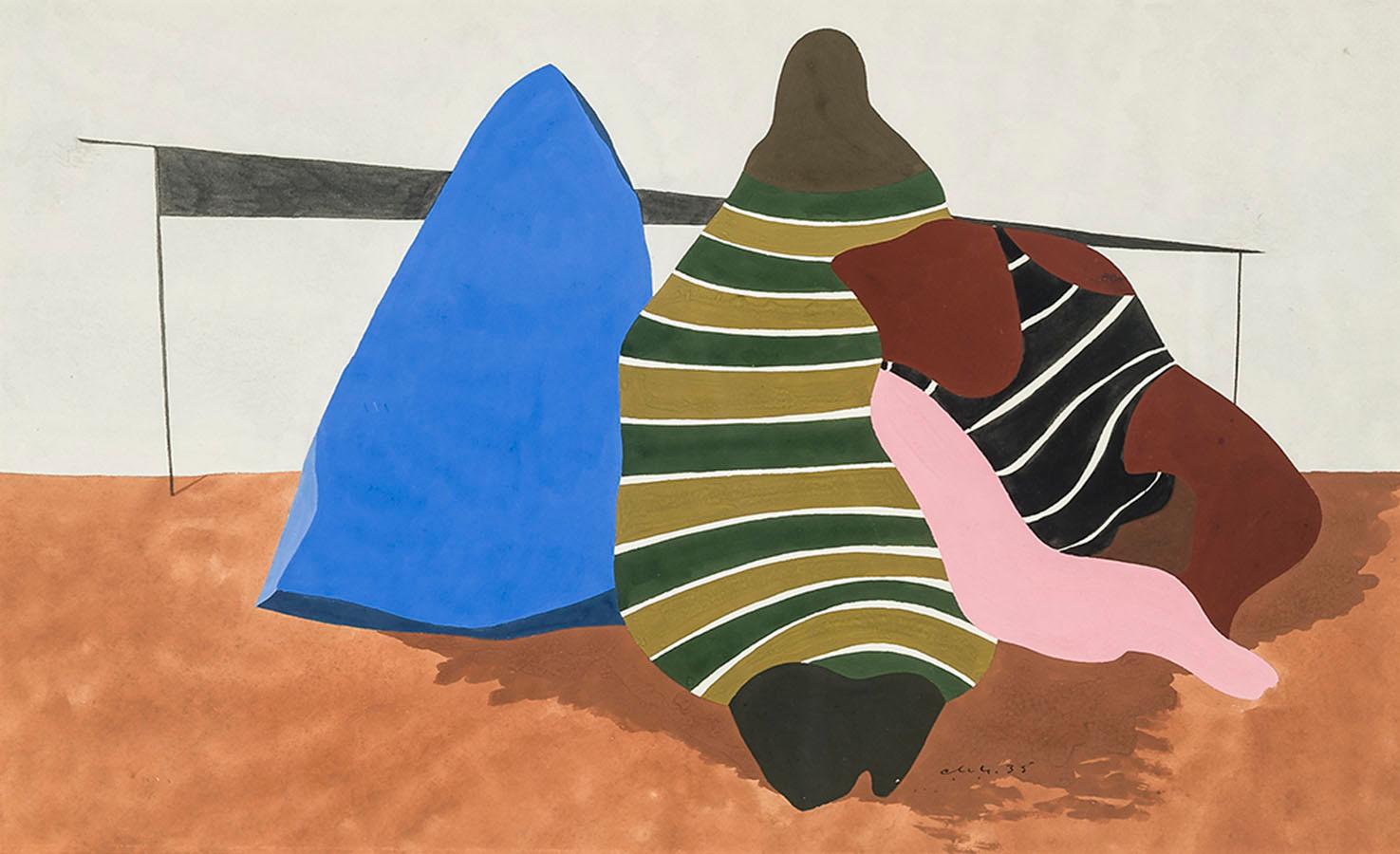
Charles Houghton HowardUntitled1936
1936
About the Item
- Creator:Charles Houghton Howard (1899 - 1978, American)
- Creation Year:1936
- Dimensions:Height: 11.5 in (29.21 cm)Width: 17.5 in (44.45 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:New York, NY
- Reference Number:Seller: APG 8915.0031stDibs: LU234875201
Charles Houghton Howard
Charles Houghton Howard was born in Montclair, New Jersey, the third of five children in a cultured and educated family with roots going back to the Massachusetts Bay colony. His father, John Galen Howard, was an architect who had trained at M.I.T. and the École des Beaux Arts in Paris, and apprenticed in Boston with H. H. Richardson. In New York, the elder Howard worked for McKim, Mead and White before establishing a successful private practice. Mary Robertson Bradbury, Charles’s mother, had studied art before her marriage. John Galen Howard moved his household to California in 1902 to assume the position of supervising architect of the new University of California campus at Berkeley and to serve as Professor of Architecture and the first Dean of the School of Architecture (established in 1903). The four Howard boys grew up to be artists and all married artists, leaving a combined family legacy of art making in the San Francisco Bay area that endures to this day, most notably in design, murals and reliefs at the Coit Tower and in buildings on the Berkeley campus.
Charles Howard graduated from the University of California at Berkeley in 1921 as a journalism major, and pursued graduate studies in English at Harvard and Columbia Universities before embarking on a two-year trip to Europe. Howard went to Europe as a would-be writer. But a near-religious experience, seeing a picture by Giorgione in a remote town outside of Venice, proved a life-altering epiphany. In his own words, “I cut the tour at once and hurried immediately back to Paris, to begin painting. I have been painting whenever I could ever since” (Charles Howard, “What Concerns Me,” Magazine of Art 39, no. 2 [February 1946], p. 63). Giorgione’s achievement, in utilizing a structured and rational visual language of art to convey high emotion on canvas, instantly convinced Howard that painting, and not literature, offered the best vehicle to express what he wanted to say. Howard returned to the United States in 1925, confirmed in his intent to become an artist.
Howard settled in New York and supported himself as a painter in the decorating workshop of Louis Bouché and Rudolph Guertler, where he specialized in mural painting. Devoting spare time to his own work, he lived in Greenwich Village and immersed himself in the downtown avant-garde cultural milieu. The late 1920s and early 1930s were the years of Howard’s art apprenticeship. He never pursued formal art instruction, but his keen eye, depth of feeling and intense commitment to the process of art making, allowed him to assimilate elements of painting intuitively from the wide variety of art that interested him. He found inspiration in the modernist movements of the day, both for their adherence to abstract formal qualities and for the cosmopolitan, international nature of the movements themselves. Influenced deeply by Surrealism, Howard was part of a group of American and European Surrealists clustered around Julien Levy. Levy opened his eponymously-named gallery in 1931, and rose to fame in January 1932, when he organized and hosted Surrealisme, the first ever exhibition of Surrealism in America, which included one work by Howard. Levy remained the preeminent force in advocating for Surrealism in America until he closed his gallery in 1949. Howard’s association with Levy in the early 1930s confirms the artist’s place among the avant-garde community in New York at that time.
In 1933, Howard left New York for London. It is likely that among the factors that led to the move were Howard’s desire to be a part of an international art community, as well as his marriage to English artist, Madge Knight (1895–1974). In London, he became associated with Unit One, a group of modernist painters, sculptors, and architects defined by its members’ commitment to abstract and surrealist art. Howard flourished in this environment, developing a personal surrealist style of abstract, biomorphic forms combined with vaguely representational imagery, similar in many ways to the work of Wassily Kandinsky, Jean Arp, Joan Miró, and Alexander Calder. Howard’s own comment on stylistic affinities is apt (and much more honest than is usual among artists): “I have welcomed the influence of other painters. I don’t believe in pure originality, and in the elaboration of my work I have relied upon my own obsession. If that weren’t strong enough to integrate its own expression, it seems to me it would be no use painting anyway” (as quoted in Dorothy Miller, ed., Americans 1942, exhib. cat. [New York: The Museum of Modern Art, 1942], p. 75). Howard participated in the landmark International Surrealist Exhibition at the New Burlington Galleries, London, in 1936, the first show of Surrealism to be held in England, evidence once again of the high regard his art commanded in London art circles. In 1939, Peggy Guggenheim mounted a solo Howard show at her London gallery, Guggenheim-Jeune.
Howard understood his works as steps in a process of psychological self-discovery: “They are in fact all portraits of the same general subject, of the same idea, carried as far as I am able at the time.” At the same time, they were not intended as specific to the artist, but, rather, as accessible statements of a shared humanity.
I do not belong to an elite. I don’t uncover secrets. I am dealing with material which is the possession of all people, presenting it with the fundamental anonymity of a human being on the face of the earth. I make pictures with shapes common to man anywhere, of any race, of any generation, regardless of time. (Howard, “What Concerns Me,” p. 64).
Art historian Douglas Dreishpoon notes:
Surrealism appealed to [Howard] for several reasons: it was European and modern; it had the potential, especially when combined with abstraction, to function symbolically as an analogue for psychological states and internal conditions; it acknowledged the mind as a battleground of conflicting forces, a repository of archetypal images; and it embodied a world view that courted anarchy and chaos, change and transformation (Dreishpoon, “Some Thoughts on the Enigmatic Charles Howard,” in Charles Howard 1899–1978: Drama of the Mind, exhib. cat. [New York: Hirschl & Adler Galleries, 1993], pp. 6–7).
Howard’s art is one of strict discipline and control, reflected in his working method. He toiled endlessly on individual pictures, making numerous studies before beginning painting, and then creating slowly and carefully until he achieved the desired result. Although Howard employed some automatist techniques in the germinal stages of developing his compositions, when it came time to lay paint on canvas, he left nothing to chance. The act of painting in oils never became “easy” for Howard. He stated: “[Painting] is not a frisky business. It is drudgery. It is a tedious, circuitous battle with an intractable medium. It is disappointing at every turn, painstaking as one may be, and using every bit of experience and adroitness that one may” (Howard, “What Concerns Me,” pp. 63–64).
Howard lived for seven years in London before returning to San Francisco in 1940 at the beginning of World War II. He worked at home as a ship-fitter in a wartime shipyard; served as an Editor in the Office of War Information in San Francisco, and latterly taught painting at the California School of Fine Arts. He continued to paint in his methodical fashion, exhibiting regularly at prominent contemporary venues including the Carnegie Institute, Pittsburgh; the Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Art, Philadelphia; the Whitney Museum, New York; and the Corcoran Gallery, Washington, D.C, thus building a critical reputation in his native country. Howard was included in the landmark Americans 1942 exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art, New York, and that same year he participated in the inaugural exhibition of Peggy Guggenheim’s New York gallery, Art of This Century. In 1946, Howard’s work was the subject of a major retrospective exhibition of thirty-three oils and a number of gouaches and drawings at the California Palace of the Legion of Honor in San Francisco, which established the artist as a major figure in American modernism.
Charles and Madge Knight Howard returned to England in 1946, eventually settling in Helions Bumpstead, a small village in northwest Essex, near the boundary with Suffolk, and Cambridgeshire. Howard quickly reengaged himself in the London art community that had nourished his career in the 1930s. From 1959 to 1963, he taught painting at the Camberwell School of Arts and Crafts in London. Shy and scholarly by nature, Howard adhered closely to the pictorial mode he had established in the 1930s and ‘40s, remaining true to his vision of a surrealistic art capable of expressing complex inner psychological states. Although his stance placed him outside of contemporary currents in art, a position reinforced by his removal from his home country, Howard was comfortable following an independent course. His oeuvre thus comprises a consistent and unified body of work that represents a distinctive personal style perfected over time. Howard remained in England until 1970, when he and Madge retired to Bagna di Lucca, Italy.
Excavation, dated 1932, is an important early oil work by Howard, painted in New York prior to his initial departure for London and marking the end of his apprentice years. The painting evokes a dreamscape street excavation site, combining Howard’s firm and assured modeling and his crisply outlined forms in a careful composition employing the distortions that distinguish the surrealist style. The painting offers an early expression of the hard-edged abstraction that made Howard’s later work so distinctive. Excavation was included in Howard’s first one-man exhibition at the Julien Levy Gallery, New York, in 1932–33. The show puzzled reviewers who were unprepared for Howard’s avant-garde style. It wasn’t until the 1940s that American critics began to understand Howard’s stalwart devotion to hard-edged abstraction By the time of his retrospective at the California Palace of the Legion of Honor, San Francisco, in 1946, and a subsequent solo show of his work that year at the Nierendorf Gallery, New York, the critics had finally “got” what Howard was doing. A review of the Nierendorf show offered a typically glowing assessment:
An event of interest to lovers of the abstract is the present showing of canvases from the brush of Charles Howard, at the Nierendorf Galleries. The showing is retrospective and includes works executed between the years 1925 and 1946. . . .
These considered canvases, by a painter widely acknowledged to be in the forefront of the American abstract stream (although he is at present an expatriate, residing in England), will richly reward careful scrutiny by those who deal seriously with problems of composition, space and color. The artist’s sense of composition in placement of forms is uncanny and he never misses (Ben Wolf, “Charles Howard, Veteran Abstractionist,” Art Digest 21 [October 1, 1946], p. 18).
It took nearly 15 years but, as evidenced by the above, Howard’s uncompromising style ultimately received its due.
Few of Howard’s works from the early 1930s have come to light. Excavation itself was in a private collection for many years and has not been seen by the public since 1946. As other major works of Howard’s early period emerge, we will hopefully better understand the early career of one of America’s most important early abstract artists. That said, Howard remains, today, an underrated and insufficiently recognized artist, and thus of particular interest to the discerning collector. Partly his low profile is due to the limited size of his oeuvre, a reflection of the extreme deliberation and time he took with each work. More importantly, Howard followed his own muse, eluding any easy label, part surrealist, part abstract painter. He stood firmly outside the expressionism that dominated the art world in the latter half of the 20th century. While he was a member of an important Bay Area artistic family, he painted there only during the war years and left little evidence of his presence. He was a young artist in New York, and departed in 1933, thus never affiliated with any “New York School.” The bulk of his creative life was spent as an expatriate in England, an American to be sure, but again, a hard man to categorize. Married, but childless, he left no heirs to promote his posthumous reputation. All of this notwithstanding, for decades during his life Howard enjoyed the enthusiastic admiration of his colleagues in art as well as art critics. His work is included in such important collections as The Art Institute of Chicago, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art.
(Biography provided by Hirschl & Adler)
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Shipping from: New York, NY
- Return Policy
More From This Seller
View All20th Century American Modern Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Paper, Watercolor, Gouache, Graphite
20th Century American Modern Abstract Paintings
Canvas, Oil
1940s American Modern Abstract Paintings
Paper, Gouache
Mid-20th Century Abstract Expressionist Abstract Paintings
Oil
2010s Contemporary Landscape Drawings and Watercolors
Paper, Watercolor
20th Century American Modern Portrait Drawings and Watercolors
Pastel, Board
You May Also Like
Late 20th Century American Modern Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Pastel
2010s Contemporary Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Canvas, Acrylic
Late 20th Century American Modern Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Pastel
1960s Post-War Abstract Paintings
Masonite, Oil
20th Century Abstract Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Acrylic
1960s Abstract Expressionist Abstract Drawings and Watercolors
Watercolor
Read More
With Works Like ‘Yours Truly,’ Arthur Dove Pioneered Abstract Art in America
New York gallery Hirschl & Adler is exhibiting the bold composition by Dove — who’s hailed as the first American abstract painter — at this year’s Winter Show.
Remarkably, Elizabeth Turk’s Sculptures Highlight the Lost Voices of Extinct Birds
In one of the first live and in-person exhibitions at a Manhattan gallery since last spring, the California-based sculptor gives the lost voices of endangered and extinct birds and animals a magnificent embodied form.

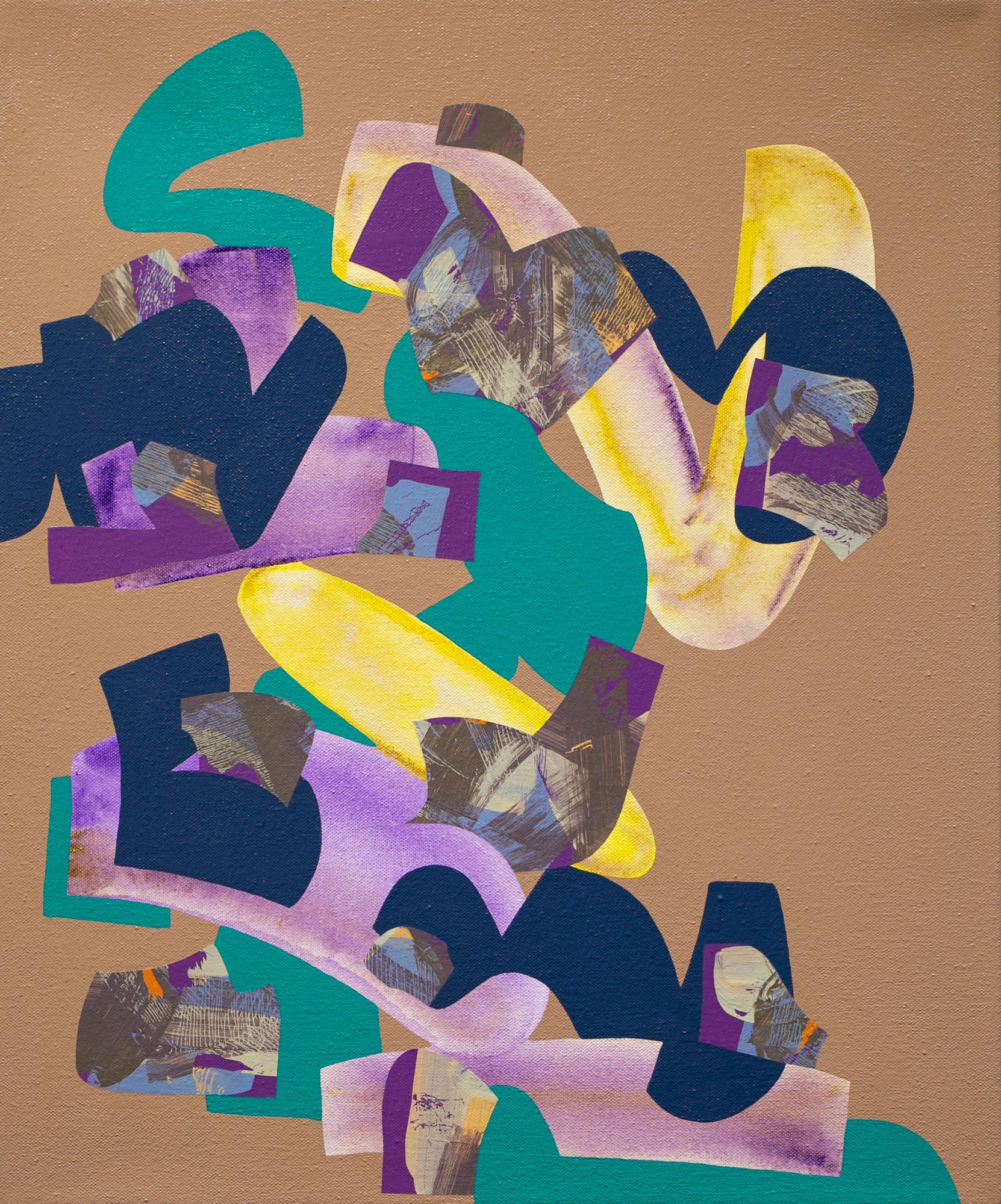





![Untitled [Abstraction]](https://a.1stdibscdn.com/george-lk-morris-1905-1975-american-paintings-untitled-abstraction-for-sale/a_23/1652214284908/APG_8941_unfr_master.jpg?width=240)


