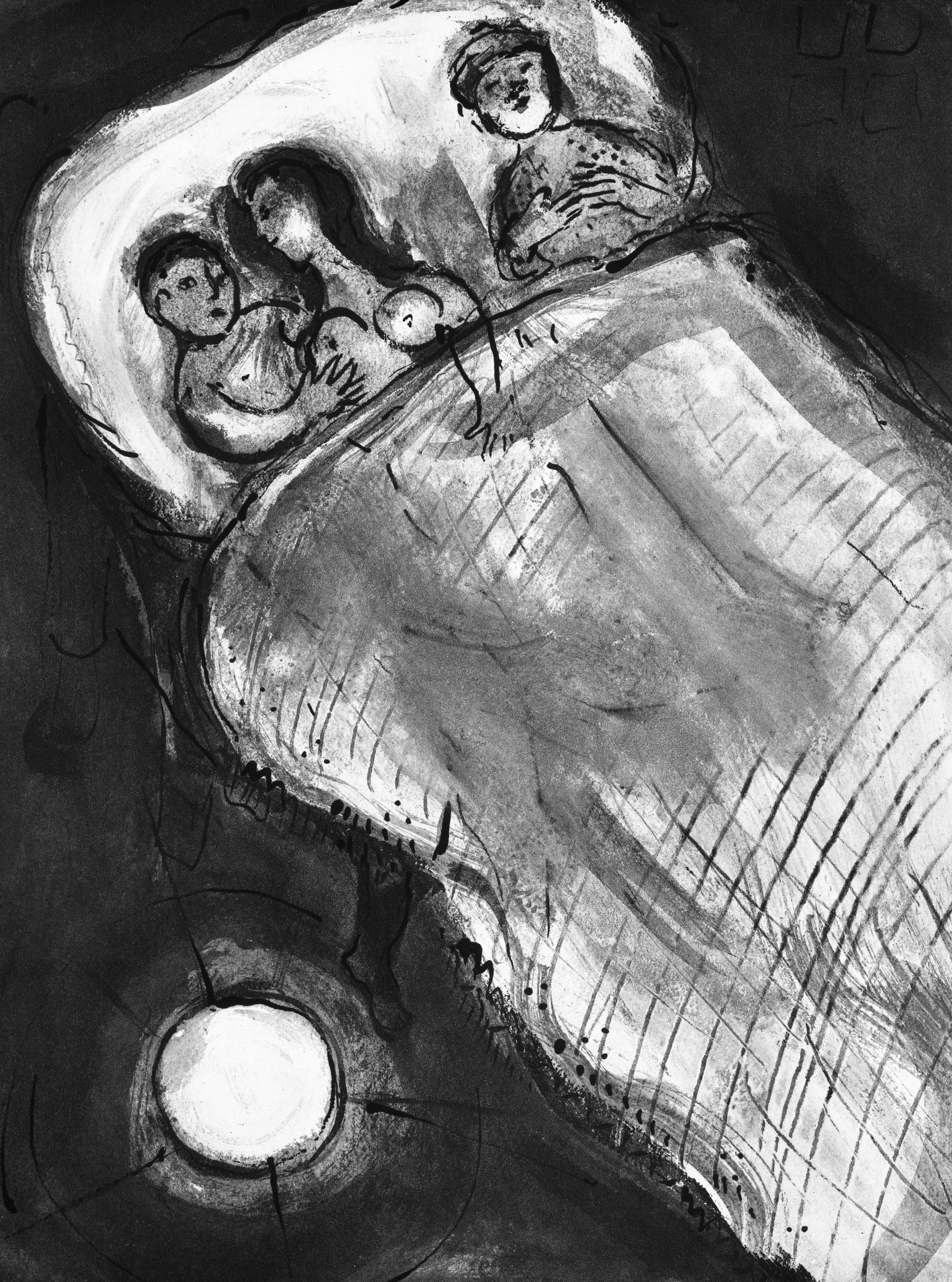
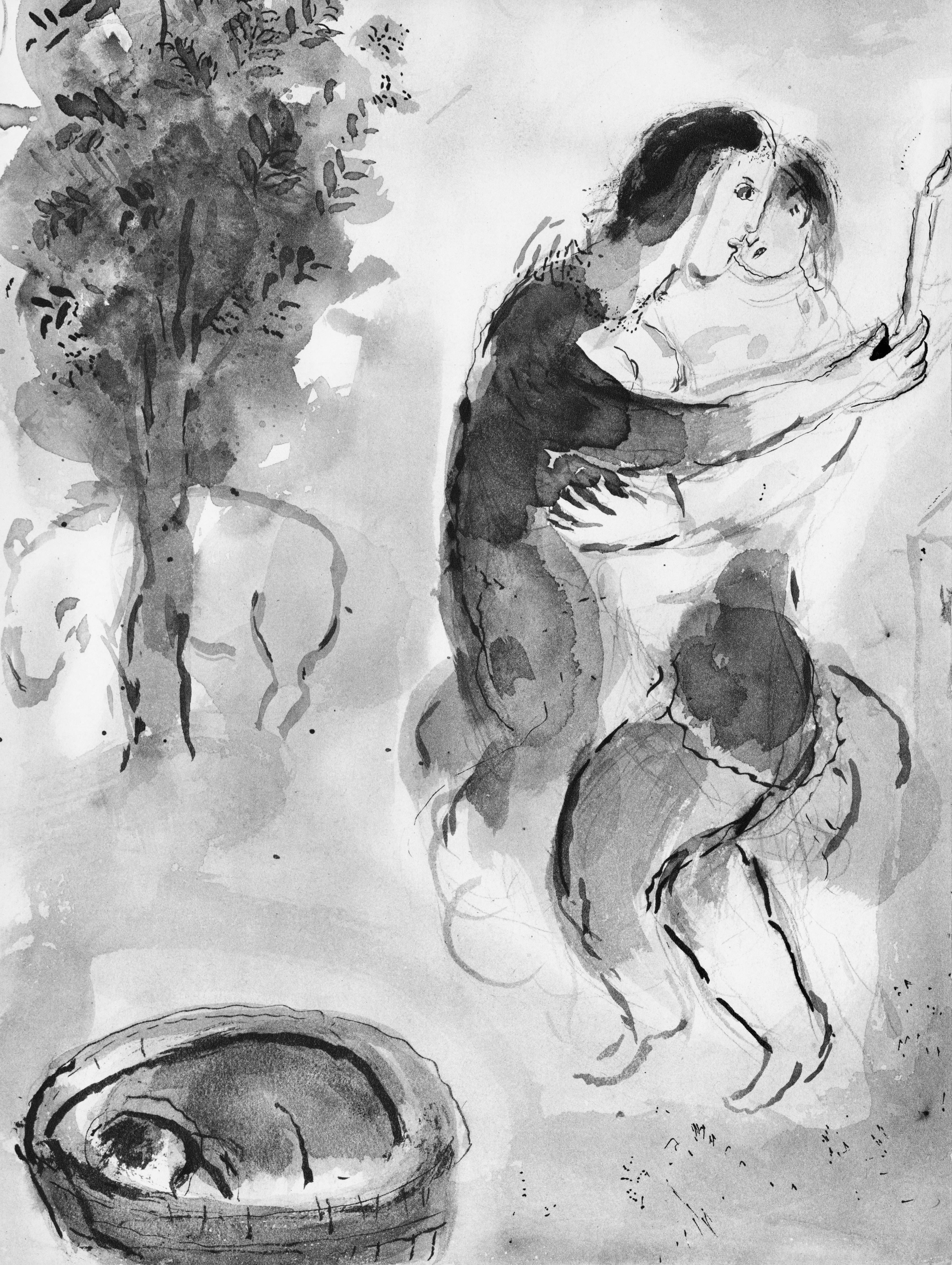
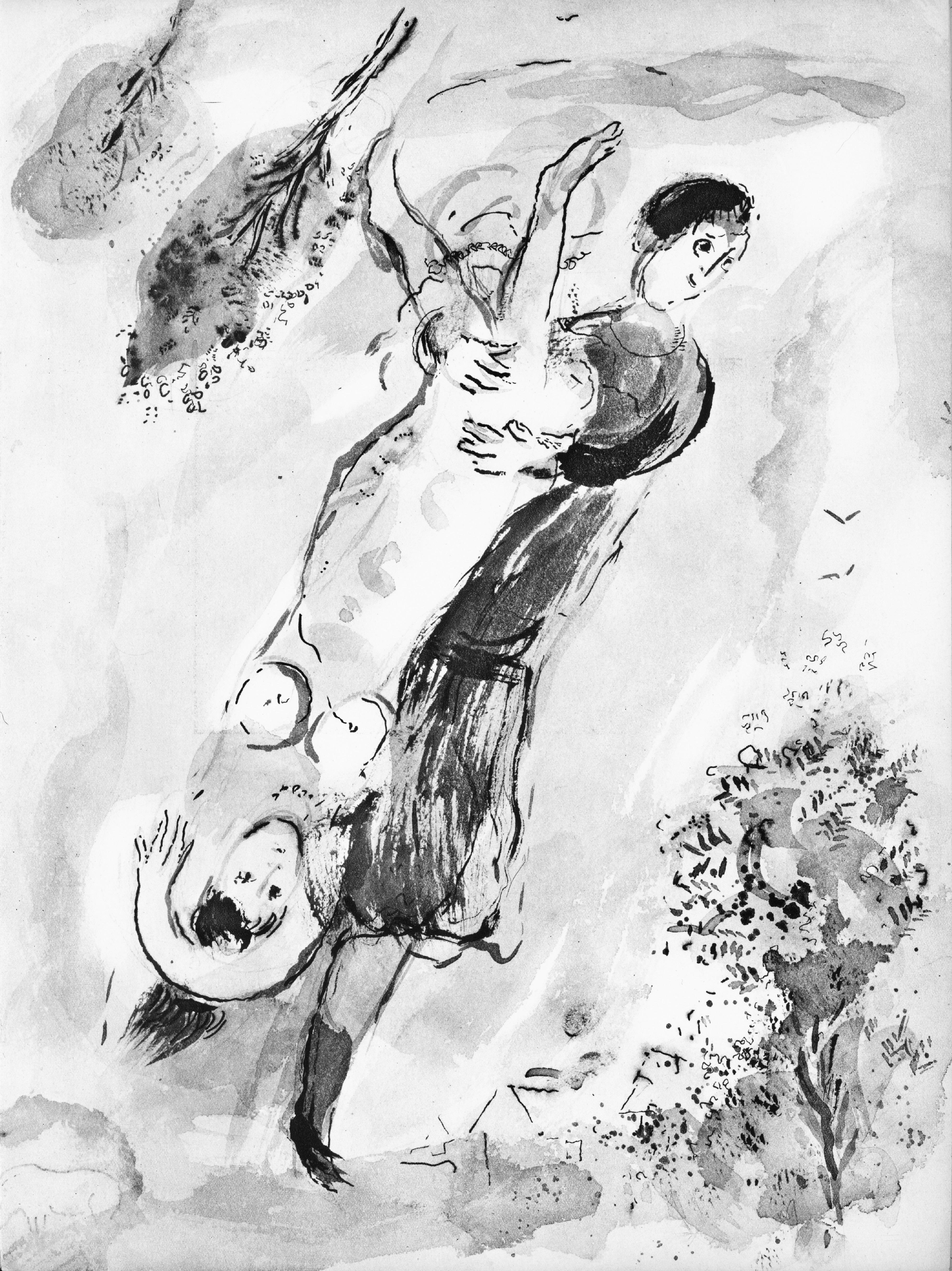
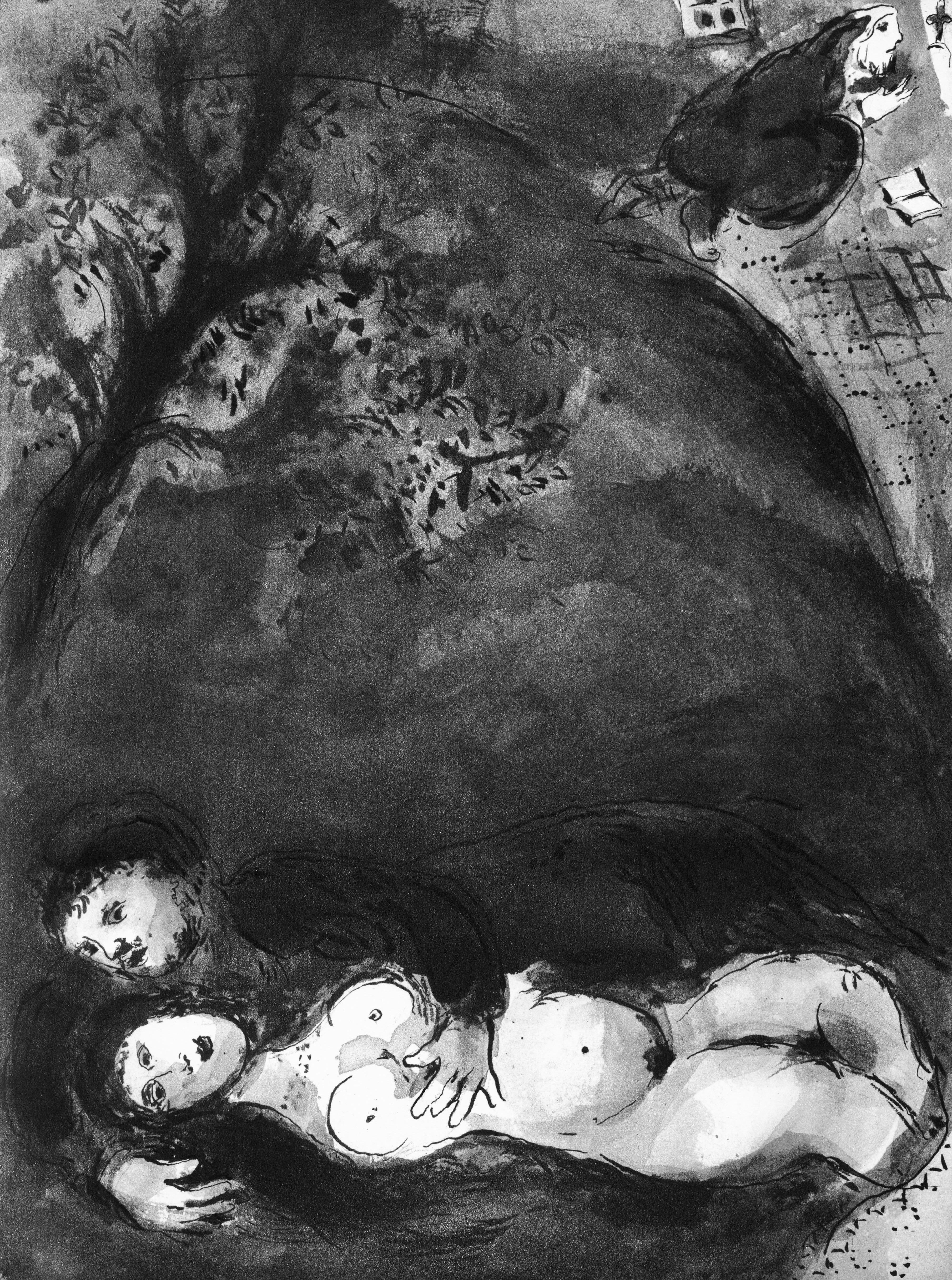
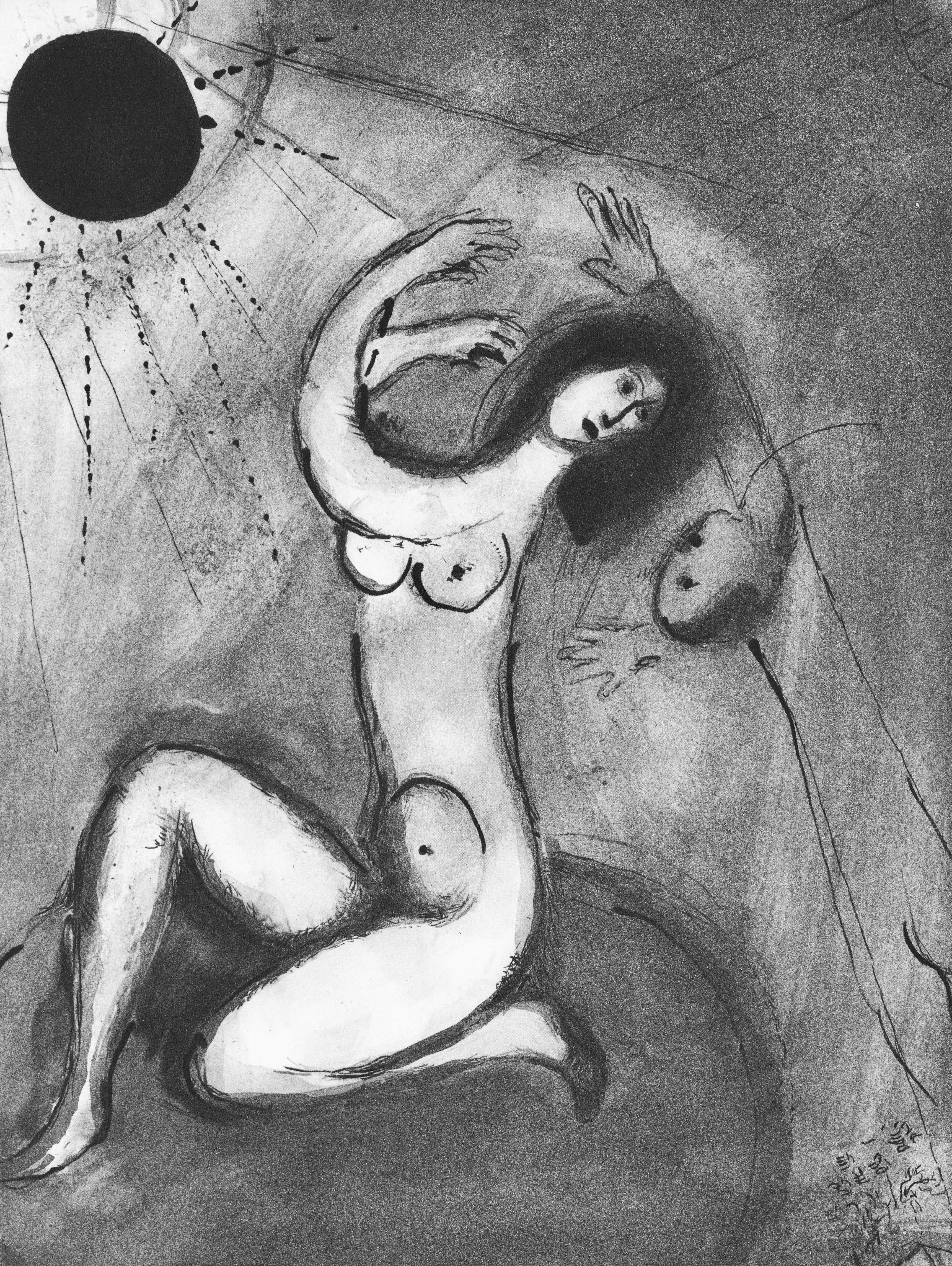
This exquisite lithograph by Marc Chagall (1887–1985), titled L’Ange du soir (The Evening Angel), from Contes de Boccace, peintures du manuscrit des ducs de Bourgogne, Bibliotheque de l'Arsenal (Ms. no. 5193) (Tales of Boccaccio, Paintings from the Manuscript of the Dukes of Burgundy, Library of the Arsenal), Lavis de Marc Chagall, from Verve, Revue Artistique et Litteraire, Vol. VI, No. 24, originates from the 1950 issue published by Editions de la revue Verve, Paris, under the direction of Teriade, Editeur, Paris, and printed by Draeger Freres, Maitres-Imprimeurs, Paris, 1950. This ethereal composition captures Chagall’s profound sense of spirituality and wonder. L’Ange du soir reveals the artist’s fascination with the celestial and the divine, portraying a poetic vision where angels descend into human dreams, uniting heaven and earth through luminous symbolism and graceful form.
Executed as a lithograph on velin du Marais paper, this work measures 14 x 10.5 inches. Unsigned and unnumbered as issued. The edition exemplifies the exquisite craftsmanship of the Draeger Freres atelier, celebrated for its precision and tonal richness in printing fine artworks.
Artwork Details:
Artist: Marc Chagall (1887–1985)
Title: L’Ange du soir (The Evening Angel), from Contes de Boccace (Tales of Boccaccio), Verve, Revue Artistique et Litteraire, Vol. VI, No. 24, 1950
Medium: Lithograph on velin du Marais paper
Dimensions: 14 x 10.5 inches
Inscription: Unsigned and unnumbered as issued
Date: 1950
Publisher: Editions de la revue Verve, Paris, under the direction of Teriade, Editeur, Paris
Printer: Draeger Freres, Maitres-Imprimeurs, Paris
Condition: Well preserved, consistent with age and medium
Provenance: From Verve, Revue Artistique et Litteraire, Vol. VI, No. 24, published by Editions de la revue Verve, Paris, 1950
Notes:
Excerpted from the album (translated from French), This Verve issue contains the lavis that Marc Chagall composed to illustrate Tales of Boccaccio's Decameron and the paintings on the same theme of the Manuscript of the Dukes of Burgundy preserved in the Arsenal Library. Marc Chagall executed the cover of this work which was completed printing on April 20, 1950 on the presses of Maitres-Imprimeurs, the Draeger Freres.
About the Publication:
This 1950 issue of Verve, Revue Artistique et Litteraire, titled Contes de Boccace (Tales of Boccaccio), was devoted to the great Italian humanist Giovanni Boccaccio and illuminated manuscripts from the 15th century, interpreted and revived through the eyes of modern artists. Under the artistic direction of Teriade, Marc Chagall contributed a series of lyrical paintings and lavis that reimagined these Renaissance themes with his signature dreamlike color, tenderness, and spiritual symbolism. The issue juxtaposed Chagall’s contemporary vision with the rich heritage of medieval illumination, bridging centuries of artistic imagination. Printed by the master craftsmen of Draeger Freres, the publication stands as a testament to Verve’s tradition of uniting art, literature, and history in one luxurious volume that celebrates the continuity of human creativity from the Middle Ages to modernity.
About the Artist:
Marc Chagall (1887–1985) was a Belarus-born French painter, printmaker, and designer whose visionary imagination, radiant color, and deeply poetic symbolism made him one of the most beloved and influential artists of the 20th century. Rooted in the imagery of his Jewish heritage and the memories of his childhood in Vitebsk, Chagall’s art wove together themes of faith, love, folklore, and fantasy with a dreamlike modern sensibility. His unique style—merging elements of Cubism, Fauvism, Expressionism, and Surrealism—defied categorization, transforming ordinary scenes into lyrical meditations on memory and emotion. Influenced by Russian icon painting, medieval religious art, and the modern innovations of artists such as Pablo Picasso, Henri Matisse, and Georges Braque, Chagall developed a profoundly personal visual language filled with floating figures, vibrant animals, musicians, and lovers that symbolized the transcendent power of imagination and love. During his early years in Paris, he became an integral part of the Ecole de Paris circle, forming friendships with Amedeo Modigliani, Fernand Leger, and Sonia Delaunay, and his creative spirit resonated with that of his peers and successors—Alexander Calder, Alberto Giacometti, Salvador Dali, Joan Miro, Wassily Kandinsky, Marcel Duchamp, and Man Ray—artists who, like Chagall, sought to push the boundaries of perception, emotion, and form. Over a prolific career that spanned painting, printmaking, stained glass, ceramics, and stage design, Chagall brought an unparalleled poetic sensibility to modern art, infusing even the most abstract subjects with human warmth and spiritual depth. His works are held in the most prestigious museums around the world, including the Museum of Modern Art, the Centre Pompidou, the Tate, and the Guggenheim, where they continue to inspire generations of artists and collectors. The highest price ever paid for a Marc Chagall artwork is approximately $28.5 million USD, achieved in 2017 at Sotheby’s New York for Les Amoureux (1928).
Marc Chagall L’Ange du soir, Chagall Verve, Chagall Draeger Freres, Chagall Teriade, Chagall 1950 lithograph, Chagall velin du Marais, Chagall Revue Artistique et Litteraire, Chagall collectible print, Chagall modernist lithograph.