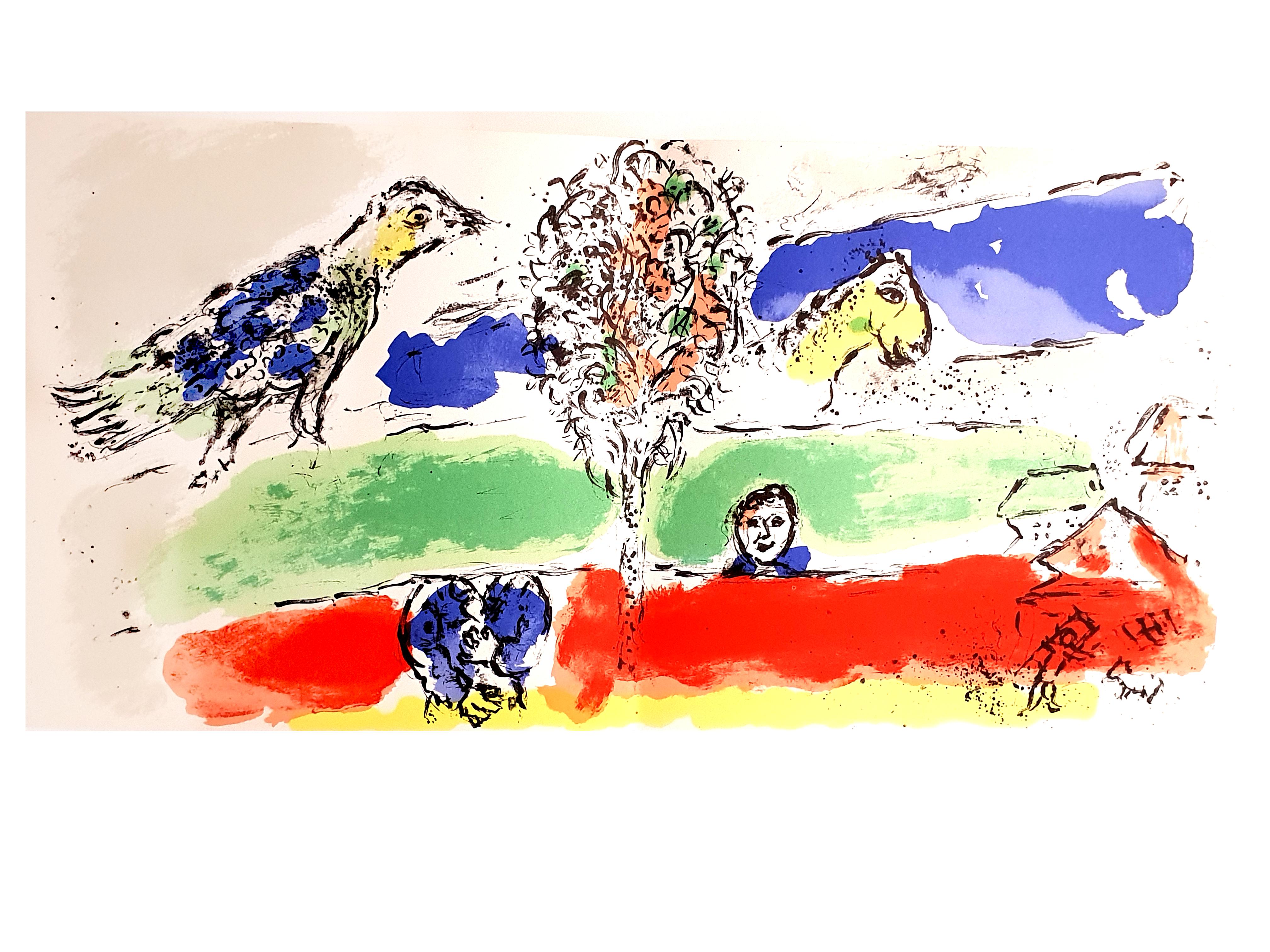
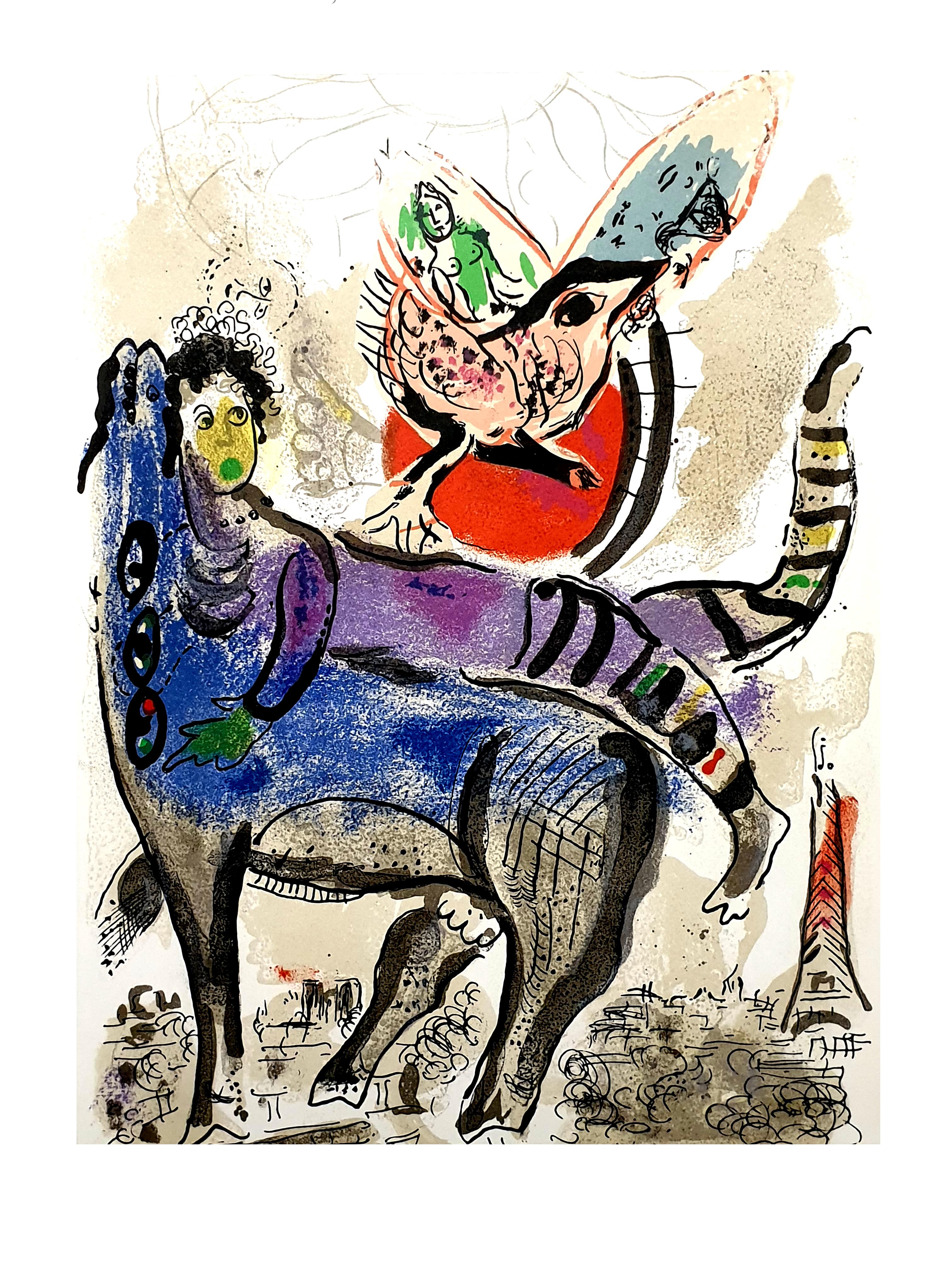
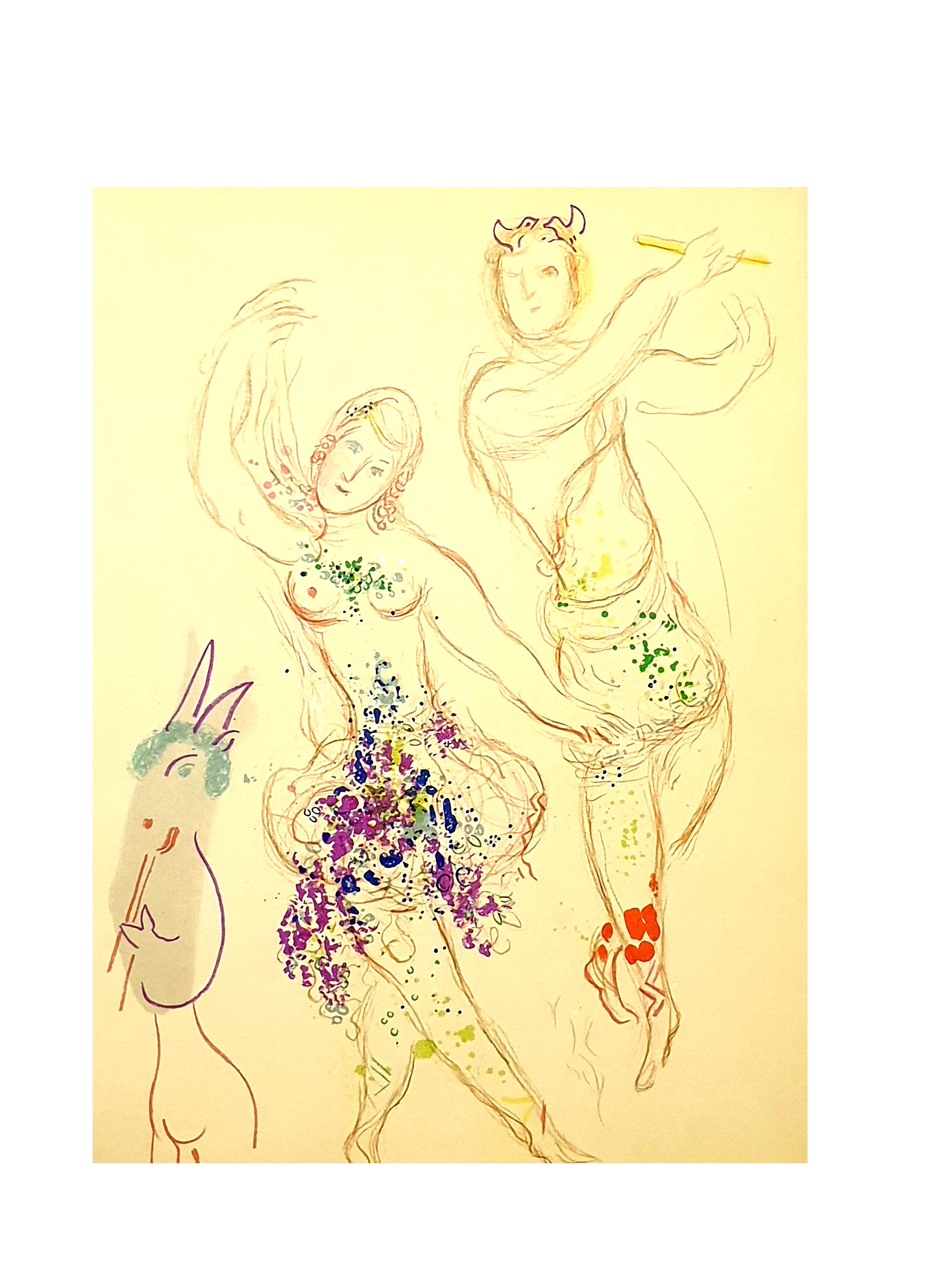
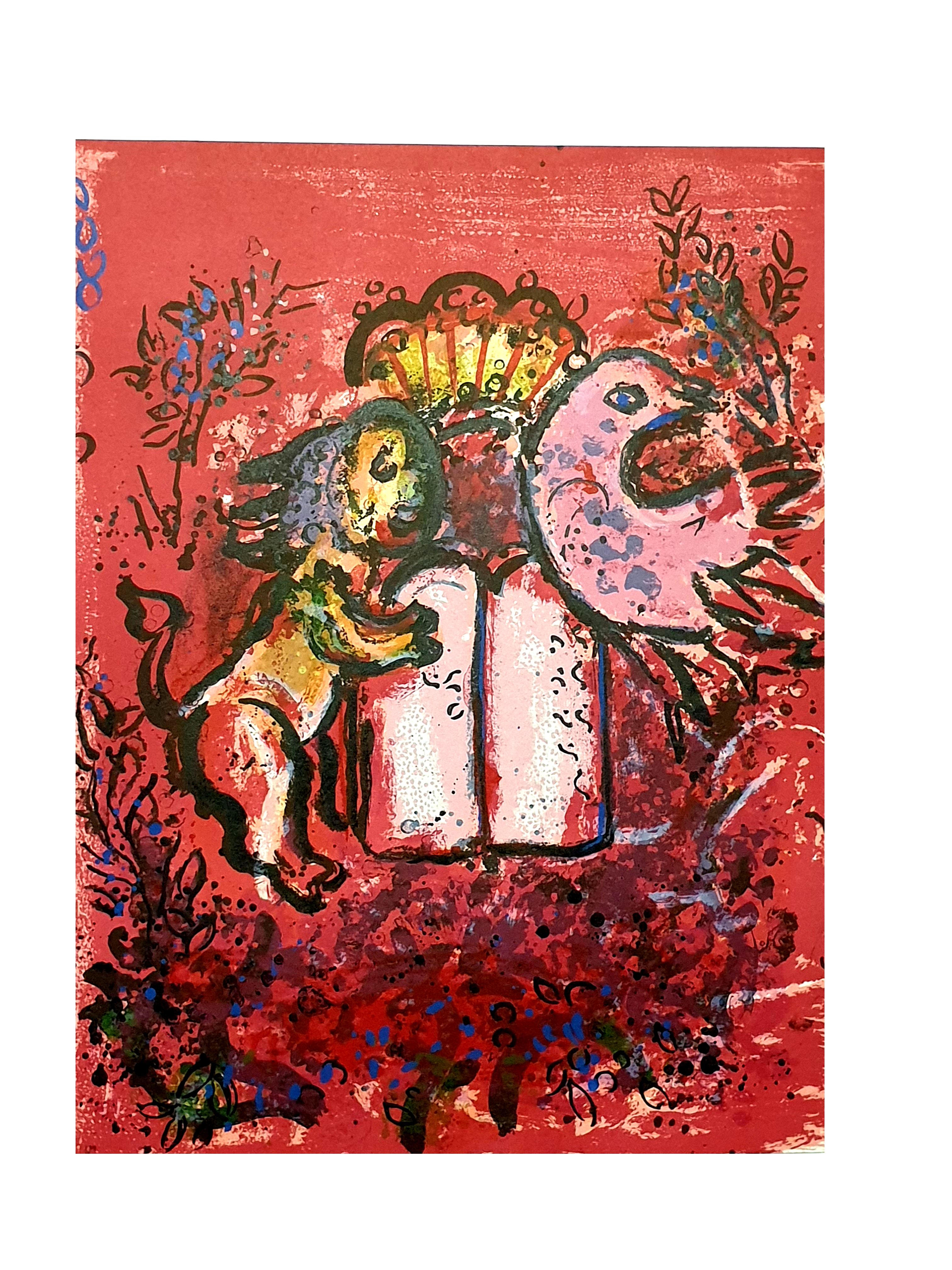
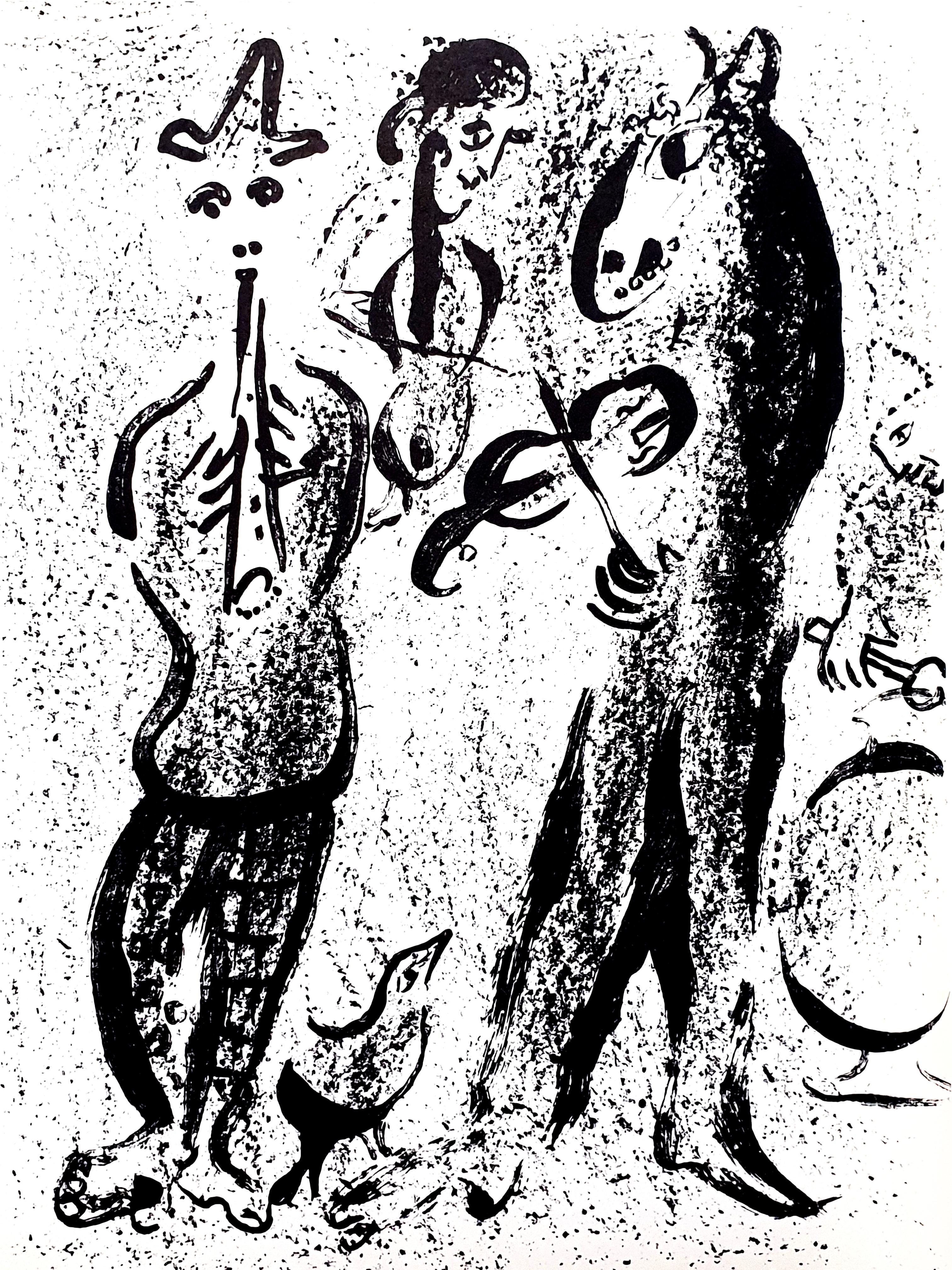Marc Chagall
Original Lithograph
1963
Dimensions: 32 x 24 cm
As published in Chagall Lithographe 1957-1962. VOLUME II.
Unsigned, as issued, from the edition of several thousand
Condition : Excellent
Reference: Mourlot/Gauss 401
Marc Chagall (born in 1887)
Marc Chagall was born in Belarus in 1887 and developed an early interest in art. After studying painting, in 1907 he left Russia for Paris, where he lived in an artist colony on the city’s outskirts. Fusing his own personal, dreamlike imagery with hints of the fauvism and cubism popular in France at the time, Chagall created his most lasting work—including I and the Village (1911)—some of which would be featured in the Salon des Indépendants exhibitions. After returning to Vitebsk for a visit in 1914, the outbreak of WWI trapped Chagall in Russia. He returned to France in 1923 but was forced to flee the country and Nazi persecution during WWII. Finding asylum in the U.S., Chagall became involved in set and costume design before returning to France in 1948. In his later years, he experimented with new art forms and was commissioned to produce numerous large-scale works. Chagall died in St.-Paul-de-Vence in 1985.
The Village
Marc Chagall was born in a small Hassidic community on the outskirts of Vitebsk, Belarus, on July 7, 1887. His father was a fishmonger, and his mother ran a small sundries shop in the village. As a child, Chagall attended the Jewish elementary school, where he studied Hebrew and the Bible, before later attending the Russian public school. He began to learn the fundamentals of drawing during this time, but perhaps more importantly, he absorbed the world around him, storing away the imagery and themes that would feature largely in most of his later work.
At age 19 Chagall enrolled at a private, all-Jewish art school and began his formal education in painting, studying briefly with portrait artist Yehuda Pen. However, he left the school after several months, moving to St. Petersburg in 1907 to study at the Imperial Society for the Protection of Fine Arts. The following year, he enrolled at the Svanseva School, studying with set designer Léon Bakst, whose work had been featured in Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. This early experience would prove important to Chagall’s later career as well.
Despite this formal instruction, and the widespread popularity of realism in Russia at the time, Chagall was already establishing his own personal style, which featured a more dreamlike unreality and the people, places and imagery that were close to his heart. Some examples from this period are his Window Vitebsk (1908) and My Fianceé with Black Gloves (1909), which pictured Bella Rosenfeld, to whom he had recently become engaged.
The Beehive
Despite his romance with Bella, in 1911 an allowance from Russian parliament member and art patron Maxim Binaver enabled Chagall to move to Paris, France. After settling briefly in the Montparnasse neighborhood, Chagall moved further afield to an artist colony known as La Ruche (“The Beehive”), where he began to work side by side with abstract painters such as Amedeo Modigliani and Fernand Léger as well as the avant-garde poet Guillaume Apollinaire. At their urging, and under the influence of the wildly popular fauvism and cubism, Chagall lightened his palette and pushed his style ever further from reality. I and the Village (1911) and Homage to Apollinaire (1912) are among his early Parisian works, widely considered to be his most successful and representative period.
Though his work stood stylistically apart from his cubist contemporaries, from 1912 to 1914 Chagall exhibited several paintings at the annual Salon des Indépendants exhibition, where works by the likes of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp and Robert Delaunay were causing a stir in the Paris art world. Chagall’s popularity began to spread beyond La Ruche, and in May 1914 he traveled to Berlin to help organize his first solo exhibition, at Der Sturm Gallery. Chagall remained in the city until the highly acclaimed show opened that June. He then returned to Vitebsk, unaware of the fateful events to come.
War, Peace and Revolution
In August 1914 the outbreak of World War I precluded Chagall’s plans to return to Paris. The conflict did little to stem the flow of his creative output, however, instead merely giving him direct access to the childhood scenes so essential to his work, as seen in paintings such as Jew in Green (1914) and Over Vitebsk (1914). His paintings from this period also occasionally featured images of the war’s impact on the region, as with Wounded Soldier (1914) and Marching (1915). But despite the hardships of life during wartime, this would also prove to be a joyful period for Chagall. In July 1915 he married Bella, and she gave birth to a daughter, Ida, the following year. Their appearance in works such as Birthday (1915), Bella and Ida by the Window (1917) and several of his “Lovers” paintings give a glimpse of the island of domestic bliss that was Chagall’s amidst the chaos.
To avoid military service and stay with his new family, Chagall took a position as a clerk in the Ministry of War Economy in St. Petersburg. While there he began work on his autobiography and also immersed himself in the local art scene, befriending novelist Boris Pasternak, among others. He also exhibited his work in the city and soon gained considerable recognition. That notoriety would prove important in the aftermath of the 1917 Russian Revolution when he was appointed as the Commissar of Fine Arts in Vitebsk. In his new post, Chagall undertook various projects in the region, including the 1919 founding of the Academy of the Arts. Despite these endeavors, differences among his colleagues eventually disillusioned Chagall. In 1920 he relinquished his position and moved his family to Moscow, the post-revolution capital of Russia.
In Moscow, Chagall was soon commissioned to create sets and costumes for various productions at the Moscow State Yiddish Theater, where he would paint a series of murals titled Introduction to the Jewish Theater as well. In 1921, Chagall also found work as a teacher at a school for war orphans. By 1922, however, Chagall found that his art had fallen out of favor, and seeking new horizons he left Russia for good.
Flight
After a brief stay in Berlin, where he unsuccessfully sought to recover the work exhibited at Der Sturm before the war, Chagall moved his family to Paris in September 1923. Shortly after their arrival, he was commissioned by art dealer and publisher Ambroise Vollard to produce a series of etchings for a new edition of Nikolai Gogol's 1842 novel Dead Souls. Two years later Chagall began work on an illustrated edition of Jean de la Fontaine’s Fables, and in 1930 he created etchings for an illustrated edition of the Old Testament, for which he traveled to Palestine to conduct research.
Chagall’s work during this period brought him new success as an artist and enabled him to travel throughout Europe in the 1930s. He also published his autobiography, My Life (1931), and in 1933 received a retrospective at the Kunsthalle in Basel, Switzerland. But at the same time that Chagall’s popularity was spreading, so, too, was the threat of Fascism and Nazism. Singled out during the cultural "cleansing" undertaken by the Nazis in Germany, Chagall’s work was ordered removed from museums throughout the country. Several pieces were subsequently burned, and others were featured in a 1937 exhibition of “degenerate art” held in Munich. Chagall’s angst regarding these troubling events and the persecution of Jews in general can be seen in his 1938 painting
White Crucifixion...