Items Similar to Fish Bowl Looks Like the Living Room -School of Macabre Charles Addams
Video Loading
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 9
Gahan WilsonFish Bowl Looks Like the Living Room -School of Macabre Charles Addams1996
1996
$4,000
£3,020.43
€3,480.72
CA$5,645.70
A$6,224.26
CHF 3,256.33
MX$76,360.06
NOK 40,990.74
SEK 38,332.82
DKK 25,994.09
About the Item
Welcome to Gahan Wilson's magnificently morbid mind, where viewing his cartoons/illustrations gives the viewer the creeps. In this work, a husband designs the interior of a fish tank to resemble their living room identically. This provokes a soft cry of outrage from his knitting wife who declares "Well, it gives me the creeps"
Sgned lower left. Unframed.
Sheet 12 x 9 in. (30.5 x 22.9 cm.)
Published: ''Gahan Wilson's Even Weirder'', Macmillan: New York, 1996.
- Creator:Gahan Wilson (1930 - 2019, American)
- Creation Year:1996
- Dimensions:Height: 12 in (30.48 cm)Width: 9 in (22.86 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:Creases and stain to the lower left quadrant. Crease to the upper left quadrant. Some evidence of minor handling. Mostly visible on close inspection.
- Gallery Location:Miami, FL
- Reference Number:1stDibs: LU385314544542

About the Seller
5.0
Gold Seller
Premium sellers maintaining a 4.3+ rating and 24-hour response times
Established in 2005
1stDibs seller since 2016
117 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 1 hour
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Shipping from: Miami, FL
- Return Policy
Authenticity Guarantee
In the unlikely event there’s an issue with an item’s authenticity, contact us within 1 year for a full refund. DetailsMoney-Back Guarantee
If your item is not as described, is damaged in transit, or does not arrive, contact us within 7 days for a full refund. Details24-Hour Cancellation
You have a 24-hour grace period in which to reconsider your purchase, with no questions asked.Vetted Professional Sellers
Our world-class sellers must adhere to strict standards for service and quality, maintaining the integrity of our listings.Price-Match Guarantee
If you find that a seller listed the same item for a lower price elsewhere, we’ll match it.Trusted Global Delivery
Our best-in-class carrier network provides specialized shipping options worldwide, including custom delivery.More From This Seller
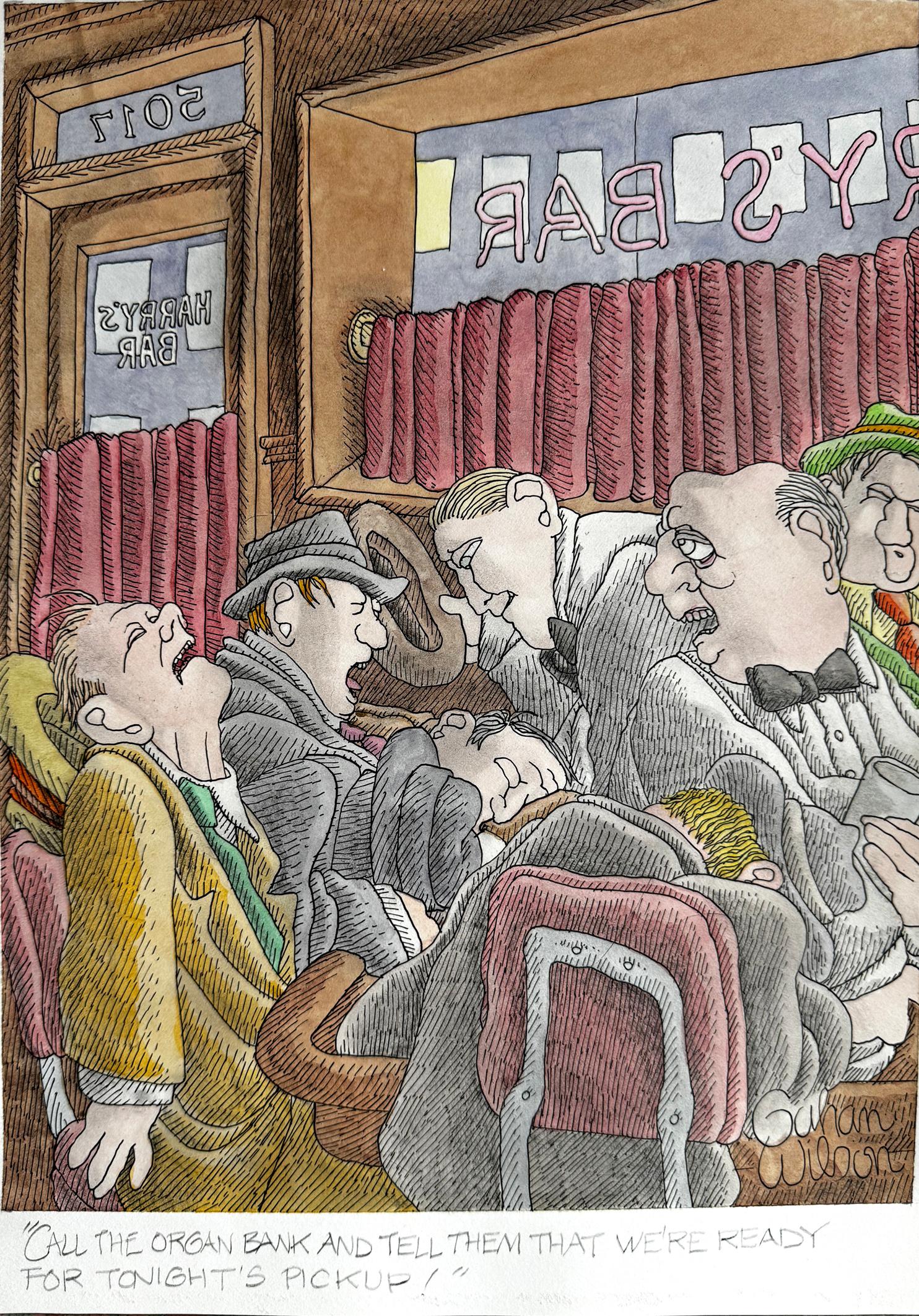
View AllMacabre Bar Scene - School of Charles Addams - Playboy Cartoon
Located in Miami, FL
Even without the punch line, Gahan Wilson's highly stylized paintings are marvelous to behold. He is one of a few artists with a unique style instantly re...
Category
Early 2000s Contemporary Figurative Paintings
Materials
Paper, Ink, Watercolor, Pen
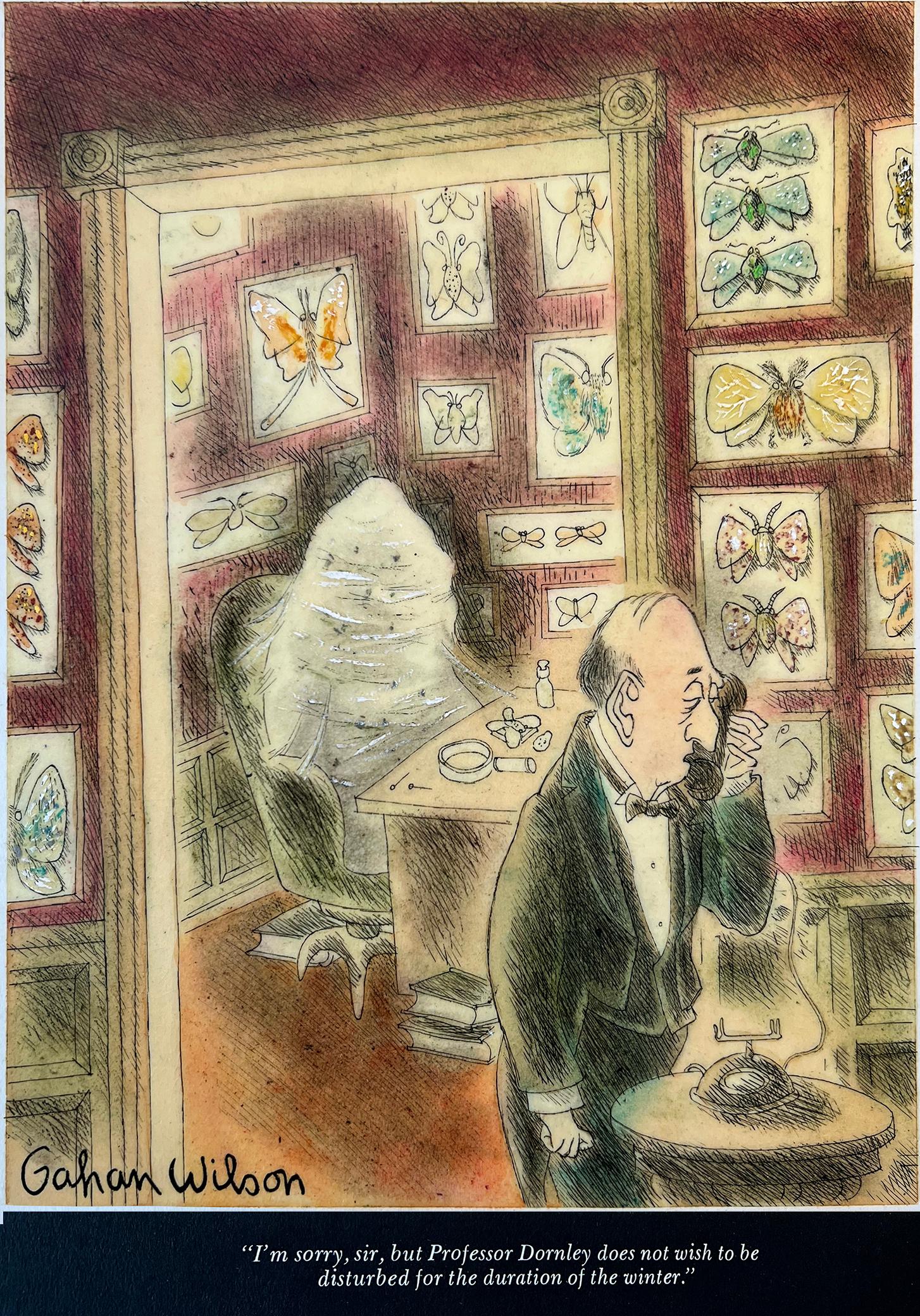
Wish Not to Be Disturbed for the Duration of Winter - Playboy Cartoon
Located in Miami, FL
Gahan Wilson was the Master of the macabre, and most of his work is associated with Charles Addams. The beauty of a Gahan Wilson is that is a payoff pu...
Category
1960s Conceptual Figurative Paintings
Materials
Ink, Gouache, Color Pencil
Macabre Sacrifice in the Office - New Yorker Cartoon Dark Humor
Located in Miami, FL
Gahan Wilson's artistic output of original ideas, masterfully executed, seems endless. He has a conceptual style that, like Charles Addams, delves into the macabre. Yet, one immedia...
Category
2010s American Realist Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Ink, Paper, Pen
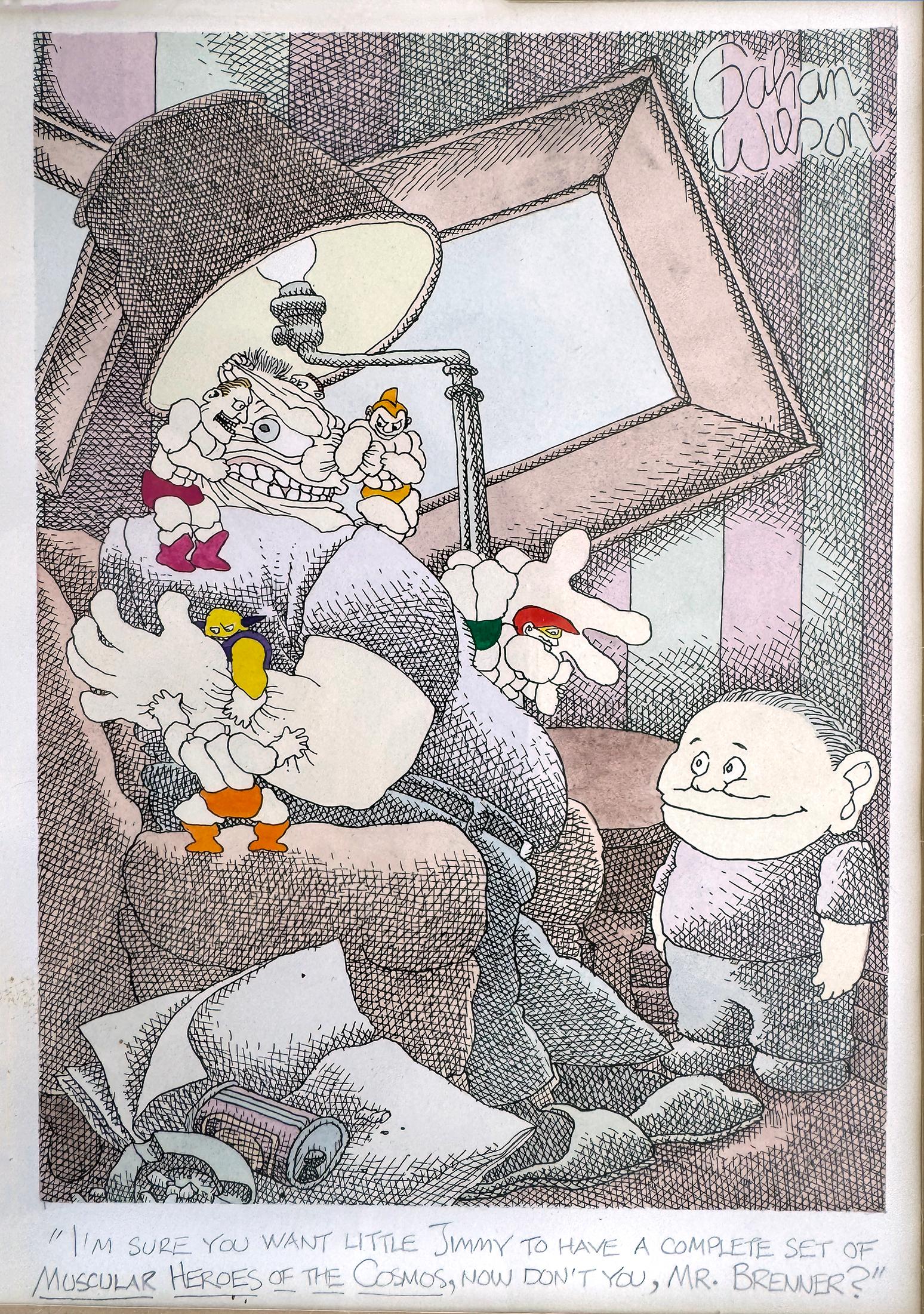
Macabre Cartoon Children's Toys Attack Father - Playboy Cartoon
Located in Miami, FL
A child looks on with glee as his "Muscular Heroes of the Cosmos" Toys transform from inanimate objects to real, actionable beings and beat up his father. Signed upper right, Gahan...
Category
1980s Outsider Art Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Ink, Watercolor
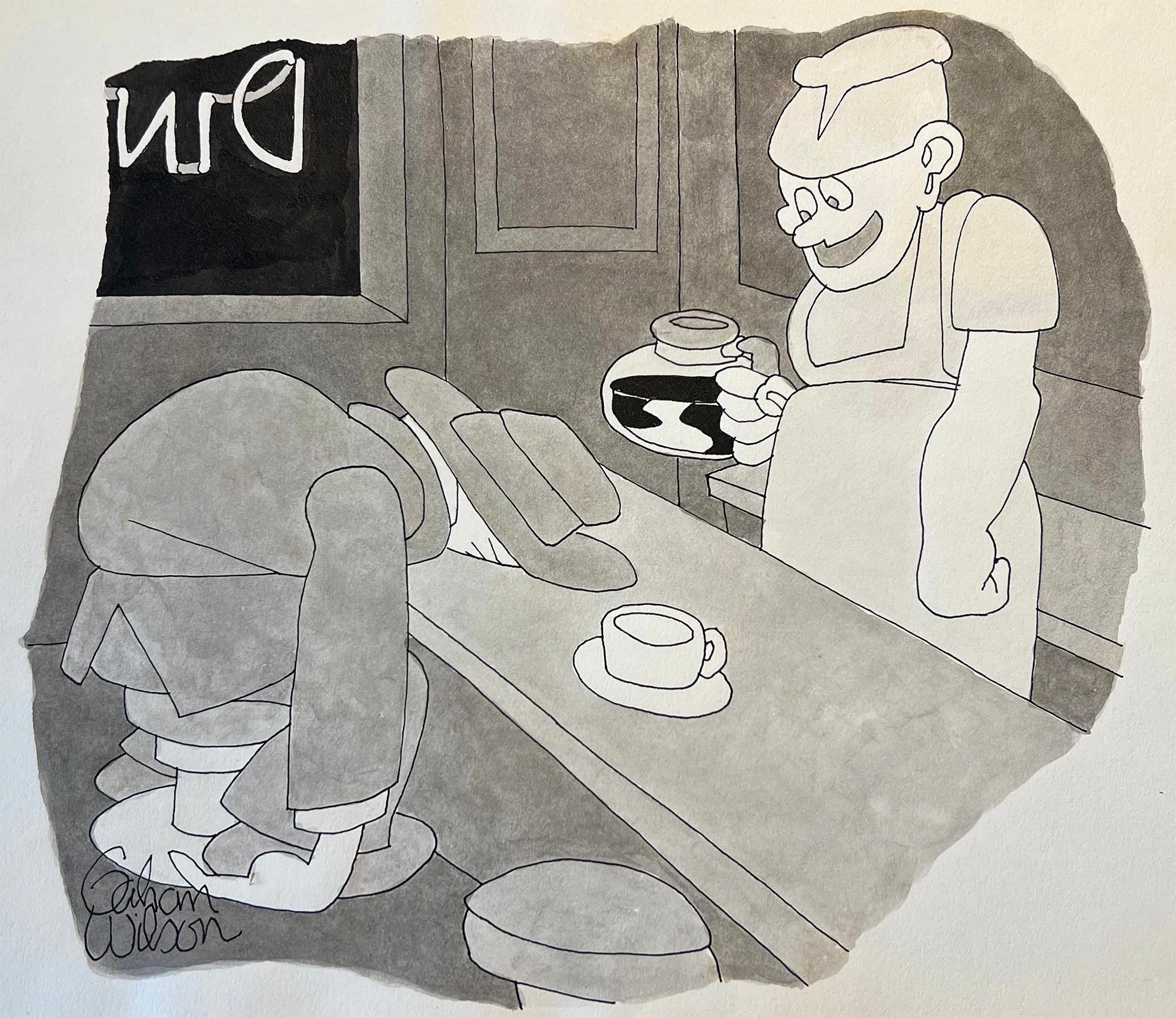
How About a Little More Coffee, New Yorker Cartoon
Located in Miami, FL
Interpretation 1: An utterly exhausted man collapses face-first into a diner's countertop. His face and the countertop become one. Seemingly oblivious to the acute nature of the man's condition, the night server gleefully offers him coffee instead of more appropriate help. Interpretation 2: The night server/psycho killer pours unsuspecting customer poisoned coffee and then taunts his lifeless body in a victorious tone. Like Charles Addams...
Category
1990s Modern Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Ink, Watercolor
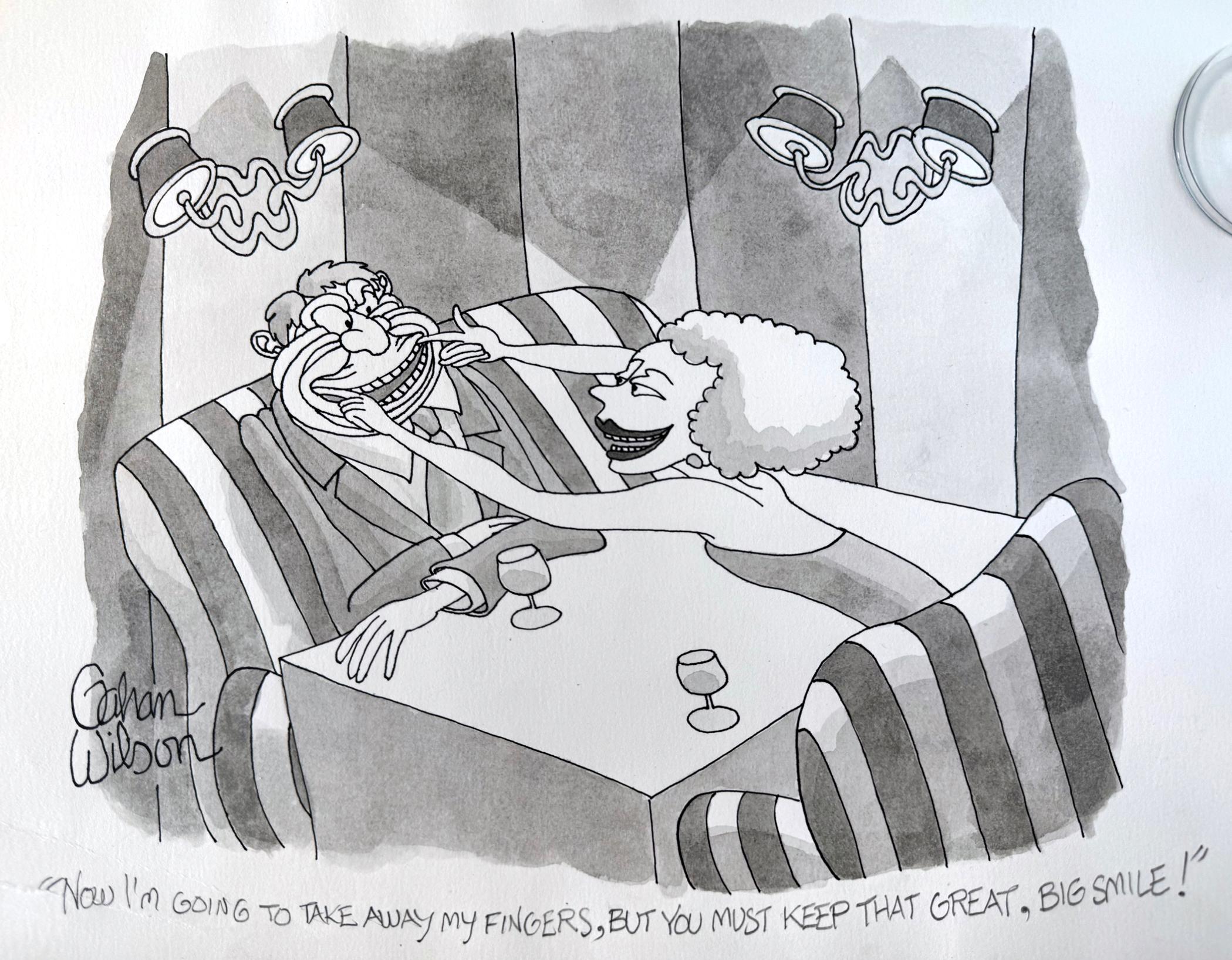
Man with Big Smile - New Yorker Cartoon
Located in Miami, FL
If a smile is an expression of momentary happiness, then the female in this cartoon appears driven to turn a moment into a more extended period of time. Leave it to Gahan Wilson to ...
Category
Early 2000s Outsider Art Portrait Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Ink, Watercolor, Pen
You May Also Like
Fred Lundy CA Great Depression Cartoon Illustration, circa 1938
Located in San Francisco, CA
Rare original cartoon illustration by listed American cartoonist Fred Lundy.
Fred Ralph Lundy (1902-1989) studied art at the University of Oregon before moving to California in 1924. Following further study at the CCAC, he was an artist with the Oakland Tribune from 1935-1935 and an editorial cartoonist for the San Francisco Examiner from 1935 until retirement in 1976. His cartoons appeared in Saturday Evening Post, Colliers, Esquire, New Yorker, and other national magazines. He died in Daly City...
Category
Early 20th Century American Drawings
Materials
Paper
Humorous Gentleman's Magazine cartoon
Located in Wilton Manors, FL
Cartoon sketch, ca. 1955. Pencil on paper, sheet measures 8.5 x 11 inches. Unsigned with editor's notations.
From a group of sketches meant to be preliminary drafts for editor appro...
Category
Mid-20th Century Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Pencil
$125 Sale Price
50% Off
UNTITLED DRAWING
By William Gropper
Located in Portland, ME
Gropper, William (American, 1897-1977). UNTITLED DRAWING. Blue chalk
on fibrous handmade paper. Signed lower right, and inscribed at left
to Irwin and Sarah Lefcourt. 26 1/2 x 20 1/...
Category
Mid-20th Century Portrait Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Chalk
Large George Grosz 1923 Lithograph Die Rauber German Expressionism WPA Realism
By George Grosz
Located in Surfside, FL
From The robbers. lithographs by George Grosz for the drama of the same name.
photolithography on laid paper. 19 X 25.5 inches (sheet size). This is not hand signed or numbered in ...
Category
1930s American Modern Figurative Prints
Materials
Lithograph
Ed Fisher (1926-2013) Original Cartoon Drawing From "The New Yorker"
Located in San Francisco, CA
Ed Fisher (1926-2013) Original Cartoon
From "The New Yorker"
Circa 2009
Graphite on Paper
9" x 12.5" unframed
12" x 16" framed
Category
Early 2000s Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Graphite
Laboratory - Drawing by Mino Maccari - Mid-20th Century
By Mino Maccari
Located in Roma, IT
Laboratory is a china ink drawing realized by Mino Maccari (1924-1989) in the Mid-20th Century.
Hand-signed.
Good conditions with slight foxing.
Mino Maccari (Siena, 1924-Rome, J...
Category
Mid-20th Century Modern Figurative Drawings and Watercolors
Materials
Paper, Charcoal
More Ways To Browse
Fish Bowl
Fish Bowls
Macabre Art
Vintage Fish Bowl
Cartoon Illustration
Fish Tank
Emmy Lou Packard
Erte Gouache 1940
Etienne Berne Bellecour
Francisca Ahlers
Martell Cognac
Pie Bird Vintage
South Africa Watercolor
South African Watercolour
Vintage Speedy Gonzales
Alison Dunlop
Broadway Caricature
Chinese Horse Drawing